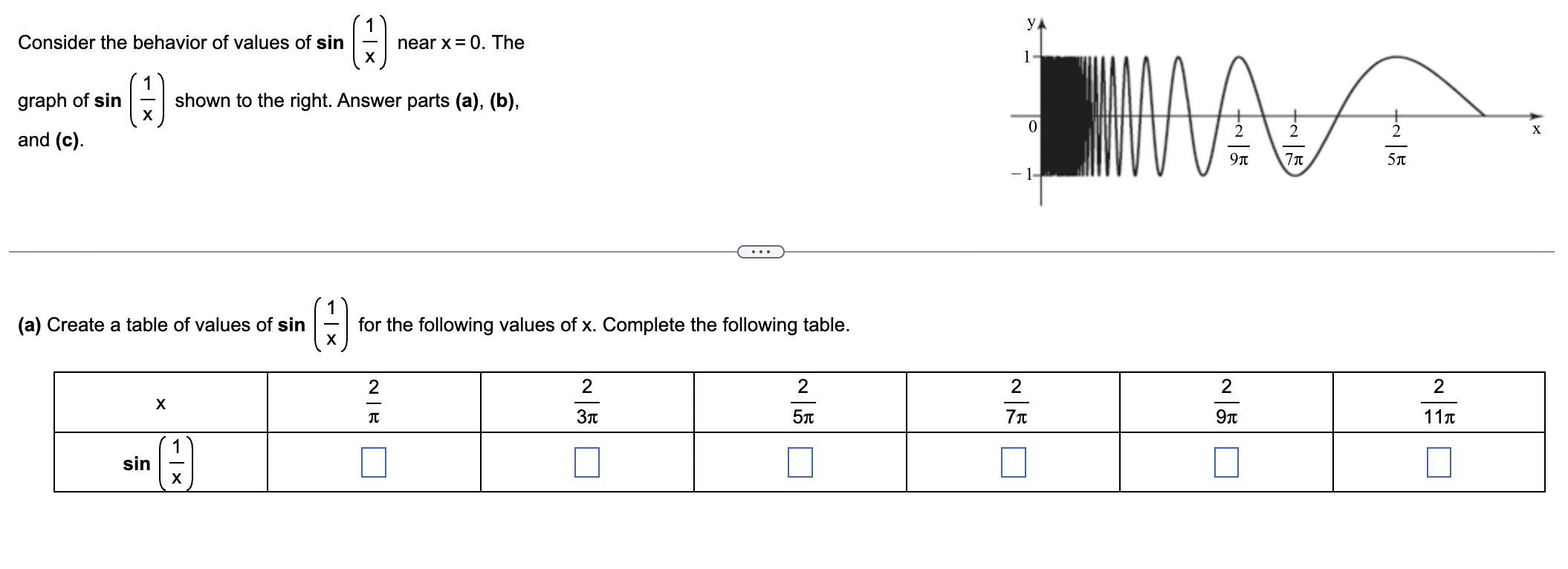
Create a table of values of sin(1/x) for the following values of x: 2/π, 2/3π, 2/5π, 2/7π, 2/9π, 2/11π. Complete the following table.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to create a table of values for the function sin(1/x) at specific values of x provided in the table. This requires understanding the behavior of the sine function and substituting the given x values into sin(1/x) to compute the corresponding outputs.
Answer
The completed table of values is: | x | \( \sin(1/x) \) | |---------------|-------------------| | \( \frac{2}{\pi} \) | \( 1 \) | | \( \frac{2}{3\pi} \) | \( -1 \) | | \( \frac{2}{5\pi} \) | \( 1 \) | | \( \frac{2}{7\pi} \) | \( -1 \) | | \( \frac{2}{9\pi} \) | \( 1 \) | | \( \frac{2}{11\pi} \) | \( -1 \) |
Answer for screen readers
The completed table is:
| x | ( \sin(1/x) ) |
|---|---|
| ( \frac{2}{\pi} ) | ( 1 ) |
| ( \frac{2}{3\pi} ) | ( -1 ) |
| ( \frac{2}{5\pi} ) | ( 1 ) |
| ( \frac{2}{7\pi} ) | ( -1 ) |
| ( \frac{2}{9\pi} ) | ( 1 ) |
| ( \frac{2}{11\pi} ) | ( -1 ) |
Steps to Solve
- Identify given x values The x values in the table are:
- ( \frac{2}{\pi} )
- ( \frac{2}{3\pi} )
- ( \frac{2}{5\pi} )
- ( \frac{2}{7\pi} )
- ( \frac{2}{9\pi} )
- ( \frac{2}{11\pi} )
- Calculate ( \frac{1}{x} ) for each value For each of these x values, calculate ( \frac{1}{x} ):
- For ( x = \frac{2}{\pi} ), ( \frac{1}{x} = \frac{\pi}{2} )
- For ( x = \frac{2}{3\pi} ), ( \frac{1}{x} = \frac{3\pi}{2} )
- For ( x = \frac{2}{5\pi} ), ( \frac{1}{x} = \frac{5\pi}{2} )
- For ( x = \frac{2}{7\pi} ), ( \frac{1}{x} = \frac{7\pi}{2} )
- For ( x = \frac{2}{9\pi} ), ( \frac{1}{x} = \frac{9\pi}{2} )
- For ( x = \frac{2}{11\pi} ), ( \frac{1}{x} = \frac{11\pi}{2} )
- Calculate ( \sin\left(\frac{1}{x}\right) ) Now, compute ( \sin\left(\frac{1}{x}\right) ) for each calculated ( \frac{1}{x} ):
- For ( \frac{\pi}{2} ), ( \sin\left(\frac{\pi}{2}\right) = 1 )
- For ( \frac{3\pi}{2} ), ( \sin\left(\frac{3\pi}{2}\right) = -1 )
- For ( \frac{5\pi}{2} ), ( \sin\left(\frac{5\pi}{2}\right) = 1 )
- For ( \frac{7\pi}{2} ), ( \sin\left(\frac{7\pi}{2}\right) = -1 )
- For ( \frac{9\pi}{2} ), ( \sin\left(\frac{9\pi}{2}\right) = 1 )
- For ( \frac{11\pi}{2} ), ( \sin\left(\frac{11\pi}{2}\right) = -1 )
The completed table is:
| x | ( \sin(1/x) ) |
|---|---|
| ( \frac{2}{\pi} ) | ( 1 ) |
| ( \frac{2}{3\pi} ) | ( -1 ) |
| ( \frac{2}{5\pi} ) | ( 1 ) |
| ( \frac{2}{7\pi} ) | ( -1 ) |
| ( \frac{2}{9\pi} ) | ( 1 ) |
| ( \frac{2}{11\pi} ) | ( -1 ) |
More Information
The sine function oscillates between -1 and 1. In this case, it alternates between these extremes at every half-period of ( \pi ) due to the nature of the sine function.
Tips
- Not calculating ( \frac{1}{x} ) correctly could lead to incorrect sine values.
- Confusing the values of ( \sin\left(\frac{1}{x}\right) ) for odd multiples of ( \frac{\pi}{2} ) can lead to errors.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information