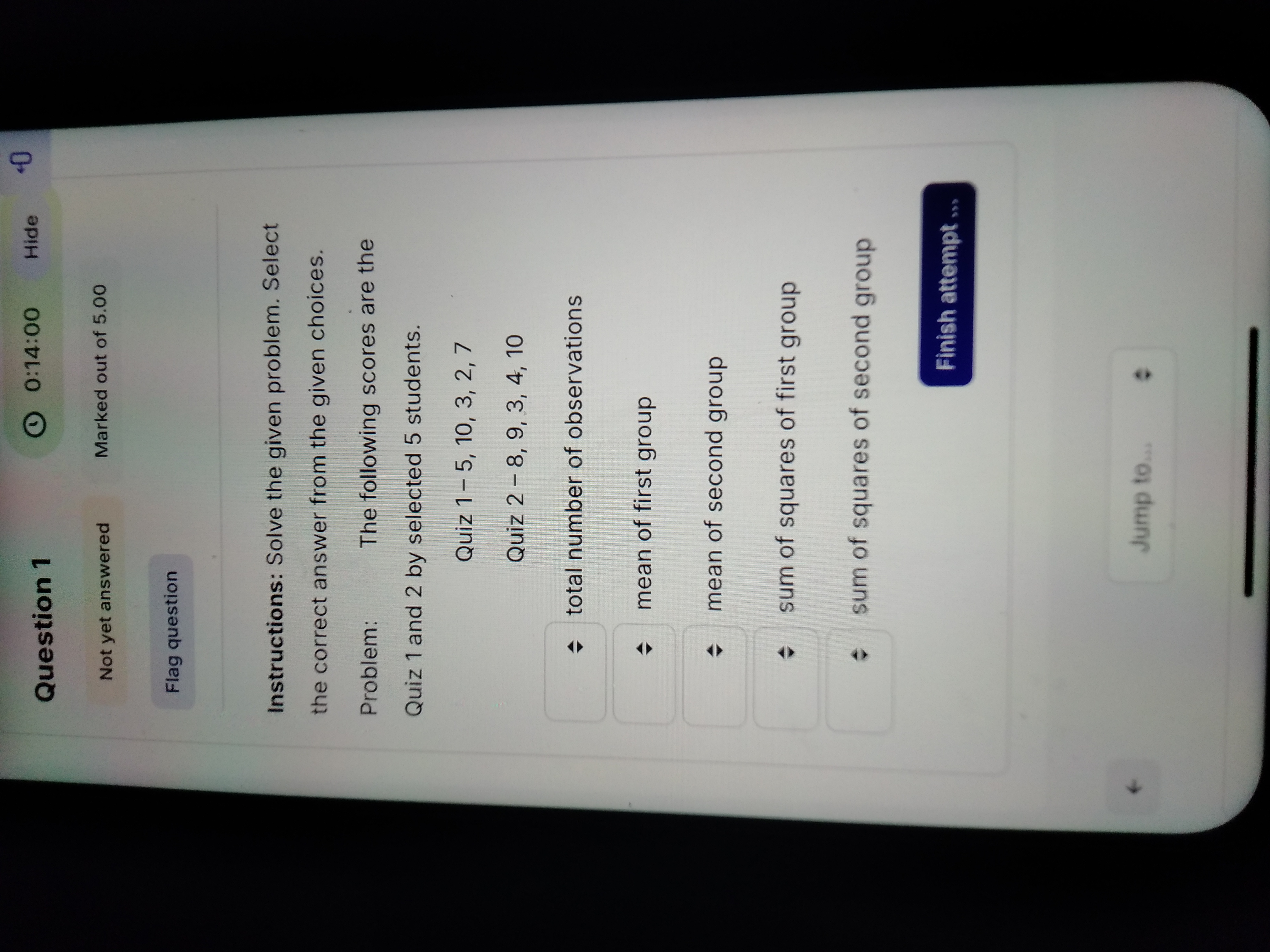
Quiz 1 scores are 5, 10, 3, 2, 7 and Quiz 2 scores are 8, 9, 3, 4, 10. What are the total number of observations, the mean of the first group, the mean of the second group, the sum... Quiz 1 scores are 5, 10, 3, 2, 7 and Quiz 2 scores are 8, 9, 3, 4, 10. What are the total number of observations, the mean of the first group, the mean of the second group, the sum of squares of the first group, and the sum of squares of the second group?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking us to calculate various statistical measures based on the scores of two quizzes taken by five students. Specifically, we need to determine the total number of observations, the means of the first and second groups, and the sums of squares for both groups based on the provided scores.
