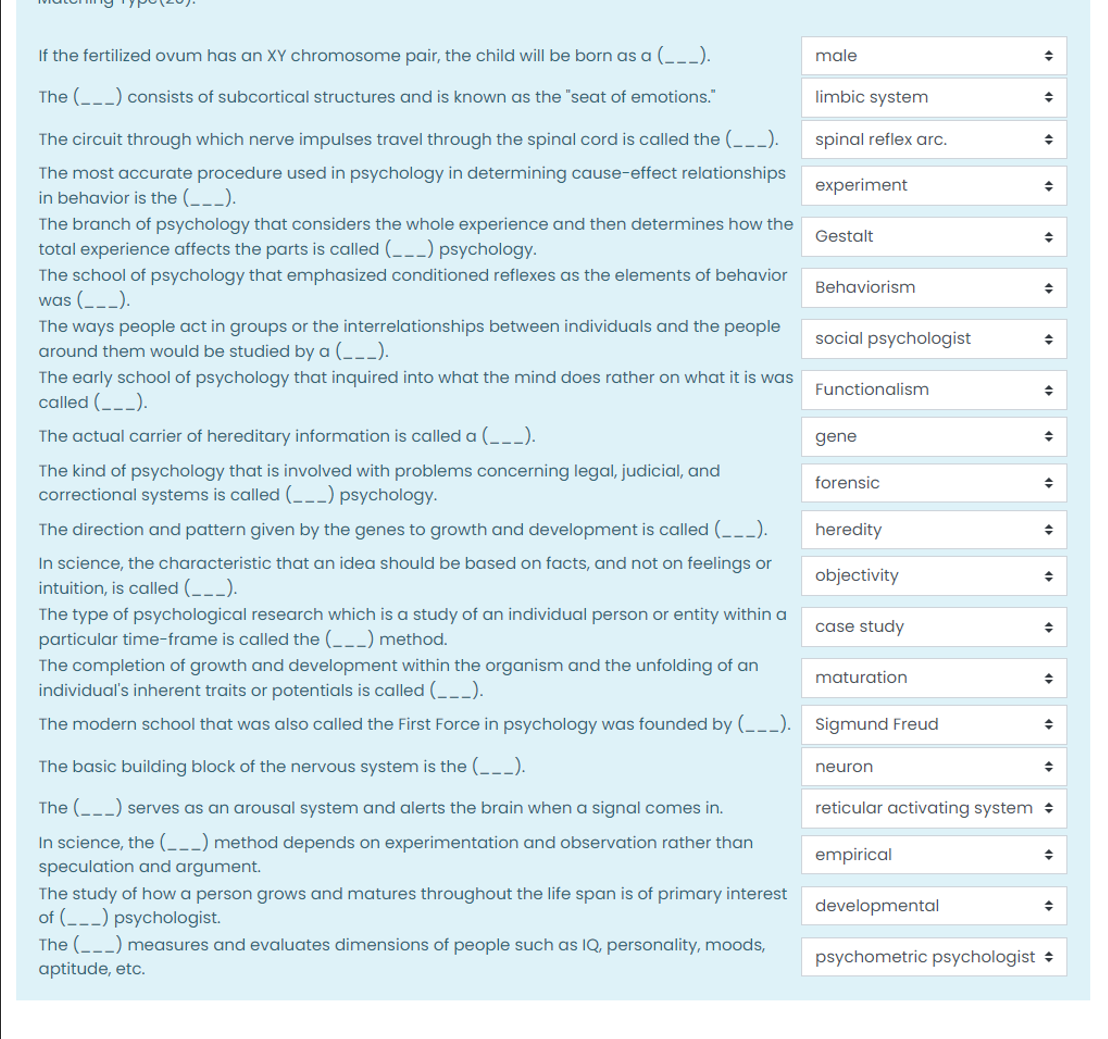
If the fertilized ovum has an XY chromosome pair, the child will be born as a (___). The (___) consists of subcortical structures and is known as the 'seat of emotions.' The circui... If the fertilized ovum has an XY chromosome pair, the child will be born as a (___). The (___) consists of subcortical structures and is known as the 'seat of emotions.' The circuit through which nerve impulses travel through the spinal cord is called the (___). The most accurate procedure used in psychology in determining cause-effect relationships in behavior is the (___). The branch of psychology that considers the whole experience and then determines how the total experience affects the parts is called (___) psychology. The school of psychology that emphasized conditioned reflexes as the elements of behavior was (___). The ways people act in groups or the interrelationships between individuals and the people around them would be studied by a (___). The early school of psychology that inquired into what the mind does rather on what it is called (___). The actual carrier of hereditary information is called a (___). The kind of psychology that is involved with problems concerning legal, judicial, and correctional systems is called (___) psychology. The direction and pattern given by the genes to growth and development is called (___). In science, the characteristic that an idea should be based on facts, and not on feelings or intuition, is called (___). The type of psychological research which is a study of an individual person or entity within a particular time-frame is called the (___) method. The completion of growth and development within the organism and the unfolding of an individual's inherent traits or potentials is called (___). The modern school that was also called the First Force in psychology was founded by (___). The basic building block of the nervous system is the (___). The (___) serves as an arousal system and alerts the brain when a signal comes in. In science, the (___) method depends on experimentation and observation rather than speculation and argument. The study of how a person grows and matures throughout the life span is of primary interest of (___) psychologist. The (___) measures and evaluates dimensions of people such as IQ, personality, moods, aptitude, etc.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for the completion of various sentences related to psychology, requiring knowledge of psychological terms and concepts.
