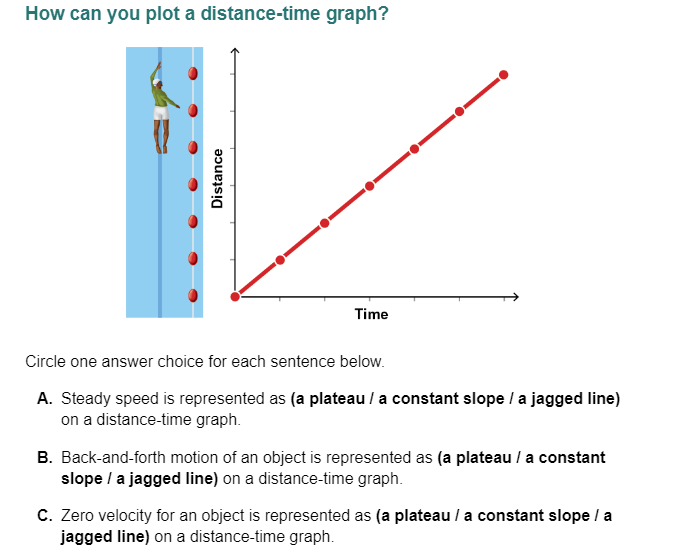
How can you plot a distance-time graph? Circle one answer choice for each sentence below. A. Steady speed is represented as (a plateau / a constant slope / a jagged line) on a dist... How can you plot a distance-time graph? Circle one answer choice for each sentence below. A. Steady speed is represented as (a plateau / a constant slope / a jagged line) on a distance-time graph. B. Back-and-forth motion of an object is represented as (a plateau / a constant slope / a jagged line) on a distance-time graph. C. Zero velocity for an object is represented as (a plateau / a constant slope / a jagged line) on a distance-time graph.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking how to represent different aspects of motion on a distance-time graph, specifically identifying representations for steady speed, back-and-forth motion, and zero velocity.
Answer
A: constant slope, B: jagged line, C: plateau
A. Steady speed is represented as a constant slope on a distance-time graph. B. Back-and-forth motion of an object is represented as a jagged line on a distance-time graph. C. Zero velocity for an object is represented as a plateau on a distance-time graph.
Answer for screen readers
A. Steady speed is represented as a constant slope on a distance-time graph. B. Back-and-forth motion of an object is represented as a jagged line on a distance-time graph. C. Zero velocity for an object is represented as a plateau on a distance-time graph.
More Information
Distance-time graphs represent motion: a constant slope indicates steady speed, a plateau shows no movement (zero velocity), and a jagged line reflects variable motion, like back-and-forth movement.
Tips
Common mistakes include confusing the graph representation of steady speed with zero velocity. Remember, steady speed results in a constant slope, while zero velocity is a horizontal line (plateau).
Sources
- Distance Time Graphs - GeeksforGeeks - geeksforgeeks.org
- Distance Time Graph - Definition And Examples With Conclusion - byjus.com