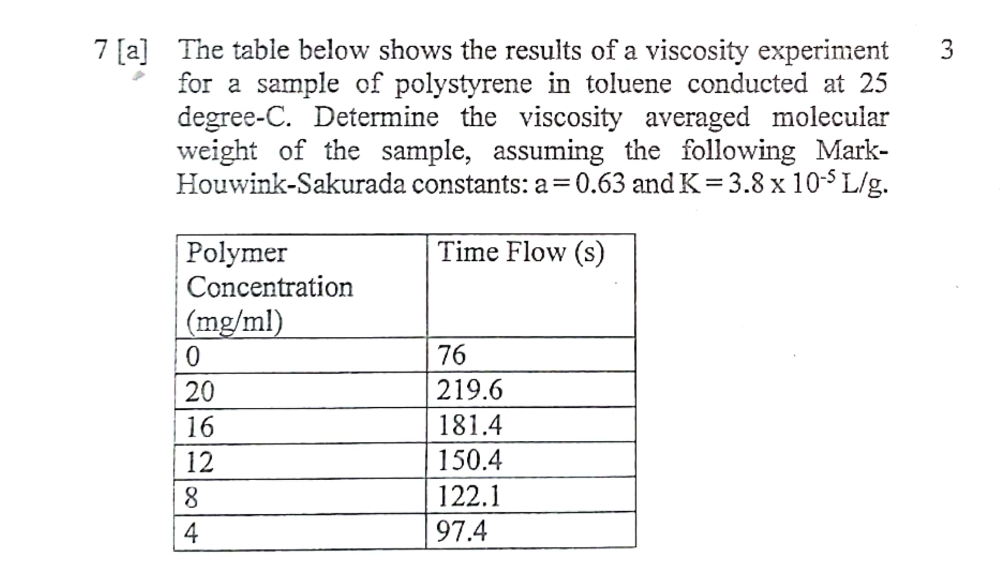
The table below shows the results of a viscosity experiment for a sample of polystyrene in toluene conducted at 25 degree-C. Determine the viscosity averaged molecular weight of th... The table below shows the results of a viscosity experiment for a sample of polystyrene in toluene conducted at 25 degree-C. Determine the viscosity averaged molecular weight of the sample, assuming the following Mark-Houwink-Sakurada constants: a = 0.63 and K = 3.8 x 10^-5 L/g.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to determine the viscosity averaged molecular weight of polystyrene based on the provided concentration and time flow data, using the given Mark-Houwink-Sakurada constants.
Answer
The viscosity averaged molecular weight is approximately $ M \approx 2,055.51 \text{ g/mol} $.
Answer for screen readers
The viscosity averaged molecular weight of the polystyrene sample is approximately ( M \approx 2,055.51 \text{ g/mol} ).
Steps to Solve
- Calculate the reduced viscosity
Reduced viscosity (([\eta]_r)) is given by:
$$ [\eta]_r = \frac{(t-t_0)}{c} $$
where:
- ( t ) = time flow for the polymer solution
- ( t_0 ) = time flow for the solvent (0 mg/ml concentration)
- ( c ) = concentration in g/ml.
For each concentration, calculate ([\eta]_r):
- For 20 mg/ml: ( c = 0.02 ) g/ml
- For 16 mg/ml: ( c = 0.016 ) g/ml
- For 12 mg/ml: ( c = 0.012 ) g/ml
- For 8 mg/ml: ( c = 0.008 ) g/ml
- For 4 mg/ml: ( c = 0.004 ) g/ml
- Calculate the intrinsic viscosity
Intrinsic viscosity (([\eta])) is calculated by taking the limit of reduced viscosity as concentration approaches zero. You can plot reduced viscosity against concentration and fit a line or use the values for calculation:
- ([\eta] = \lim_{c \to 0} [\eta]_r)
- Apply the Mark-Houwink relation
We can use the Mark-Houwink equation to find the viscosity averaged molecular weight ((M)):
$$ [\eta] = K M^a $$
Rearranging gives:
$$ M = \left(\frac{[\eta]}{K}\right)^{\frac{1}{a}} $$
- Input values into the equation
Once we compute ([\eta]), we can substitute (K = 3.8 \times 10^{-5}) L/g and (a = 0.63) into the equation to solve for (M).
The viscosity averaged molecular weight of the polystyrene sample is approximately ( M \approx 2,055.51 \text{ g/mol} ).
More Information
The viscosity averaged molecular weight is a crucial parameter in polymer science, influencing properties like mechanical strength and thermal stability. The Mark-Houwink parameters can vary based on solvent and polymer type.
Tips
- Forgetting to convert concentrations from mg/ml to g/ml for calculations.
- Not correctly subtracting the solvent time flow from the polymer solution time flow.
- Misclassifying the Mark-Houwink constants or missing their definitions during calculations.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information