What are the different functional groups in organic compounds?
Understand the Problem
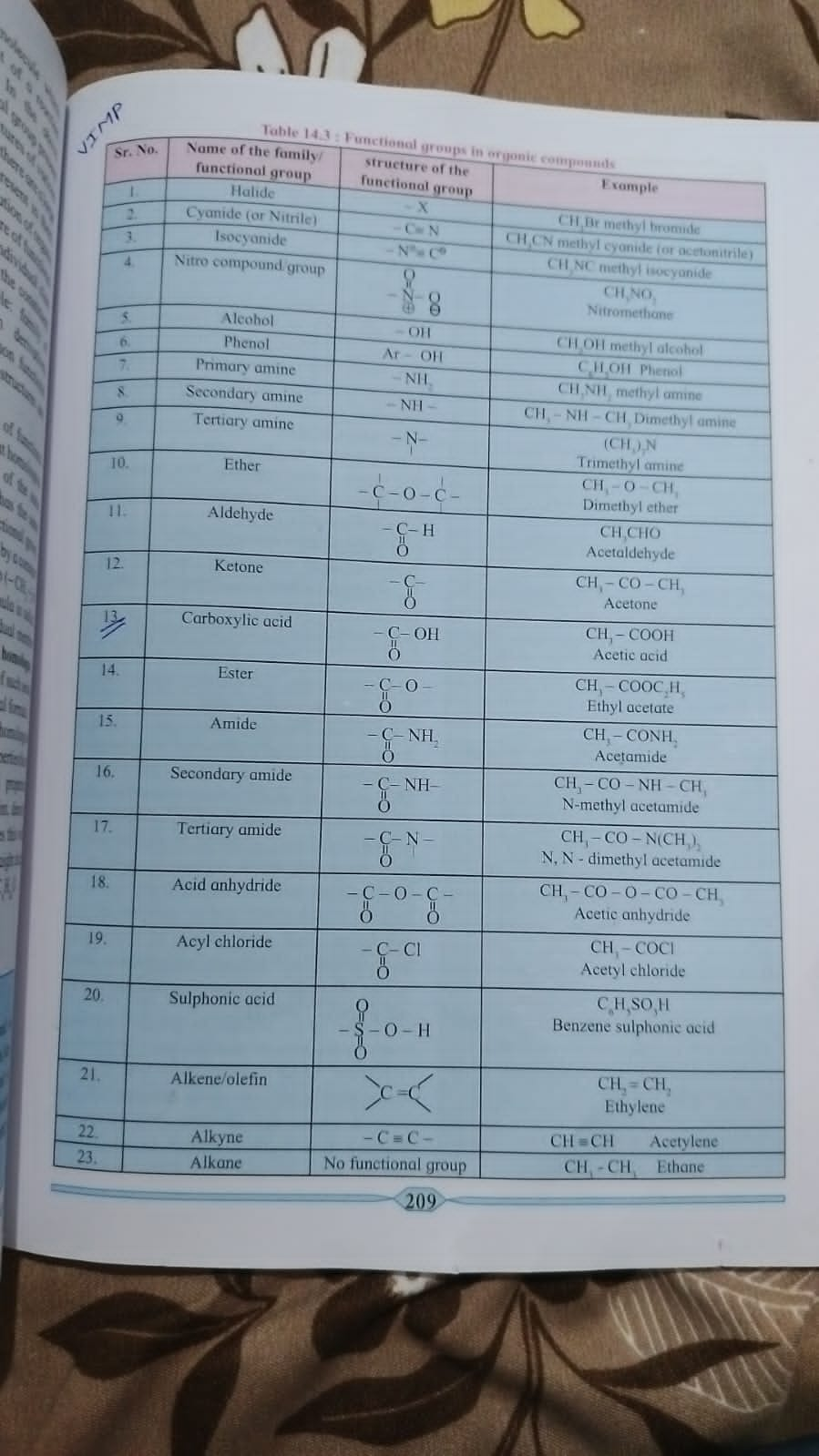
The image provides a table of functional groups in organic chemistry, detailing their names, structures, and examples. It is likely requesting information or a clarification related to these functional groups.
Answer
Halide, Cyanide, Isocyanide, Nitro, Alcohol, Phenol, Amines, Ether, Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic acid, Ester, Amides, Acid anhydride, Acyl chloride, Sulphonic acid, Alkene, Alkyne, Alkane
The functional groups in organic compounds include Halide, Cyanide (or Nitrile), Isocyanide, Nitro compound group, Alcohol, Phenol, Primary amine, Secondary amine, Tertiary amine, Ether, Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic acid, Ester, Amide, Secondary amide, Tertiary amide, Acid anhydride, Acyl chloride, Sulphonic acid, Alkene (or olefin), Alkyne, and Alkane.
Answer for screen readers
The functional groups in organic compounds include Halide, Cyanide (or Nitrile), Isocyanide, Nitro compound group, Alcohol, Phenol, Primary amine, Secondary amine, Tertiary amine, Ether, Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic acid, Ester, Amide, Secondary amide, Tertiary amide, Acid anhydride, Acyl chloride, Sulphonic acid, Alkene (or olefin), Alkyne, and Alkane.
More Information
Functional groups are specific atoms, ions, or groups of atoms having consistent properties. They are the reactive parts of molecules that define their chemical reactions.
Tips
One common mistake is confusing the Alkene group (double bond) with the Alkyne group (triple bond). Another is not recognizing that functional groups can overlap; for instance, Hydroxyl groups (-OH) are part of both Alcohols and Phenols.
Sources
- Functional Groups and Classes of Organic Compounds - BYJU'S - byjus.com
- Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry - ChemTalk - chemistrytalk.org
- Functional Groups and Classes of Organic Compounds - chem.libretexts.org