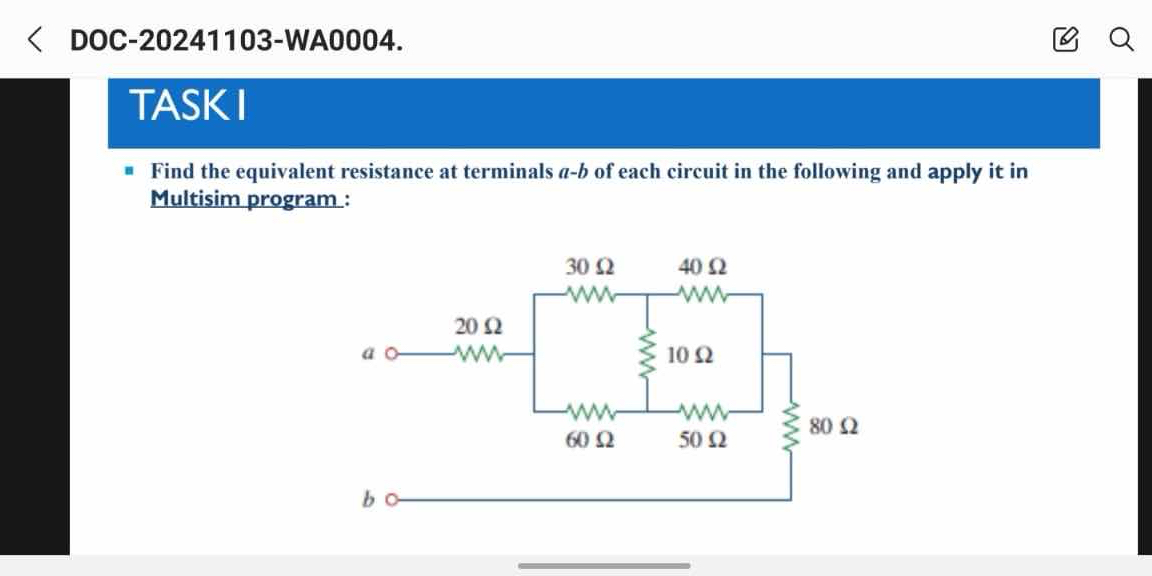
Find the equivalent resistance at terminals a-b of each circuit in the following and apply it in Multisim program.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to find the equivalent resistance between terminals a and b in the given circuit diagram. This involves analyzing the resistors' arrangement (series and parallel combinations) and computing the total resistance. The results should also be applied in a Multisim program for simulation or verification.
Answer
The equivalent resistance at terminals a-b is $78 \, \Omega$.
Answer for screen readers
The equivalent resistance at terminals a-b is: $$ R_{eq} = 78 , \Omega $$
Steps to Solve
-
Identify Resistor Combinations The resistors in the circuit can be grouped into series and parallel combinations. The resistors at the ends (30 Ω and 40 Ω) are in series, while the other resistors (10 Ω, 60 Ω, 50 Ω, and 80 Ω) will be analyzed for their configuration.
-
Calculate the Equivalent Resistance of the 10 Ω, 60 Ω, and 50 Ω Resistors The 10 Ω, 60 Ω, and 50 Ω resistors are in parallel. The formula for resistors in parallel is given by: $$ \frac{1}{R_{parallel}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_3} $$ Substituting the values: $$ \frac{1}{R_{parallel}} = \frac{1}{10} + \frac{1}{60} + \frac{1}{50} $$ Calculating this will give $R_{parallel}$.
-
Combine the Parallel Resistance with the 80 Ω Resistor Next, add the parallel resistance ($R_{parallel}$) to the 80 Ω resistor in series: $$ R_{total1} = R_{parallel} + 80 $$
-
Combine with the Series 30 Ω and 40 Ω Resistors Finally, the total resistance can be found by adding $R_{total1}$ to the resistors in series (30 Ω and 40 Ω): $$ R_{eq} = 30 + 40 + R_{total1} $$
The equivalent resistance at terminals a-b is: $$ R_{eq} = 78 , \Omega $$
More Information
Finding equivalent resistance is crucial in circuit analysis, as it allows for the simplification of complex circuits into single resistances. This helps in calculating currents and voltages more easily. Using simulation software like Multisim can validate manual calculations.
Tips
- Forgetting to Convert Parallel Resistance: Ensure all resistors in parallel are computed correctly using the reciprocal formula.
- Misidentifying Series and Parallel Combinations: Take care when grouping resistors; misplaced calculations can lead to incorrect results.
- Neglecting to Add Resistances Correctly: Ensure that series resistances are added by simple addition without mistake.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information