What are the products of the reaction between CH3-CH2-CH2-COOH and NaOH, followed by LiAlH4 dry?
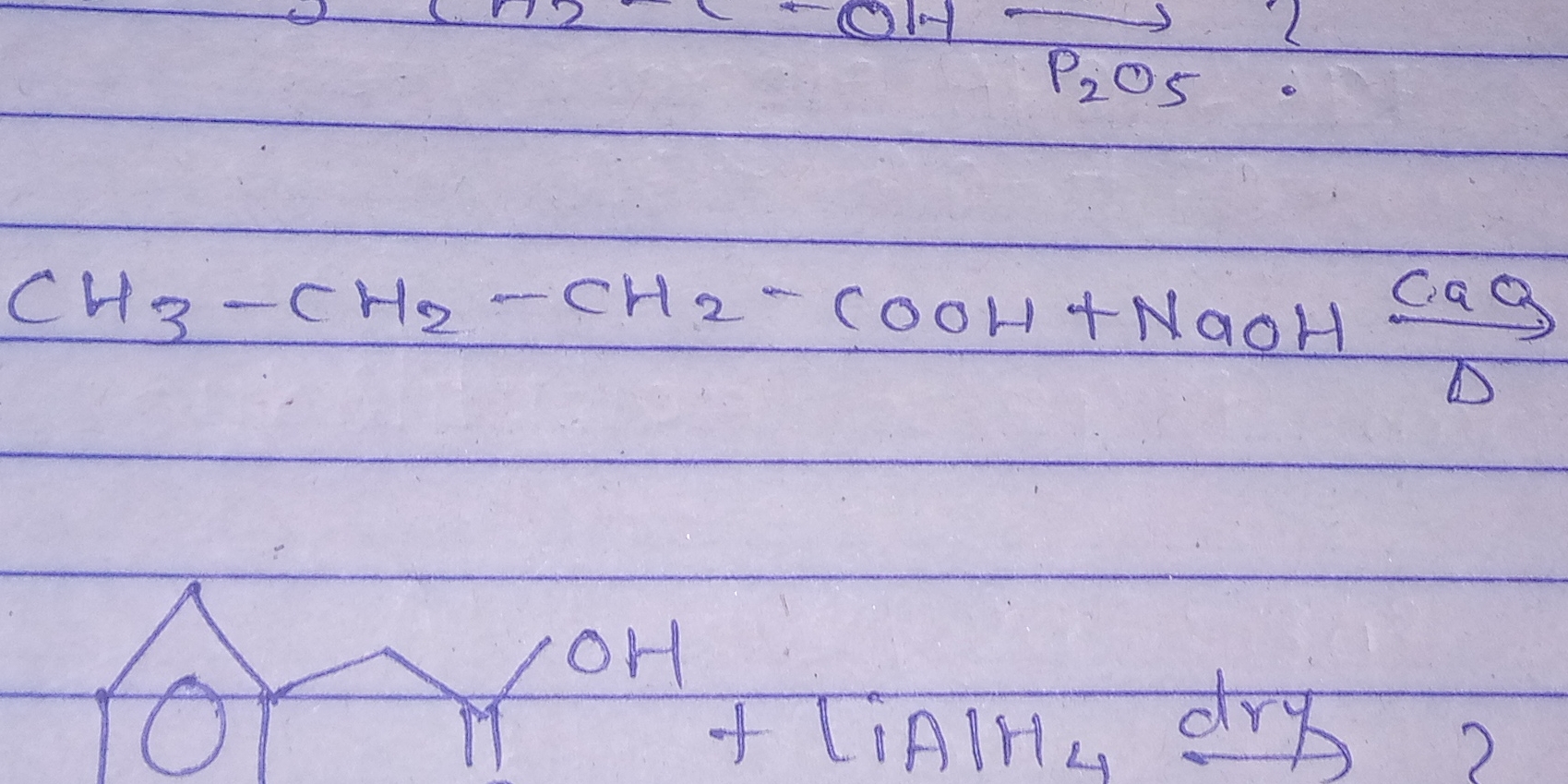
Understand the Problem
The question involves a chemical reaction process, likely asking about the reactions between various organic compounds, specifically the interaction of a carboxylic acid with sodium hydroxide and lithium aluminum hydride. It seems to be focused on the conversion of reactants to products in an organic chemistry context.
Answer
The products are $CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-CH_2OH$, $LiOH$, and $Al(OH)_3$.
Answer for screen readers
The products formed are butanol ($CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-CH_2OH$), lithium hydroxide ($LiOH$), and aluminum hydroxide ($Al(OH)_3$).
Steps to Solve
-
Identify the Reactants The reactants involved are butanoic acid ($CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-COOH$), sodium hydroxide ($NaOH$), and lithium aluminum hydride ($LiAlH_4$), with specific conditions of dilute aqueous solution and dry.
-
Reactions with NaOH When butanoic acid reacts with sodium hydroxide, a neutralization reaction occurs, forming butanoate ion and water: $$ CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-COOH + NaOH \rightarrow CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-COONa + H_2O $$
-
Formation of Alcohol with LiAlH4 Next, lithium aluminum hydride is a strong reducing agent and can reduce carboxylic acids to primary alcohols. So, when the butanoate ion reacts with $LiAlH_4$, it will reduce it to butanol ($CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-CHOH$): $$ CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-COONa + LiAlH_4 \rightarrow CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-CH_2OH + LiOH + Al(OH)_3 $$
-
Summarize the Complete Reaction Overall, the complete reaction can be summarized: $$ CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-COOH + NaOH + LiAlH_4 \rightarrow CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-CH_2OH + LiOH + Al(OH)_3 $$
The products formed are butanol ($CH_3-CH_2-CH_2-CH_2OH$), lithium hydroxide ($LiOH$), and aluminum hydroxide ($Al(OH)_3$).
More Information
This process illustrates the two-step transformation of a carboxylic acid into an alcohol: first through neutralization with a base (sodium hydroxide) and then reduction with hydride (lithium aluminum hydride). This is a common approach in organic synthesis for converting carboxylic acids to alcohols.
Tips
- Confusing the roles of reactants. Remember that $NaOH$ neutralizes the acid, and $LiAlH_4$ is the reducing agent.
- Forgetting to account for the steps in the transformation, which may lead to incomplete product prediction.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information