What are the factors affecting ionization energy and the properties of cations and anions?
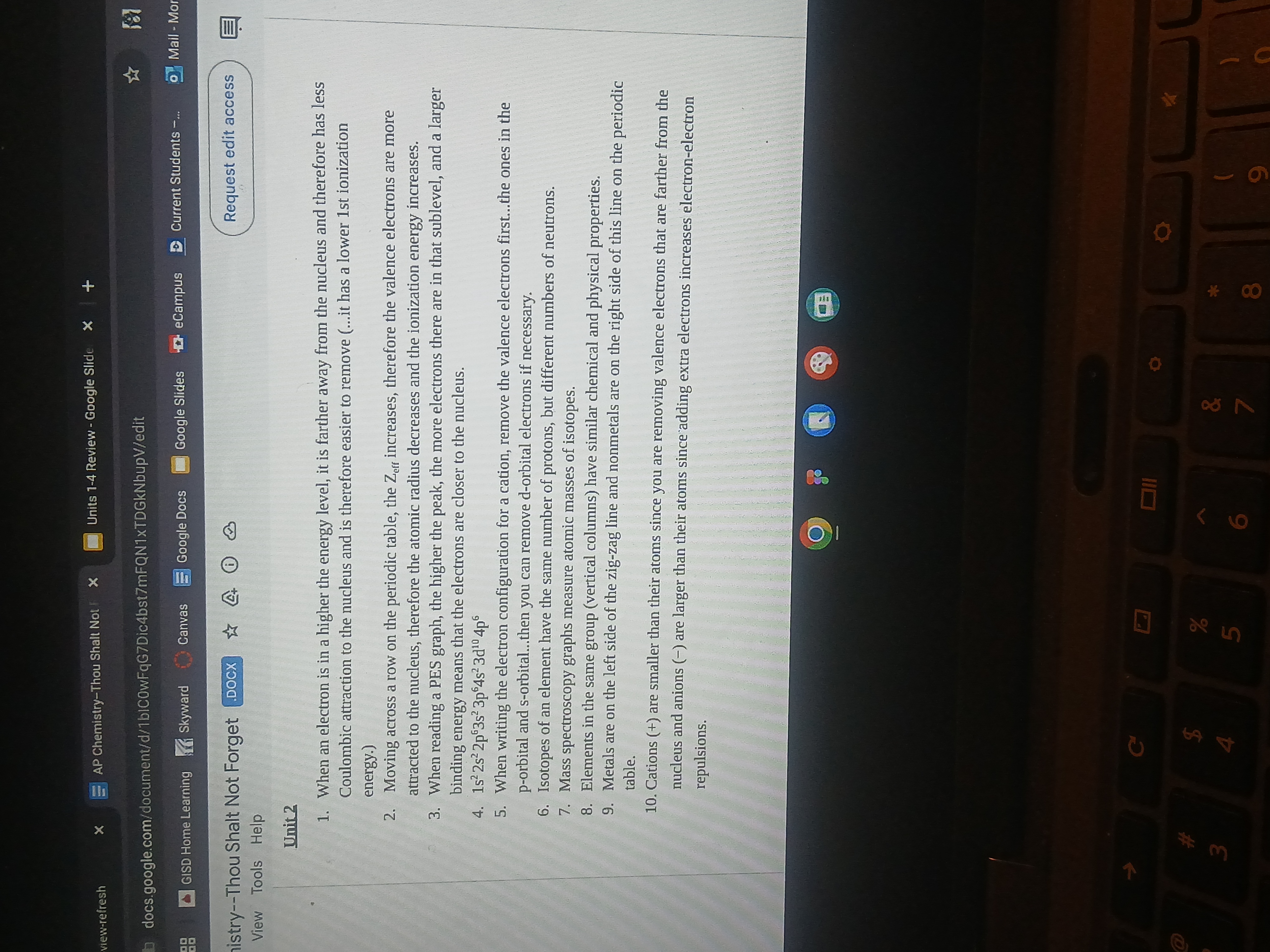
Understand the Problem
The question appears to be asking about various concepts related to atomic structure, ionization energy, and the properties of ions, which are standard topics in chemistry, particularly in the study of periodic trends.
Answer
Ionization energy is affected by atomic radius, nuclear charge, and shielding. Cations are smaller than atoms; anions are larger.
Factors affecting ionization energy include atomic radius, nuclear charge, and electron shielding. Cations are smaller than their parent atoms due to lost electrons, while anions are larger because of gained electrons increasing repulsion.
Answer for screen readers
Factors affecting ionization energy include atomic radius, nuclear charge, and electron shielding. Cations are smaller than their parent atoms due to lost electrons, while anions are larger because of gained electrons increasing repulsion.
More Information
Ionization energy generally increases across a period due to increased nuclear charge and decreases down a group due to increased atomic radius and electron shielding. Cations and anions display distinct changes in atomic size with charge considerations.
Tips
A common mistake is to overlook shielding and its role in reducing the effective nuclear charge felt by outer electrons.
Sources
- Ionization Energy - Chemistry LibreTexts - chem.libretexts.org
- Factors affecting ionization energy - Unacademy - unacademy.com
- 7.4: Ionization Energy - Chemistry LibreTexts - chem.libretexts.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information