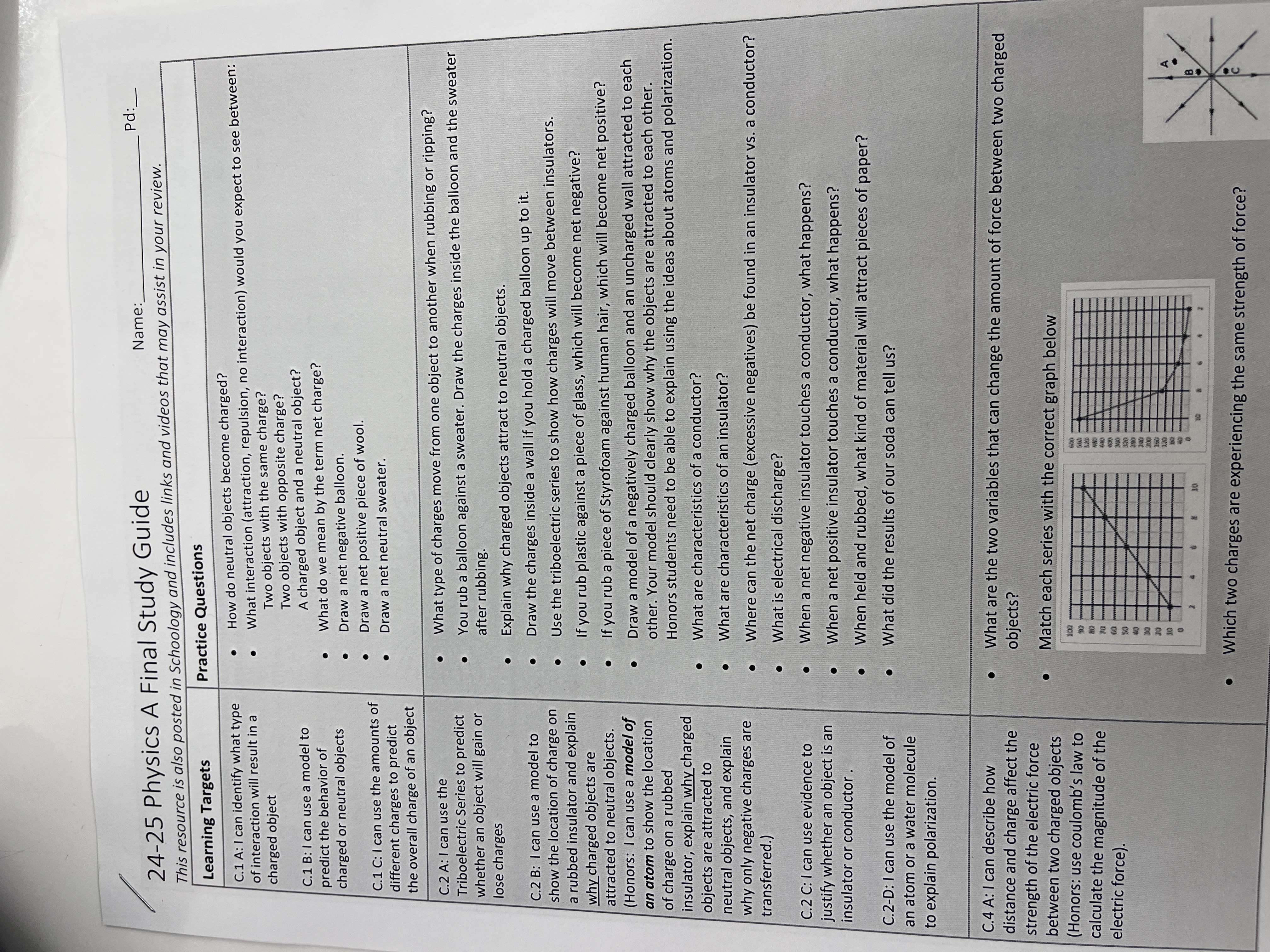
How do neutral objects become charged? What interaction would you expect to see between objects with the same charge? Explain why charged objects attract to neutral objects.
Understand the Problem
The question is related to physics concepts regarding charge interactions, forces between charged objects, and the behavior of neutral objects in the presence of charges. It also mentions the importance of understanding the characteristics of conductors and insulators.
Answer
Neutral objects get charged by electron transfer. Same charges repel. Charged objects attract neutral ones due to polarization.
Neutral objects become charged through electron transfer (friction, conduction, or induction). Objects with the same charge repel each other. Charged objects attract neutral objects due to charge polarization.
Answer for screen readers
Neutral objects become charged through electron transfer (friction, conduction, or induction). Objects with the same charge repel each other. Charged objects attract neutral objects due to charge polarization.
More Information
Charged objects affect neutral objects by causing a redistribution of charges within the neutral object. This results in an attraction due to induced charges on the neutral object's surface, opposite to the nearby charged object.
Tips
Be careful not to confuse induction with conduction. Induction involves a charge without direct contact, while conduction requires contact.
Sources
- Neutral vs. Charged Objects - The Physics Classroom - physicsclassroom.com
- Physics Tutorial: Charge Interactions - physicsclassroom.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information