Define Catalyst and state its different types. What is Lubricant? Give example. What are monomers and Polymers? What is Degree of Ionization? List out the different types of corros... Define Catalyst and state its different types. What is Lubricant? Give example. What are monomers and Polymers? What is Degree of Ionization? List out the different types of corrosion. What is the difference between hard water and soft water?
Understand the Problem
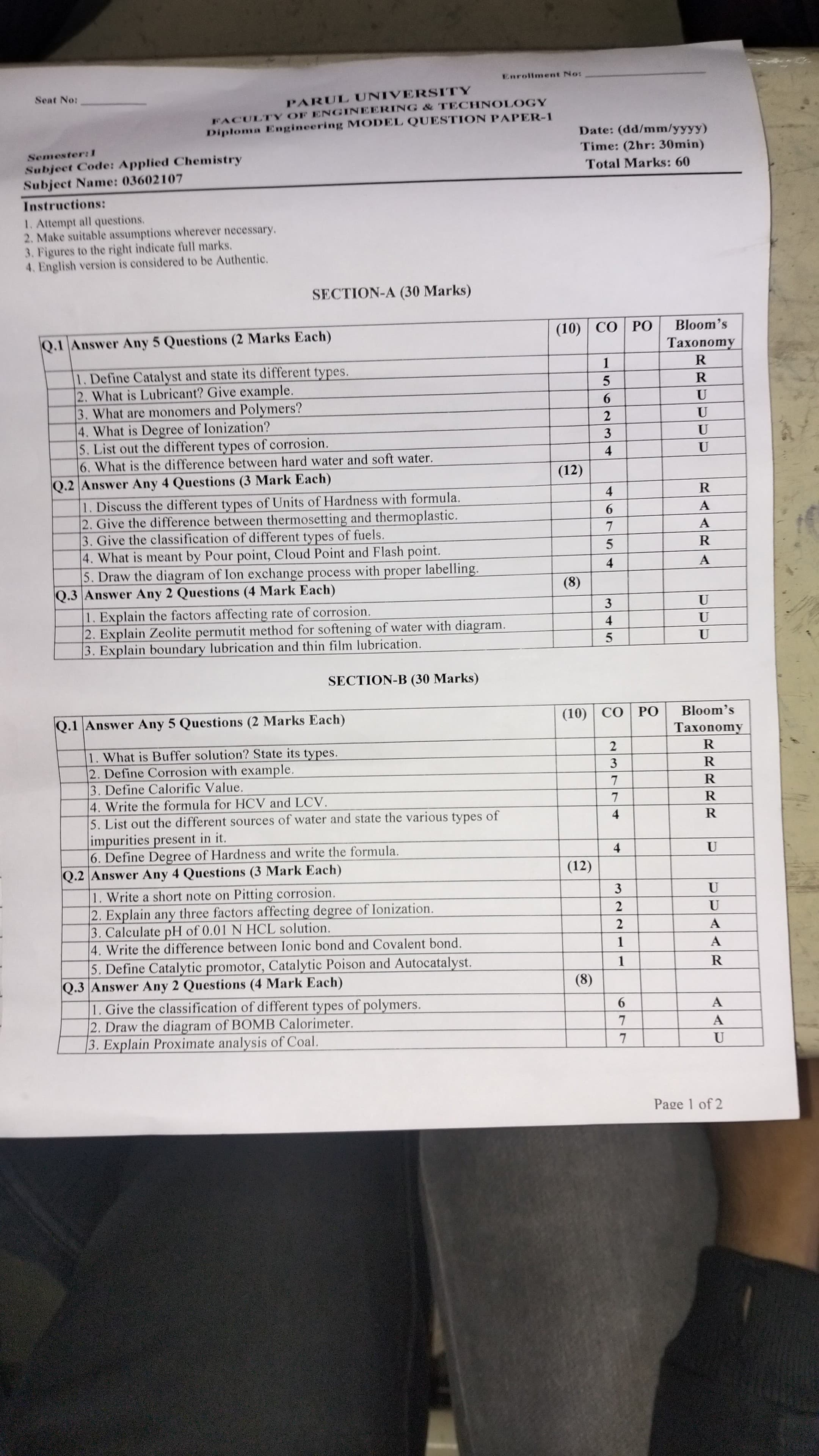
The question paper contains a series of questions related to applied chemistry, covering topics such as catalysts, lubricants, water types, and corrosion. It is structured into sections, with questions targeted at assessing knowledge and understanding of chemical principles and applications.
Answer
Catalyst speeds reactions; types: heterogeneous, homogeneous. Lubricant reduces friction; e.g., oil. Monomers form polymers. Degree of ionization: fraction ionized. Corrosion types: uniform, pitting, galvanic. Hard water is mineral-rich, unlike soft water.
A catalyst is a substance that increases reaction rate without being consumed. Types include heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts. A lubricant reduces friction between surfaces; an example is oil. Monomers are small molecules that form polymers, large chains or networks of repeating units. Degree of ionization refers to the fraction of molecules ionized in a solution. Types of corrosion include uniform, pitting, and galvanic corrosion. Hard water contains high mineral content, unlike soft water.
Answer for screen readers
A catalyst is a substance that increases reaction rate without being consumed. Types include heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts. A lubricant reduces friction between surfaces; an example is oil. Monomers are small molecules that form polymers, large chains or networks of repeating units. Degree of ionization refers to the fraction of molecules ionized in a solution. Types of corrosion include uniform, pitting, and galvanic corrosion. Hard water contains high mineral content, unlike soft water.
More Information
Catalysts are essential in many industrial processes to reduce energy consumption and speeds. Lubricants like oils are crucial in machinery to prevent wear. Polymer science plays a critical role in materials science, influencing everything from plastics to biology.
Tips
Students often confuse types of catalysis with enzyme reactions; ensure the definitions and examples are clear.
Sources
- Types of catalysts (article) | Kinetics - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
- Types of catalysts (video) | Catalysis - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
- Glossary of Terms - Machinery Lubrication - machinerylubrication.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information