Evaluate the following limits: (iv) lim x→0 tan 2x / tan 5x, (v) lim x→0 sin 3x / sin 7x, (vi) lim x→0 sin(ax) / bx, (vii) lim x→0 sin 4x / sin 2x, (viii) lim x→0 x sec x, (ix) lim... Evaluate the following limits: (iv) lim x→0 tan 2x / tan 5x, (v) lim x→0 sin 3x / sin 7x, (vi) lim x→0 sin(ax) / bx, (vii) lim x→0 sin 4x / sin 2x, (viii) lim x→0 x sec x, (ix) lim x→0 cos x / (pi - x), (x) lim x→0 (sin(ax + bx) / (ax + sin(bx)), where a, b, a + b ≠ 0.
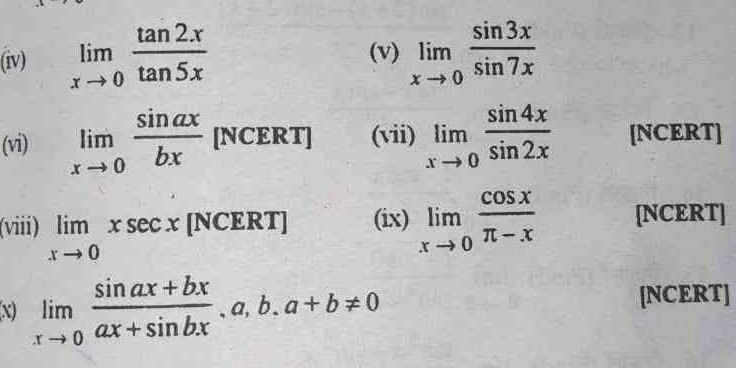
Understand the Problem
The question consists of a series of limits involving trigonometric functions as x approaches 0. Each limit requires applying L'Hôpital's rule or the small angle approximation for sine and tangent functions. Understanding these concepts will help in evaluating each limit correctly.
Answer
1. $\frac{2}{5}$ 2. $\frac{3}{7}$ 3. $\frac{a}{b}$ 4. $2$ 5. $0$ 6. $1$
Answer for screen readers
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\tan 2x}{\tan 5x} = \frac{2}{5}$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin 3x}{\sin 7x} = \frac{3}{7}$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin ax}{bx} = \frac{a}{b}$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin 4x}{\sin 2x} = 2$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} x \sec x = 0$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin ax + bx}{ax + \sin bx} = 1$
Steps to Solve
-
Limit Analysis: Identify the Indeterminate Forms
For each limit, we need to determine whether substituting $x = 0$ gives an indeterminate form (like $0/0$ or $\infty/\infty$).
-
Apply L'Hôpital's Rule or Small Angle Approximations
For limits leading to $0/0$, we can apply L'Hôpital's Rule, which states: $$ \lim_{x \to a} \frac{f(x)}{g(x)} = \lim_{x \to a} \frac{f'(x)}{g'(x)} $$ if $f(a) = g(a) = 0$.
-
Evaluate Each Limit Using Known Limits
We can utilize known limits:
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin x}{x} = 1$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\tan x}{x} = 1$
- Similarly, apply small angle approximations where useful.
-
Calculate Each Limit
Each limit will be calculated accordingly, revisiting previous results or applying simple algebra operations.
-
Final Results
Collect and express the final results of each limit clearly.
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\tan 2x}{\tan 5x} = \frac{2}{5}$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin 3x}{\sin 7x} = \frac{3}{7}$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin ax}{bx} = \frac{a}{b}$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin 4x}{\sin 2x} = 2$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} x \sec x = 0$
- $\lim_{x \to 0} \frac{\sin ax + bx}{ax + \sin bx} = 1$
More Information
These limits illustrate fundamental concepts in calculus, particularly around understanding how trigonometric functions behave near zero. The limits make use of L'Hôpital's Rule and the small angle approximations, which are essential tools in calculus.
Tips
- Not recognizing an indeterminate form before applying L'Hôpital's Rule.
- Forgetting to simplify expressions before substitution.
- Incorrectly applying trigonometric limits without confirming they lead to the correct forms.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information