Answer
If the fertilized ovum has an XY chromosome pair, the child will be born as a male. The limbic system consists of subcortical structures and is known as the 'seat of emotions.' The circuit through which nerve impulses travel through the spinal cord is called the spinal reflex arc. The most accurate procedure used in psychology in determining cause-effect relationships in behavior is the experiment. The branch of psychology that considers the whole experience and then determines how the total experience affects the parts is called Gestalt psychology. The school of psychology that emphasized conditioned reflexes as the elements of behavior was Behaviorism. The ways people act in groups or the interrelationships between individuals and the people around them would be studied by a social psychologist. The early school of psychology that inquired into what the mind does rather on what it is called Functionalism. The actual carrier of hereditary information is called a gene. The kind of psychology that is involved with problems concerning legal, judicial, and correctional systems is called forensic psychology. The direction and pattern given by the genes to growth and development is called heredity. In science, the characteristic that an idea should be based on facts, and not on feelings or intuition, is called objectivity. The type of psychological research which is a study of an individual person or entity within a particular time-frame is called the case study method. The completion of growth and development within the organism and the unfolding of an individual's inherent traits or potentials is called maturation. The modern school that was also called the First Force in psychology was founded by Sigmund Freud. The basic building block of the nervous system is the neuron. The reticular activating system serves as an arousal system and alerts the brain when a signal comes in. In science, the empirical method depends on experimentation and observation rather than speculation and argument. The study of how a person grows and matures throughout the life span is of primary interest of developmental psychologist. The psychometric psychologist measures and evaluates dimensions of people such as IQ, personality, moods, aptitude, etc.
If the fertilized ovum has an XY chromosome pair, the child will be born as a (male). The (limbic system) consists of subcortical structures and is known as the 'seat of emotions.' The circuit through which nerve impulses travel through the spinal cord is called the (spinal reflex arc). The most accurate procedure used in psychology in determining cause-effect relationships in behavior is the (experiment). The branch of psychology that considers the whole experience and then determines how the total experience affects the parts is called (Gestalt) psychology. The school of psychology that emphasized conditioned reflexes as the elements of behavior was (Behaviorism). The ways people act in groups or the interrelationships between individuals and the people around them would be studied by a (social psychologist). The early school of psychology that inquired into what the mind does rather on what it is called (Functionalism). The actual carrier of hereditary information is called a (gene). The kind of psychology that is involved with problems concerning legal, judicial, and correctional systems is called (forensic) psychology. The direction and pattern given by the genes to growth and development is called (heredity). In science, the characteristic that an idea should be based on facts, and not on feelings or intuition, is called (objectivity). The type of psychological research which is a study of an individual person or entity within a particular time-frame is called the (case study) method. The completion of growth and development within the organism and the unfolding of an individual's inherent traits or potentials is called (maturation). The modern school that was also called the First Force in psychology was founded by (Sigmund Freud). The basic building block of the nervous system is the (neuron). The (reticular activating system) serves as an arousal system and alerts the brain when a signal comes in. In science, the (empirical) method depends on experimentation and observation rather than speculation and argument. The study of how a person grows and matures throughout the life span is of primary interest of (developmental) psychologist. The (psychometric psychologist) measures and evaluates dimensions of people such as IQ, personality, moods, aptitude, etc.
Answer for screen readers
If the fertilized ovum has an XY chromosome pair, the child will be born as a (male). The (limbic system) consists of subcortical structures and is known as the 'seat of emotions.' The circuit through which nerve impulses travel through the spinal cord is called the (spinal reflex arc). The most accurate procedure used in psychology in determining cause-effect relationships in behavior is the (experiment). The branch of psychology that considers the whole experience and then determines how the total experience affects the parts is called (Gestalt) psychology. The school of psychology that emphasized conditioned reflexes as the elements of behavior was (Behaviorism). The ways people act in groups or the interrelationships between individuals and the people around them would be studied by a (social psychologist). The early school of psychology that inquired into what the mind does rather on what it is called (Functionalism). The actual carrier of hereditary information is called a (gene). The kind of psychology that is involved with problems concerning legal, judicial, and correctional systems is called (forensic) psychology. The direction and pattern given by the genes to growth and development is called (heredity). In science, the characteristic that an idea should be based on facts, and not on feelings or intuition, is called (objectivity). The type of psychological research which is a study of an individual person or entity within a particular time-frame is called the (case study) method. The completion of growth and development within the organism and the unfolding of an individual's inherent traits or potentials is called (maturation). The modern school that was also called the First Force in psychology was founded by (Sigmund Freud). The basic building block of the nervous system is the (neuron). The (reticular activating system) serves as an arousal system and alerts the brain when a signal comes in. In science, the (empirical) method depends on experimentation and observation rather than speculation and argument. The study of how a person grows and matures throughout the life span is of primary interest of (developmental) psychologist. The (psychometric psychologist) measures and evaluates dimensions of people such as IQ, personality, moods, aptitude, etc.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information