Using restriction enzymes to make recombinant DNA.
Understand the Problem
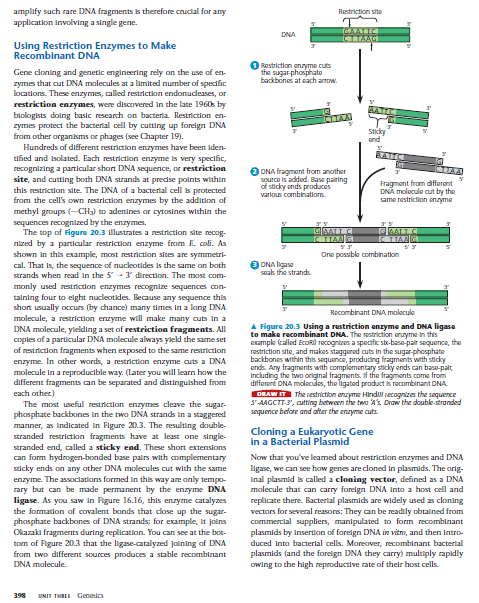
The image contains information about using restriction enzymes in genetic engineering to create recombinant DNA. It outlines the process by which these enzymes can cut DNA at specific sites and how this is fundamental for cloning applications. It explains the role of DNA ligase in recombining DNA fragments.
Answer
Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sequences; DNA ligase joins them to form recombinant DNA.
Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sequences, and DNA ligase joins DNA fragments to create recombinant DNA.
Answer for screen readers
Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sequences, and DNA ligase joins DNA fragments to create recombinant DNA.
More Information
Restriction enzymes, also known as endonucleases, were discovered in the late 1960s. They are essential tools in molecular biology for genetic research, enabling the precise cutting and manipulation of DNA.
Tips
Ensure the DNA fragments to be combined have compatible ends. Choosing appropriate restriction enzymes and optimizing the conditions for ligation are crucial for efficient recombinant DNA formation.
Sources
- Recombinant DNA - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Restriction enzymes & DNA ligase (article) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
- Restriction Enzymes | Learn Science at Scitable - Nature - nature.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information