What is function notation and how can linear functions be expressed using it?
Understand the Problem
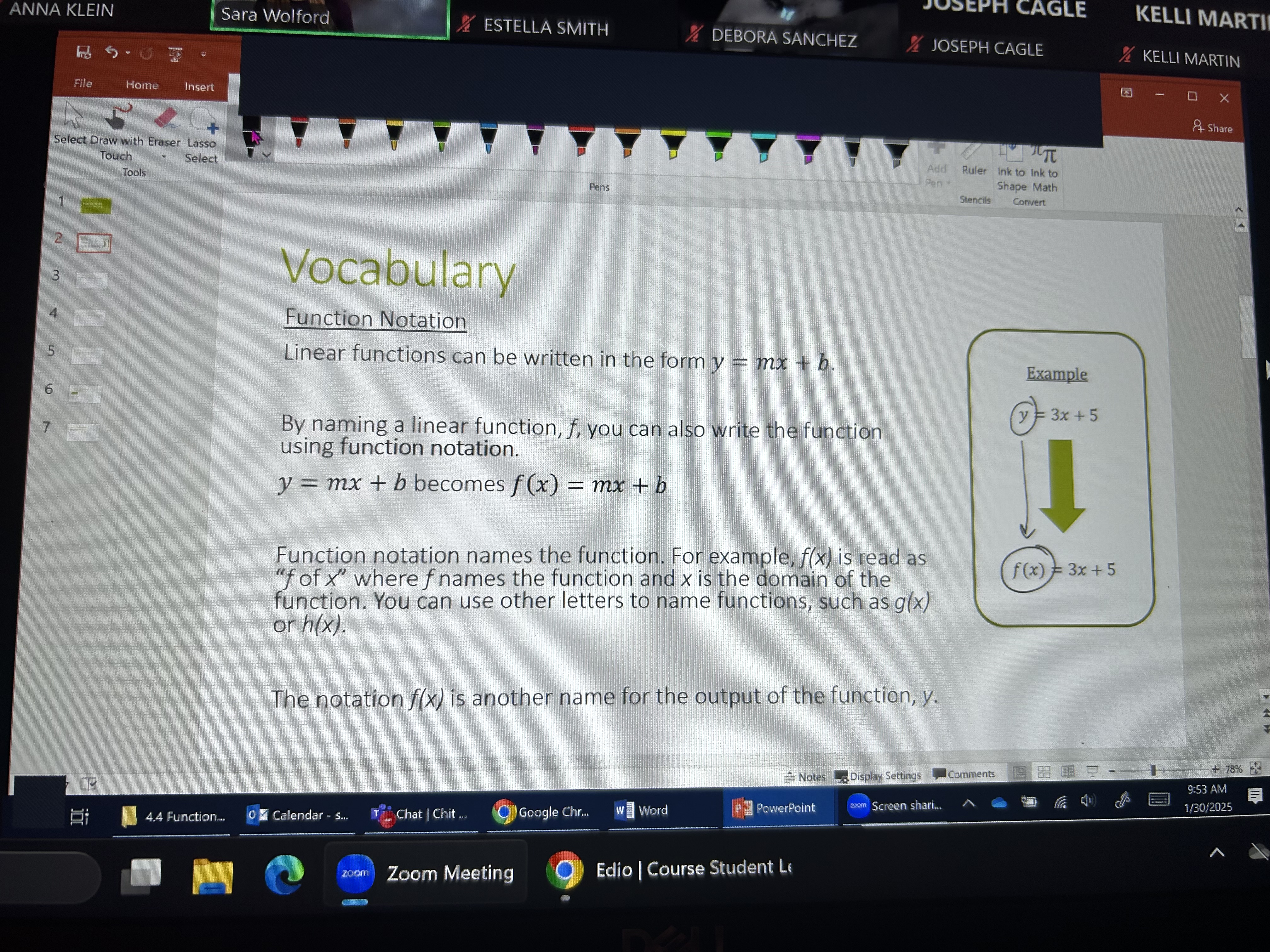
The question discusses function notation in mathematics, specifically how linear functions can be expressed in the form y = mx + b and how to denote these functions using function notation such as f(x) = mx + b.
Answer
The output \( f(2) \) is \( 11 \).
Answer for screen readers
The output for ( f(2) ) is ( 11 ).
Steps to Solve
-
Understanding Function Notation To translate the equation ( y = mx + b ) into function notation, identify the linear function and name it, typically ( f(x) ). Here, ( m ) is the slope and ( b ) is the y-intercept.
-
Rewriting the Equation Change the form from ( y = mx + b ) to ( f(x) = mx + b ). This shows that ( f(x) ) represents the output of the function for any input ( x ).
-
Example with Specific Values For instance, if the linear function is ( y = 3x + 5 ), then the function in notation would be ( f(x) = 3x + 5 ). This means if ( x ) is replaced with a specific number, ( f(x) ) gives the corresponding output.
-
Function Evaluation To find the output for a specific input using function notation, substitute the value of ( x ). For example, if ( x = 2 ), then ( f(2) = 3(2) + 5 ).
-
Calculating the Output Calculate the expression: $$ f(2) = 3(2) + 5 = 6 + 5 = 11 $$
The output for ( f(2) ) is ( 11 ).
More Information
In function notation, ( f(x) ) represents the output of the function when ( x ) is the input. This provides a clearer way to express equations and understand their relationships.
Tips
- Confusing ( y ) and ( f(x) ): Remember that ( f(x) ) is just another way of writing ( y ). Make sure to interpret them interchangeably.
- Forget to substitute correctly: When substituting values, double-check that you are replacing ( x ) appropriately in the function expression.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information