What are the differences between parenteral and nonparenteral administration of medication, and what are the techniques for intradermal, subcutaneous, and intramuscular injections?
Understand the Problem
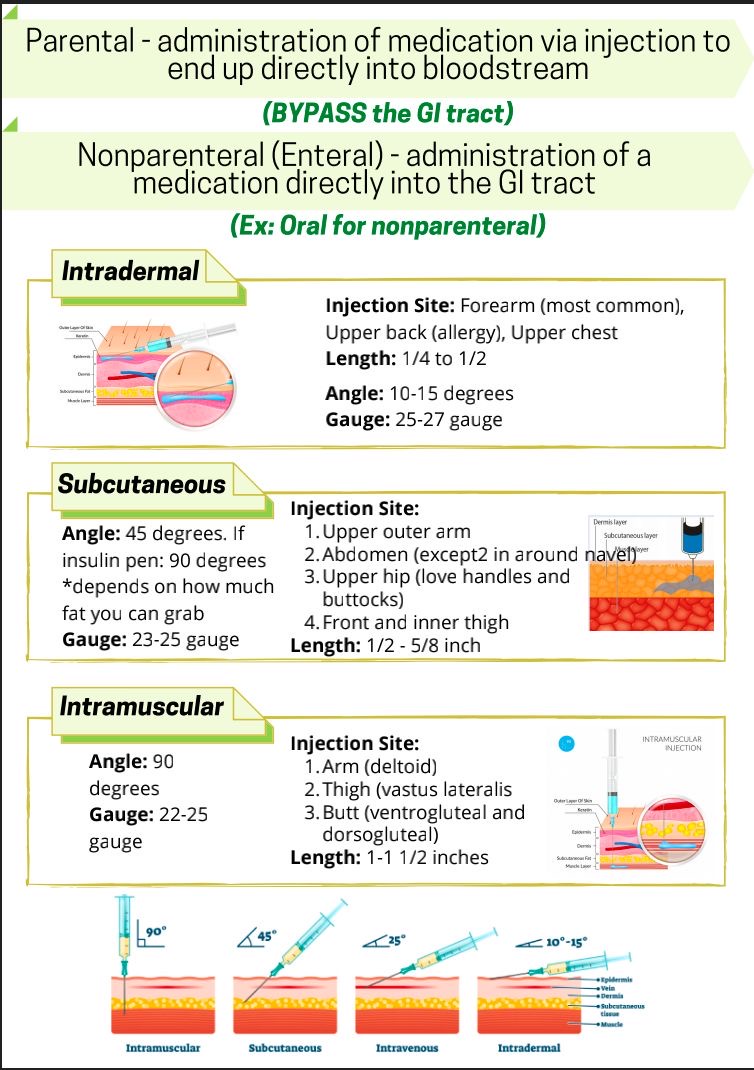
The question is asking about the differences in methods of medication administration, specifically focusing on parenteral and nonparenteral routes, as well as detailing the specific techniques and angles for intradermal, subcutaneous, and intramuscular injections.
Answer
Parenteral bypasses the GI tract. Nonparenteral (Enteral) is administered directly into the GI tract. Techniques for injections vary by site, angle, needle length, and gauge.
The differences between parenteral and nonparenteral administration lie in route and site of drug delivery. Techniques for intradermal, subcutaneous, and intramuscular injections vary in terms of site, angle, needle length, and gauge.
Answer for screen readers
The differences between parenteral and nonparenteral administration lie in route and site of drug delivery. Techniques for intradermal, subcutaneous, and intramuscular injections vary in terms of site, angle, needle length, and gauge.
More Information
Parenteral routes are often used to ensure faster absorption or for medications that are unstable in the digestive tract. Proper technique and knowledge of needle specifications are crucial for safely administering these injections.
Tips
Common mistakes include incorrect angle usage and improper site selection which can lead to ineffective delivery or damage to tissues.
Sources
- Chapter 18 Administration of Parenteral Medications - Nursing Skills - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Medication Routes of Administration - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- How to Take Your Meds: Medication Administration Routes - verywellhealth.com