What are the reactions involving methyl vinyl ether, ethanol, and the Reimer-Tiemann reaction? Explain the mechanisms of tertiary alcohol reactions.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking about several organic chemistry reactions, specifically identifying and explaining different reactions involving alcohols and electrophiles. It requires knowledge of mechanisms such as the Reimer-Tiemann reaction and electrophilic substitution mechanisms.
Answer
Methyl vinyl ether reacts with HBr. Ethanol and certain alcohols undergo haloform reactions. Reimer-Tiemann uses dichlorocarbene. Tertiary alcohols undergo SN1 reactions.
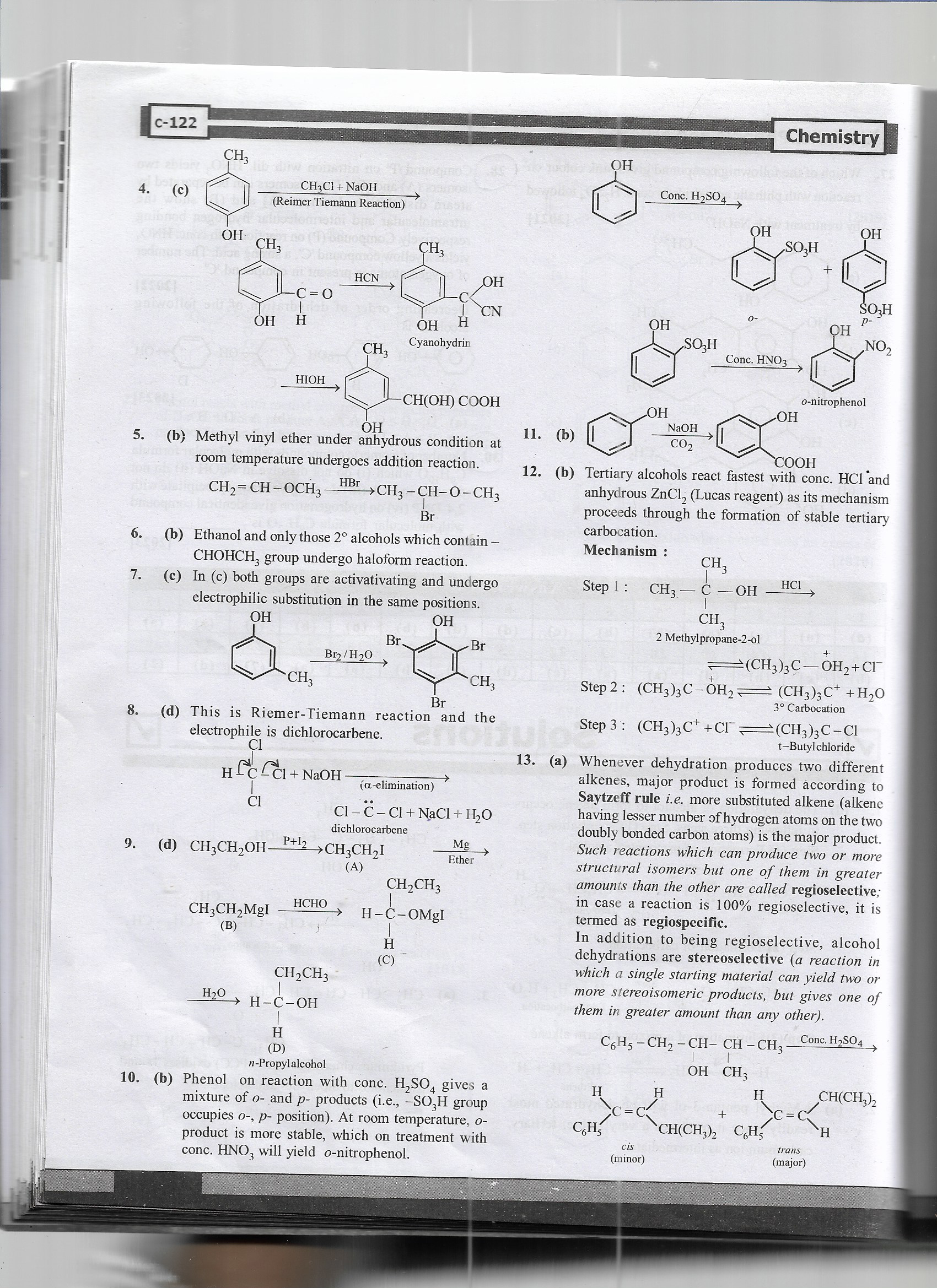
The image details: (5) Methyl vinyl ether undergoes an addition reaction with HBr. (6) Ethanol reacts in the haloform reaction with specific secondary alcohols containing the –CHOHCH3 group. (8) The Reimer-Tiemann reaction involves dichlorocarbene forming ortho-hydroxy benzaldehyde. (12-b) Tertiary alcohols undergo SN1 reactions forming stable carbocations.
Answer for screen readers
The image details: (5) Methyl vinyl ether undergoes an addition reaction with HBr. (6) Ethanol reacts in the haloform reaction with specific secondary alcohols containing the –CHOHCH3 group. (8) The Reimer-Tiemann reaction involves dichlorocarbene forming ortho-hydroxy benzaldehyde. (12-b) Tertiary alcohols undergo SN1 reactions forming stable carbocations.
More Information
The Reimer-Tiemann reaction is significant in creating functionalized aromatic compounds. The SN1 reaction in tertiary alcohols is fast and forms rearranged products.
Tips
Common mistakes include not considering the stability of intermediates in SN1 reactions or misunderstanding the role of electron-withdrawing groups in Reimer-Tiemann reactions.
Sources
- Reimer Tiemann Reaction Mechanism - Detailed Explanation - byjus.com
- 3.7: Reactions of Alcohols - Chemistry LibreTexts - chem.libretexts.org
- Alcohol Reactivity - MSU chemistry - .chemistry.msu.edu
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information