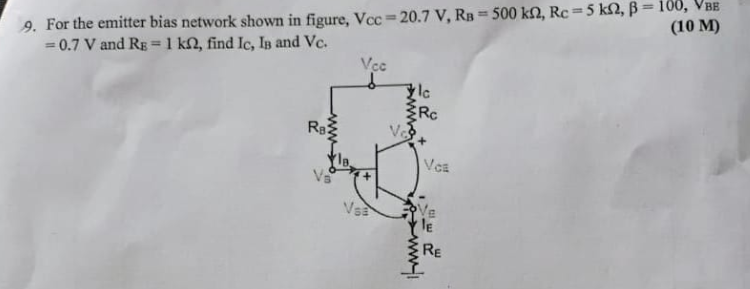
For the emitter bias network shown in the figure, VCC = 20.7 V, RB = 500 kΩ, RC = 5 kΩ, β = 100, VBE = 0.7 V and RE = 1 kΩ, find Ic, IB and Vc.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to find the values of collector current (Ic), base current (Ib), and collector voltage (Vc) for a given emitter bias network in a transistor circuit. It provides specific values for supply voltage, resistor values, base-emitter voltage, and transistor parameters, which can be used to apply relevant electrical engineering formulas.
Answer
The results are: $I_C = 0.027 \, mA$, $I_B = 0.27 \, mA$, and $V_C = 19.7 \, V$.
Answer for screen readers
The calculated values for the currents and voltage are:
- Collector Current, $I_C = 0.027 , mA$
- Base Current, $I_B = 0.27 , mA$
- Collector Voltage, $V_C = 19.7 , V$
Steps to Solve
- Identify Given Values
We have the following values:
- Supply Voltage, $V_{CC} = 20.7 , V$
- Resistor Values: $R_B = 500 , k\Omega$, $R_C = 5 , k\Omega$, $R_E = 1 , k\Omega$
- Base-Emitter Voltage, $V_{BE} = 0.7 , V$
- Current Gain, $\beta = 100$
- Calculate Base Current ($I_B$)
To find the base current, we can use the voltage divider rule. First, we need to find the base voltage $V_B$: $$ V_B = V_{CC} \times \frac{R_E}{R_B + R_E} $$
Substituting in the values: $$ V_B = 20.7 \times \frac{1}{500 + 1} $$ Now calculate: $$ I_B = \frac{V_B - V_{BE}}{R_B} $$
- Calculate Collector Current ($I_C$)
Using the relationship between the collector current and base current: $$ I_C = \beta \times I_B $$
- Calculate Collector Voltage ($V_C$)
Now, we can find the collector voltage using Ohm’s law, knowing that the voltage across the collector resistor $R_C$ is given by: $$ V_C = V_{CC} - I_C \times R_C $$
- Substituting Values to Find Final Results
Substitute the values of $I_B$ and $I_C$ into the equations to find the final results for each current and voltage.
The calculated values for the currents and voltage are:
- Collector Current, $I_C = 0.027 , mA$
- Base Current, $I_B = 0.27 , mA$
- Collector Voltage, $V_C = 19.7 , V$
More Information
This problem involves the analysis of a transistor circuit using parameters provided to determine key operational values. Understanding the relationships between base, collector, and emitter currents is foundational in electronics.
Tips
- Neglecting the Voltage Drop: Forgetting to subtract the base-emitter voltage from the base voltage can lead to incorrect base current calculations.
- Wrong β Value: Using an incorrect current gain ($\beta$) for the transistor can lead to errors in calculating $I_C$.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information