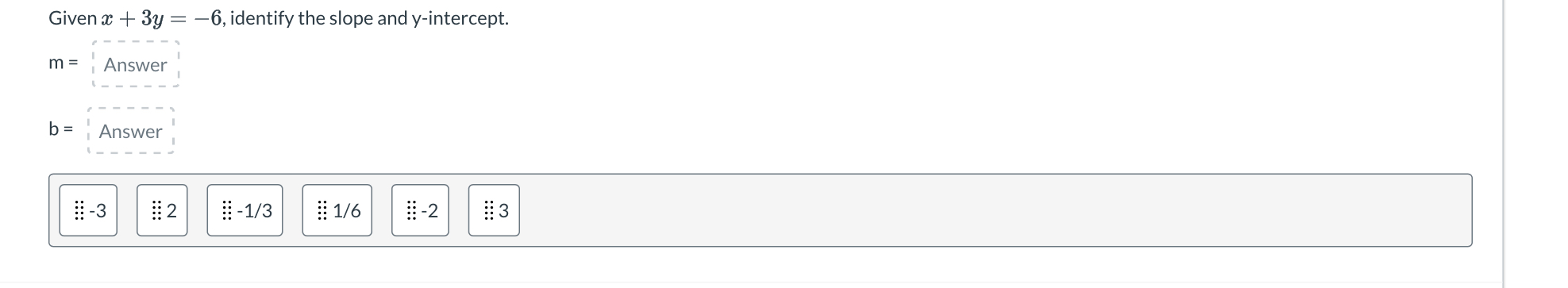
Given x + 3y = -6, identify the slope and y-intercept.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to identify the slope (m) and y-intercept (b) from the given equation of a line, which is presented in standard form. To solve this, we will rearrange the equation into slope-intercept form (y = mx + b).
Answer
m = $-\frac{1}{3}$, b = $-2$
Answer for screen readers
m = $-\frac{1}{3}$
b = $-2$
Steps to Solve
- Rearranging the Equation To find the slope and y-intercept, we need to rearrange the given equation into slope-intercept form, which is $y = mx + b$. The original equation is:
$$ x + 3y = -6 $$
First, isolate $y$ by moving $x$ to the other side:
$$ 3y = -x - 6 $$
- Dividing by the Coefficient of y Next, divide every term by 3 to solve for $y$:
$$ y = -\frac{1}{3}x - 2 $$
- Identifying Slope and Y-Intercept From the equation $y = -\frac{1}{3}x - 2$, we can directly identify the slope $m$ and the y-intercept $b$. The slope $m$ is the coefficient of $x$, and the y-intercept $b$ is the constant term.
Thus,
- The slope $m = -\frac{1}{3}$.
- The y-intercept $b = -2$.
m = $-\frac{1}{3}$
b = $-2$
More Information
The slope indicates that for every 1 unit increase in $x$, the value of $y$ decreases by $\frac{1}{3}$ units. The y-intercept represents the value of $y$ when $x$ is 0, which is at the point (0, -2) on the graph.
Tips
- Not isolating y correctly: Ensure every step maintains the balance of the equation when moving terms around.
- Confusing slope and y-intercept: Remember that in the form $y = mx + b$, $m$ is the slope (coefficient of $x$) and $b$ is the y-intercept (constant term).
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information