What are the inductive and mesomeric effects in covalent bonds?
Understand the Problem
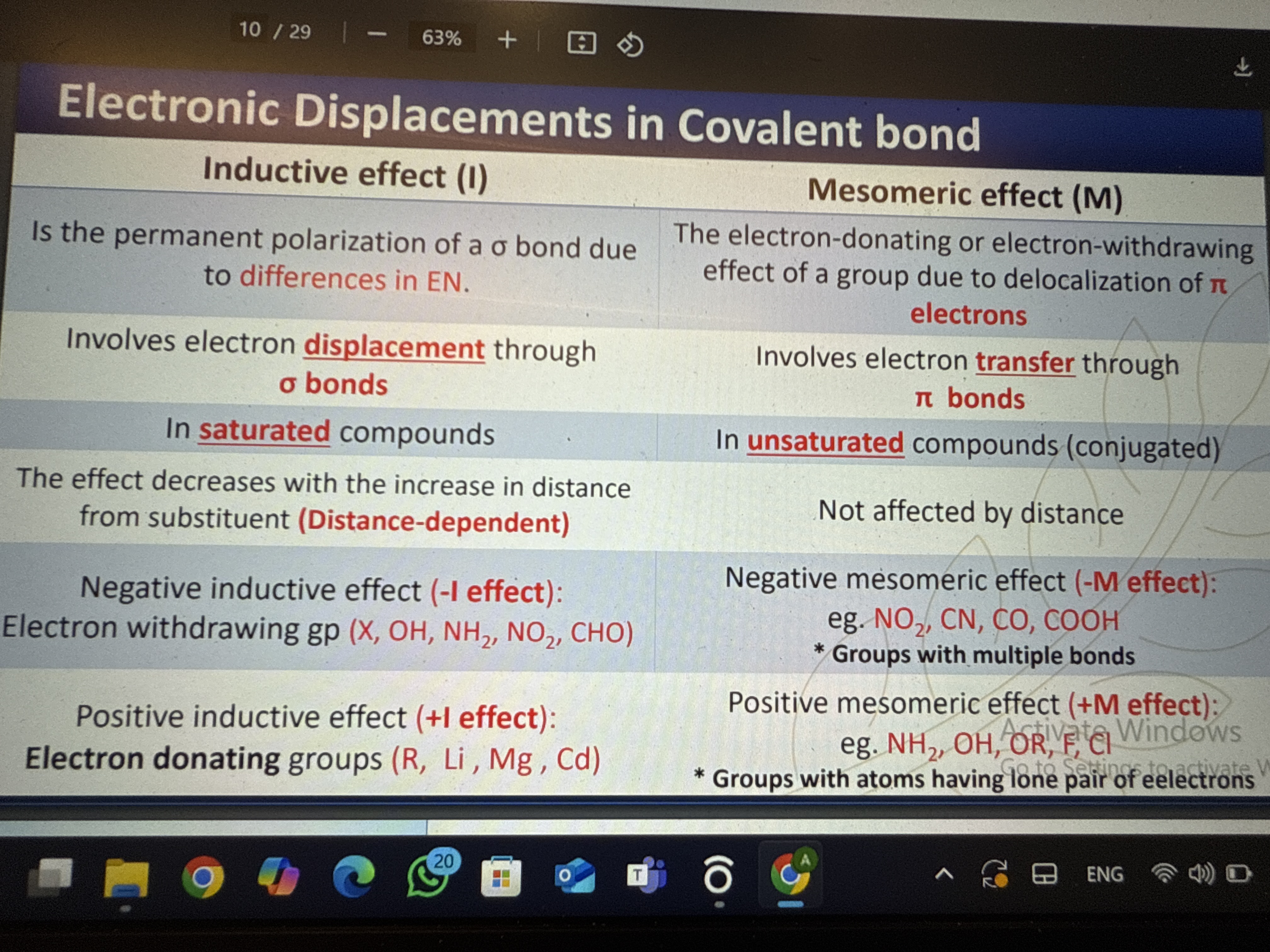
The question is asking for an explanation of electronic displacements in covalent bonds, specifically focusing on the inductive and mesomeric effects, their definitions, and their characteristics.
Answer
Inductive effects occur via sigma bonds and are distance-dependent; mesomeric effects occur via pi bonds and are not distance-dependent.
Inductive effects involve electron displacement through sigma bonds due to electronegativity differences and are distance-dependent, while mesomeric effects involve electron transfer through pi bonds, are seen in unsaturated compounds, and are not distance-dependent.
Answer for screen readers
Inductive effects involve electron displacement through sigma bonds due to electronegativity differences and are distance-dependent, while mesomeric effects involve electron transfer through pi bonds, are seen in unsaturated compounds, and are not distance-dependent.
More Information
Inductive effects are stronger in saturated compounds and decrease with distance, while mesomeric effects are crucial in conjugated systems like benzene, affecting molecule stability and reactivity.
Tips
Confusing the nature of sigma and pi bonds when determining the type of effect.
Sources
- Inductive and Resonance (Mesomeric) Effects - Chemistry Steps - chemistrysteps.com
- Difference Between Inductive and Mesomeric Effects | JEE Main - unacademy.com