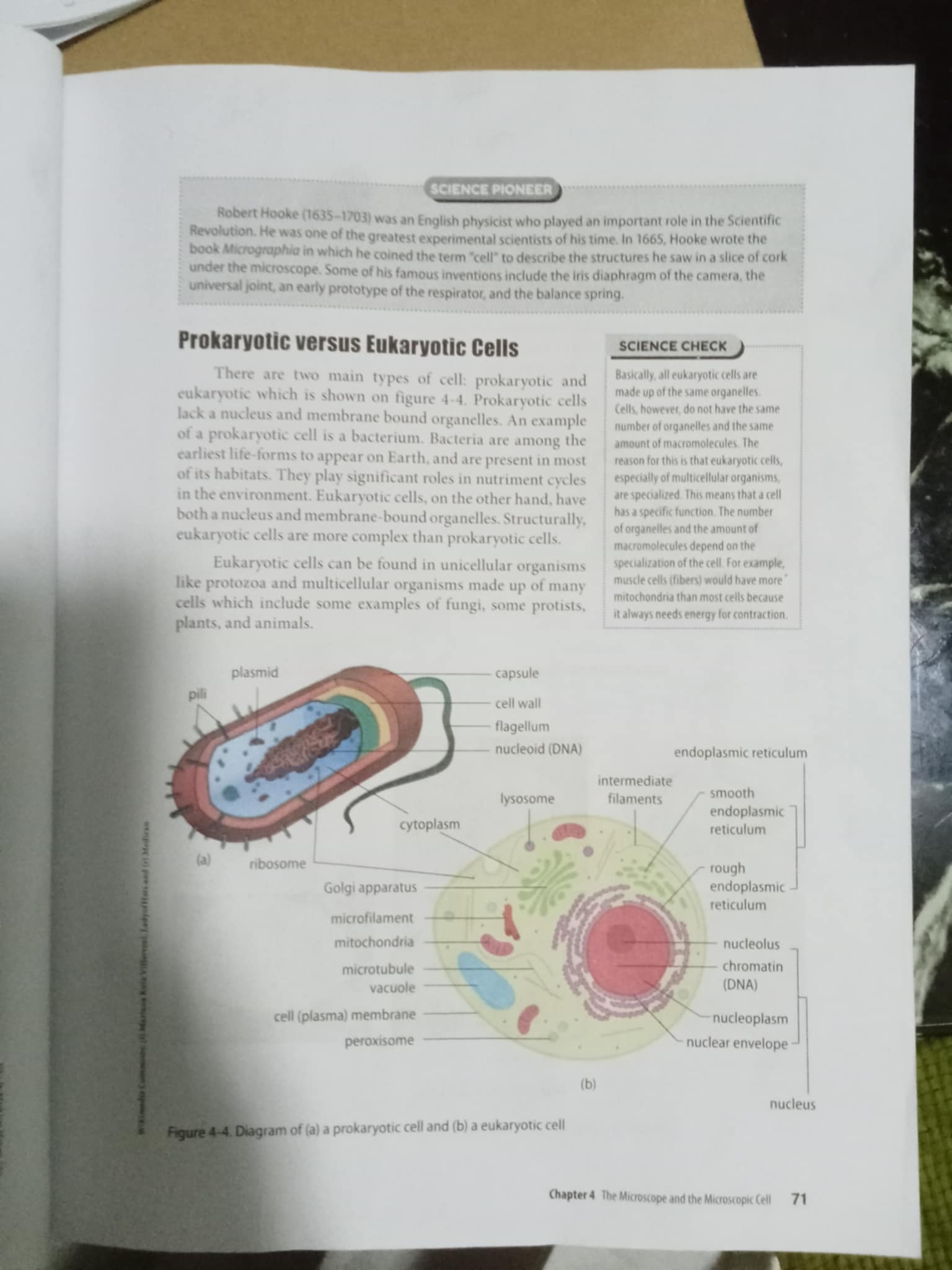
What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Understand the Problem
The question is likely asking about the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, referencing the provided diagrams and descriptions. It aims to clarify the structural and functional characteristics of these two types of cells.
Answer
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells have one.
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, and they are smaller and simpler, found in bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and are more complex, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Answer for screen readers
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, and they are smaller and simpler, found in bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and are more complex, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
More Information
Eukaryotic cells can form complex multicellular organisms, while prokaryotic cells are primarily single-celled. The presence of chloroplasts in some eukaryotes allows for photosynthesis.
Tips
Confusing organelle presence and the concept of nuclei are common mistakes. Ensure clear identification of organelles specific to each cell type.
Sources
- Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes: What Are the Key Differences? - technologynetworks.com
- Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells (article) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information