Answer
Total observations: $10$, Mean of Quiz 1: $5.4$, Mean of Quiz 2: $6.8$, Sum of squares for Quiz 1: $41.2$, Sum of squares for Quiz 2: $39.8$
Answer for screen readers
-
Total number of observations: $10$
-
Mean of Quiz 1: $5.4$
-
Mean of Quiz 2: $6.8$
-
Sum of squares for Quiz 1: $41.2$
-
Sum of squares for Quiz 2: $39.8$
Steps to Solve
- Calculate Total Number of Observations
The total number of observations is the sum of the number of scores in both quizzes.
For Quiz 1: There are 5 scores. For Quiz 2: There are also 5 scores.
So, the total number of observations is:
$$ \text{Total Observations} = 5 + 5 = 10 $$
- Calculate the Mean of Quiz 1 Scores
To find the mean of Quiz 1 scores, sum the scores and divide by the number of observations.
Quiz 1 scores: 5, 10, 3, 2, 7
Calculate the sum:
$$ \text{Sum of Quiz 1} = 5 + 10 + 3 + 2 + 7 = 27 $$
Now, calculate the mean:
$$ \text{Mean of Quiz 1} = \frac{27}{5} = 5.4 $$
- Calculate the Mean of Quiz 2 Scores
For Quiz 2, repeat the process with its scores.
Quiz 2 scores: 8, 9, 3, 4, 10
Calculate the sum:
$$ \text{Sum of Quiz 2} = 8 + 9 + 3 + 4 + 10 = 34 $$
Now, calculate the mean:
$$ \text{Mean of Quiz 2} = \frac{34}{5} = 6.8 $$
- Calculate the Sum of Squares for Quiz 1
The sum of squares is calculated by finding the squared difference from the mean for each score, summing them up.
First, calculate the individual squared differences:
- For 5: $(5 - 5.4)^2 = 0.16$
- For 10: $(10 - 5.4)^2 = 21.16$
- For 3: $(3 - 5.4)^2 = 5.76$
- For 2: $(2 - 5.4)^2 = 11.56$
- For 7: $(7 - 5.4)^2 = 2.56$
Now sum the squared differences:
$$ \text{Sum of Squares for Quiz 1} = 0.16 + 21.16 + 5.76 + 11.56 + 2.56 = 41.2 $$
- Calculate the Sum of Squares for Quiz 2
Repeat the process for Quiz 2 scores.
First, calculate the individual squared differences:
- For 8: $(8 - 6.8)^2 = 1.44$
- For 9: $(9 - 6.8)^2 = 4.84$
- For 3: $(3 - 6.8)^2 = 14.44$
- For 4: $(4 - 6.8)^2 = 7.84$
- For 10: $(10 - 6.8)^2 = 10.24$
Now sum the squared differences:
$$ \text{Sum of Squares for Quiz 2} = 1.44 + 4.84 + 14.44 + 7.84 + 10.24 = 39.80 $$
-
Total number of observations: $10$
-
Mean of Quiz 1: $5.4$
-
Mean of Quiz 2: $6.8$
-
Sum of squares for Quiz 1: $41.2$
-
Sum of squares for Quiz 2: $39.8$
More Information
The means and sums of squares provide insights into the central tendencies and variability of the scores for each quiz, important for statistical analysis.
Tips
- Forgetting to square the differences when calculating the sum of squares.
- Not dividing by the correct number when calculating the mean.
- Mixing up the scores of the two quizzes.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information