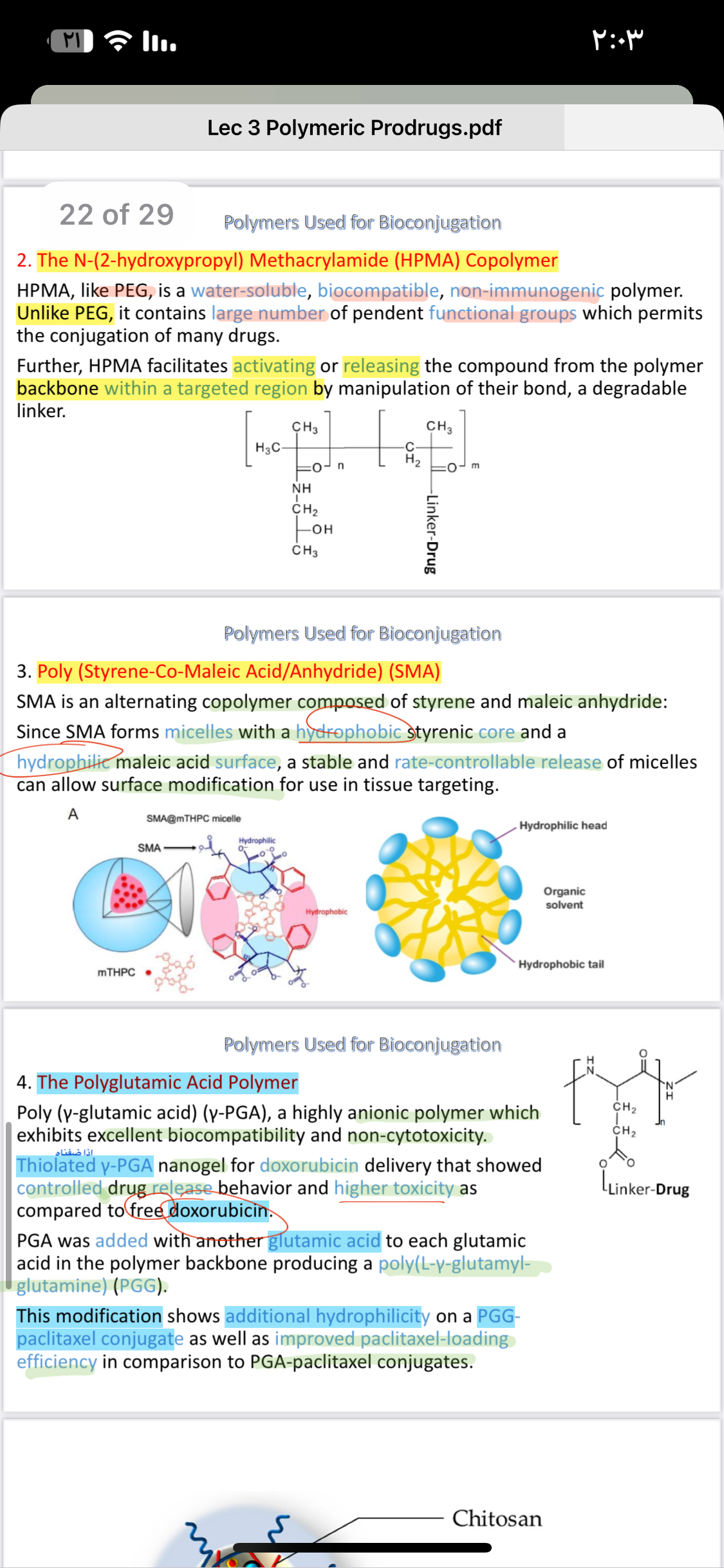
What are the characteristics and applications of HPMA, SMA, and PGA polymers in bioconjugation?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking about the details and characteristics of various types of polymers used for bioconjugation, particularly focusing on their chemical properties and applications in drug delivery systems.
Answer
HPMA: drug delivery; SMA: micelle formation, tissue targeting; PGA: drug delivery, tissue engineering.
HPMA is biocompatible and non-immunogenic, used in drug delivery. SMA forms micelles for controlled release and surface modification. PGA is biodegradable with applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering.
Answer for screen readers
HPMA is biocompatible and non-immunogenic, used in drug delivery. SMA forms micelles for controlled release and surface modification. PGA is biodegradable with applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering.
More Information
HPMA's non-immunogenicity is ideal for prolonged circulation. SMA's micelle arrangement makes it perfect for hydrophilic and hydrophobic substance delivery. PGA's full biodegradability makes it well-suited for temporary applications like sutures.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing polymer properties; for example, assuming PGA is not biodegradable or SMA doesn't form micelles.
Sources
- HPMA copolymers: Origins, early developments, present, and future - pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Sustainable and Biodegradable Polymers: PGA, PLA and PLGA - specificpolymers.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information