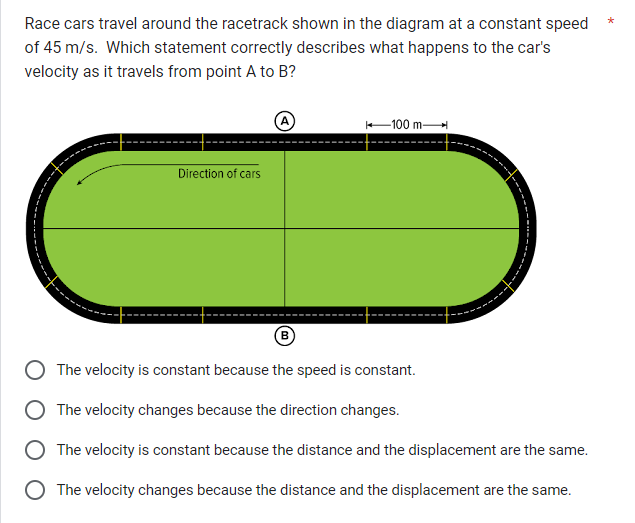
Race cars travel around the racetrack shown in the diagram at a constant speed of 45 m/s. Which statement correctly describes what happens to the car's velocity as it travels from... Race cars travel around the racetrack shown in the diagram at a constant speed of 45 m/s. Which statement correctly describes what happens to the car's velocity as it travels from point A to B?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking about the physics concept of velocity as a race car travels along a curved path at a constant speed. It aims to determine how the car's velocity changes due to directional changes while maintaining the same speed.
Answer
The velocity changes because the direction changes.
The velocity changes because the direction changes.
Answer for screen readers
The velocity changes because the direction changes.
More Information
Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction. Despite the constant speed, the direction change as the car moves from point A to B results in a change in velocity.
Tips
Remember that speed is scalar and does not involve direction, while velocity is vectorial and does.
Sources
- Explain Race cars travel around a racetrack at a constant speed - gauthmath.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information