What are the different types of membrane transport mechanisms, and how do they function?
Understand the Problem
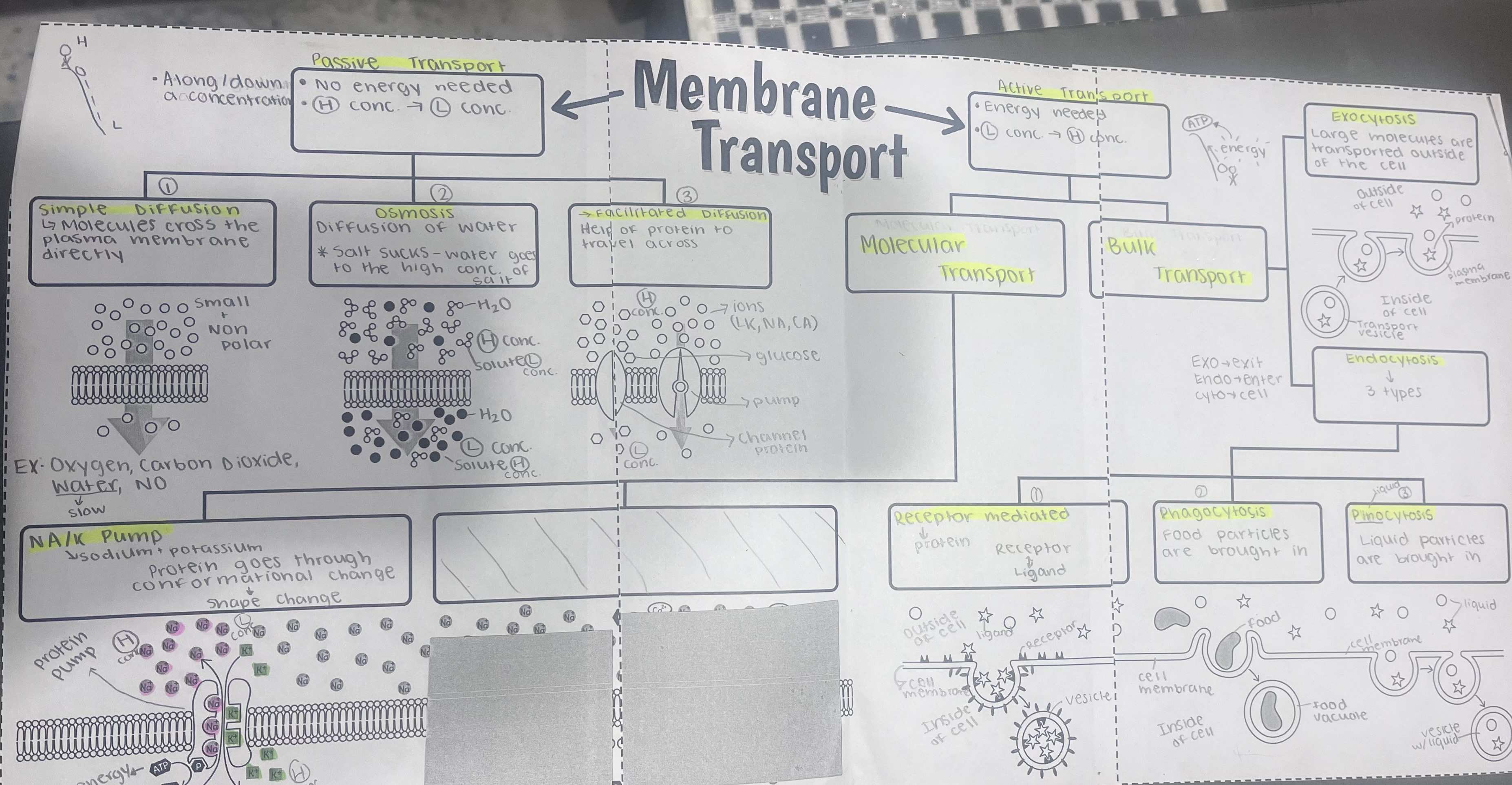
The question is asking for a detailed overview and explanation of membrane transport processes, including passive and active transport mechanisms, examples, and their significance in cellular biology.
Answer
Passive: Simple Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated Diffusion. Active: Protein Pumps, Exocytosis, Endocytosis.
The image outlines membrane transport mechanisms: Passive Transport (Simple Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated Diffusion) and Active Transport (Molecular Transport via Protein Pumps, Bulk Transport such as Exocytosis and Endocytosis with subtypes Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, and Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis).
Answer for screen readers
The image outlines membrane transport mechanisms: Passive Transport (Simple Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated Diffusion) and Active Transport (Molecular Transport via Protein Pumps, Bulk Transport such as Exocytosis and Endocytosis with subtypes Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, and Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis).
More Information
Membrane transport is essential for cell survival, enabling exchange of nutrients and waste products. Different mechanisms ensure cells maintain homeostasis and respond to changes in their environment.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing passive transport (which doesn’t require energy) with active transport (which does).
Sources
- Transport Across Cell Membrane - Active and Passive - byjus.com
- Passive and Active Transport - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information