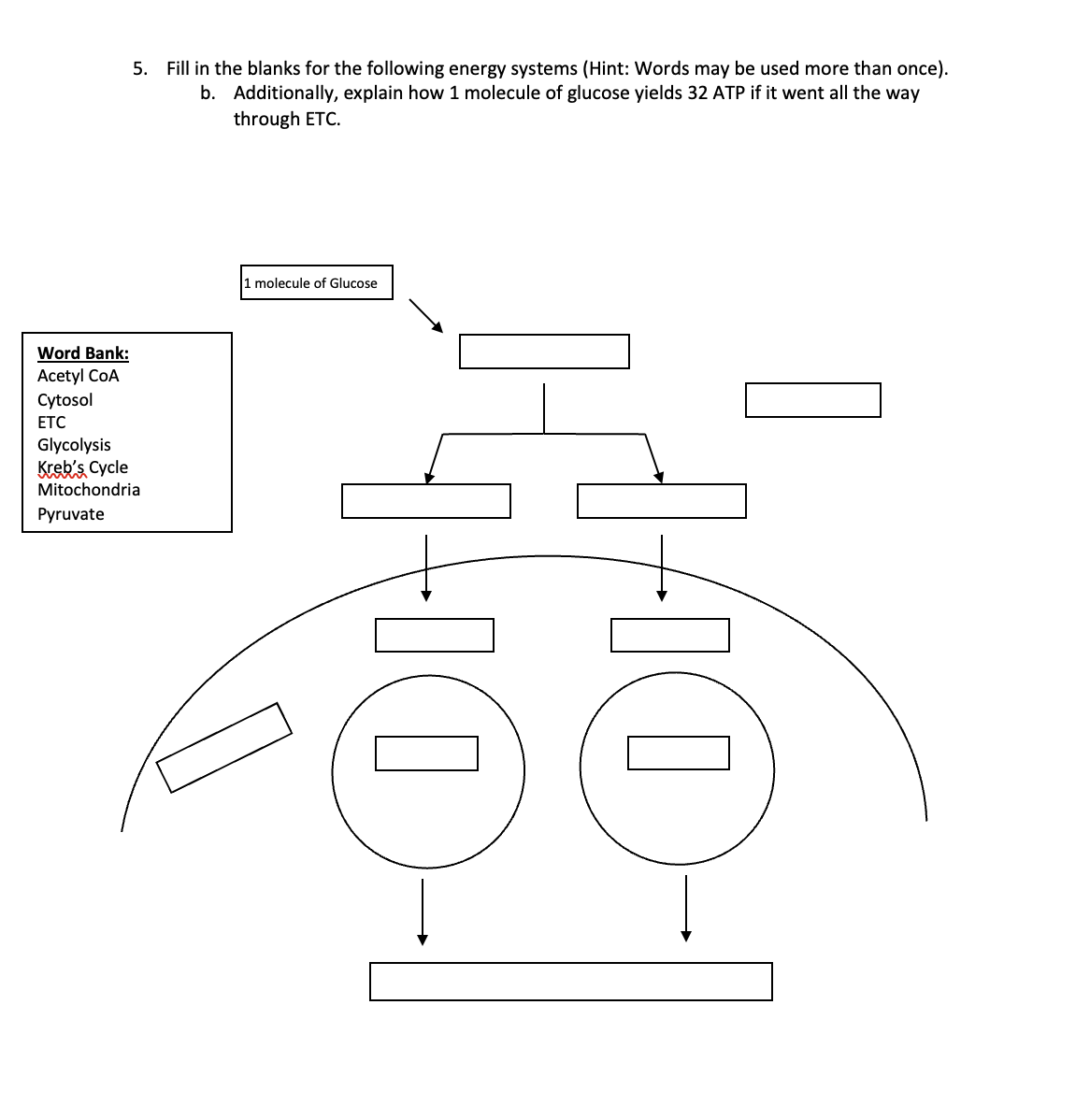
Fill in the blanks for the following energy systems (Hint: Words may be used more than once). Additionally, explain how 1 molecule of glucose yields 32 ATP if it went all the way t... Fill in the blanks for the following energy systems (Hint: Words may be used more than once). Additionally, explain how 1 molecule of glucose yields 32 ATP if it went all the way through ETC.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for a fill-in-the-blank exercise related to the energy systems of glucose metabolism, along with an explanation of how one molecule of glucose can produce 32 ATP through the electron transport chain (ETC). This involves concepts such as glycolysis, pyruvate formation, and the Krebs cycle.
Answer
Glucose yields 32 ATP through glycolysis, the Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain in mitochondria.
After glycolysis, glucose is split into pyruvate in the cytosol. Pyruvate converts to acetyl-CoA in the mitochondria. Acetyl-CoA enters the Krebs Cycle, producing NADH and FADH2. These molecules donate electrons to the ETC, creating a proton gradient that powers ATP synthase to generate ATP.
Answer for screen readers
After glycolysis, glucose is split into pyruvate in the cytosol. Pyruvate converts to acetyl-CoA in the mitochondria. Acetyl-CoA enters the Krebs Cycle, producing NADH and FADH2. These molecules donate electrons to the ETC, creating a proton gradient that powers ATP synthase to generate ATP.
More Information
Each NADH molecule from the Krebs Cycle provides approximately 2.5 ATP, and each FADH2 provides about 1.5 ATP. The total ATP yield of cellular respiration can vary slightly based on the shuttle systems transporting electrons into the mitochondria.
Tips
Common mistakes include misplacing the sequence of the cycles or stages and ignoring the spatial location where specific processes take place.
Sources
- Steps of cellular respiration | Biology (article) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
- Cellular Respiration Process | CK-12 Foundation - flexbooks.ck12.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information