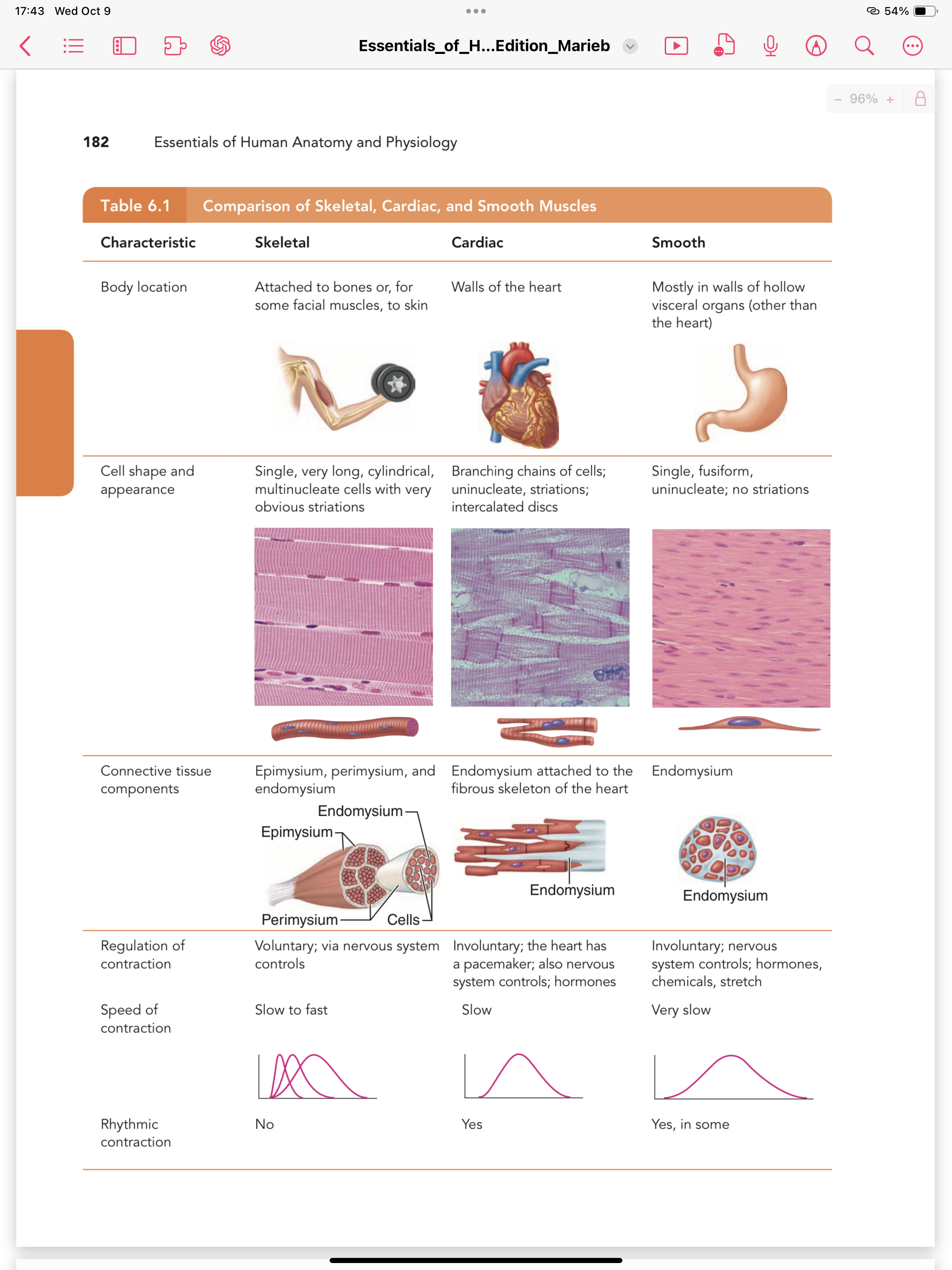
What are the differences between skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles based on the table provided?
Understand the Problem
The question appears to be related to the comparison of skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles as outlined in the table. It likely involves understanding the characteristics and differences between these muscle types.
Answer
Skeletal is voluntary, striated; cardiac is involuntary, striated; smooth is involuntary, non-striated.
Skeletal muscle is voluntary, striated, and attaches to bones, facilitating movement. Cardiac muscle is involuntary, striated, present in the heart, and contracts rhythmically. Smooth muscle is involuntary, non-striated, found in hollow organs, and controls movements like digestion.
Answer for screen readers
Skeletal muscle is voluntary, striated, and attaches to bones, facilitating movement. Cardiac muscle is involuntary, striated, present in the heart, and contracts rhythmically. Smooth muscle is involuntary, non-striated, found in hollow organs, and controls movements like digestion.
More Information
Skeletal muscle facilitates voluntary motion like walking and is controlled consciously. Cardiac muscle's rhythmic contraction is crucial for heart function. Smooth muscle manages involuntary actions such as peristalsis.
Tips
Confusing skeletal muscle's voluntary actions with the involuntary control of cardiac and smooth muscles is common.
Sources
- 13.15: Smooth, Skeletal, and Cardiac Muscles - Biology LibreTexts - bio.libretexts.org
- Types of muscle tissue: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia Image - medlineplus.gov
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information