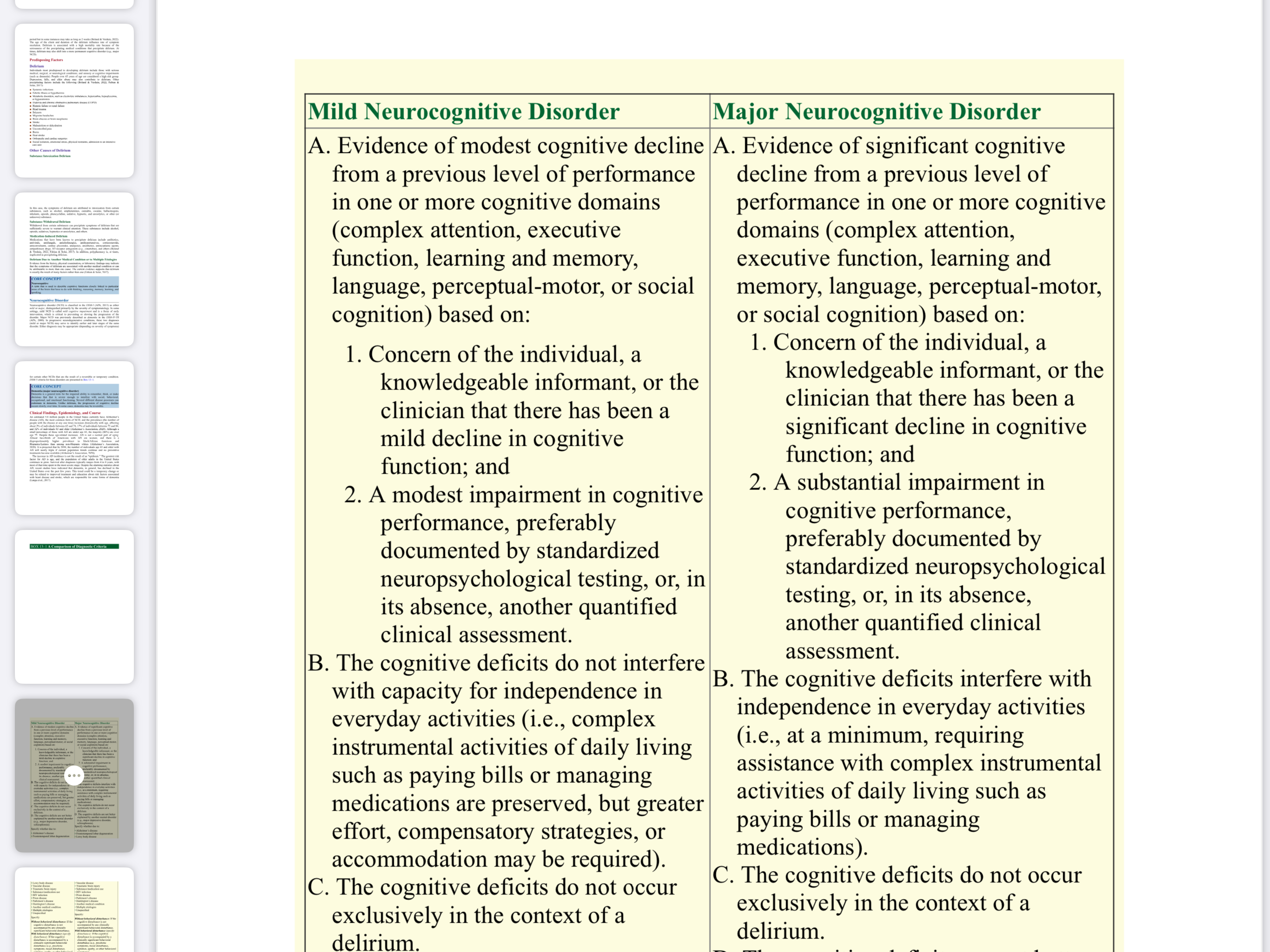
What are the differences between Mild and Major Neurocognitive Disorders?
Understand the Problem
The question is likely comparing Mild and Major Neurocognitive Disorders, highlighting the differences in criteria and assessments for each disorder.
Answer
Mild affects modestly; major affects independence.
Mild neurocognitive disorder involves modest cognitive decline without affecting independence in daily activities. Major neurocognitive disorder involves significant cognitive decline, affecting the ability to perform daily tasks independently.
Answer for screen readers
Mild neurocognitive disorder involves modest cognitive decline without affecting independence in daily activities. Major neurocognitive disorder involves significant cognitive decline, affecting the ability to perform daily tasks independently.
More Information
Mild neurocognitive disorder can sometimes progress to a major disorder. Both types can be caused by various factors including Alzheimer's disease, traumatic brain injury, or other medical conditions.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing mild neurocognitive disorder with normal age-related changes, as the former involves more noticeable effects.
Sources
- Mild and Major Neurocognitive Disorders Treatment - Baptist Health - baptisthealth.com
- Neurocognitive disorder - UF Health - ufhealth.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information