What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Compare the organelles found in plant and animal cells.
Understand the Problem
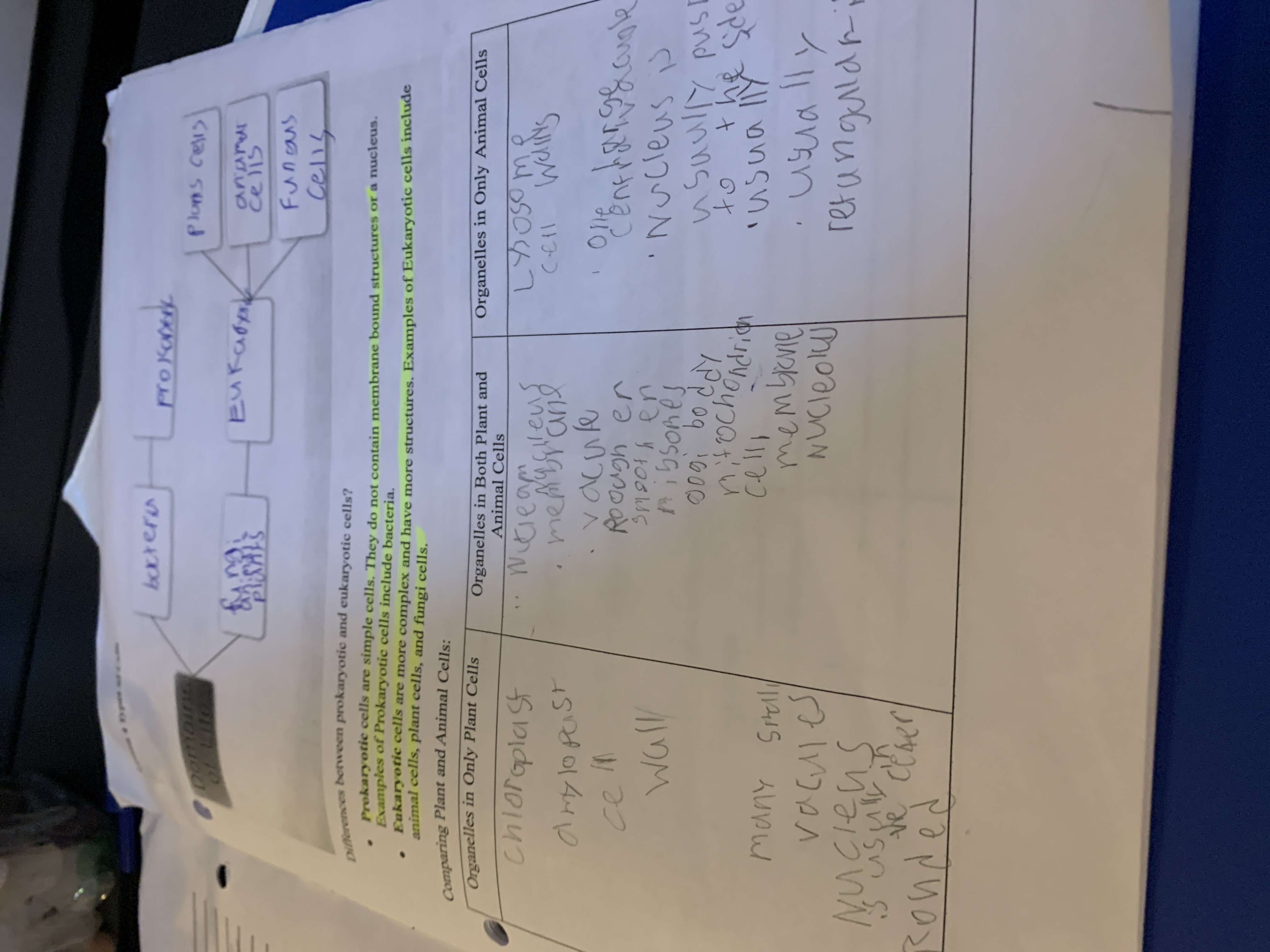
The question is asking for differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as well as a comparison of organelles in plant and animal cells. This involves understanding cell biology concepts.
Answer
Prokaryotic cells lack organelles/nucleus. Plant cells: chloroplasts, cell wall; Animal cells: lysosomes, centrioles. Common: nucleus, mitochondria.
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and a true nucleus, unlike eukaryotic cells which have both. Plant cells have chloroplasts and a cell wall, while animal cells have lysosomes and centrioles. Common organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes.
Answer for screen readers
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and a true nucleus, unlike eukaryotic cells which have both. Plant cells have chloroplasts and a cell wall, while animal cells have lysosomes and centrioles. Common organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes.
More Information
Prokaryotic cells, like bacteria, are simpler and older than eukaryotic cells. The presence of specific organelles allows for specialized functions in plant and animal cells.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing the organelles unique to plant cells (like chloroplasts) with those in animal cells (like centrioles).
Sources
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells - courses.lumenlearning.com
- Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes: What Are the Key Differences? - technologynetworks.com
- Plant vs animal cells review (article) | Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information