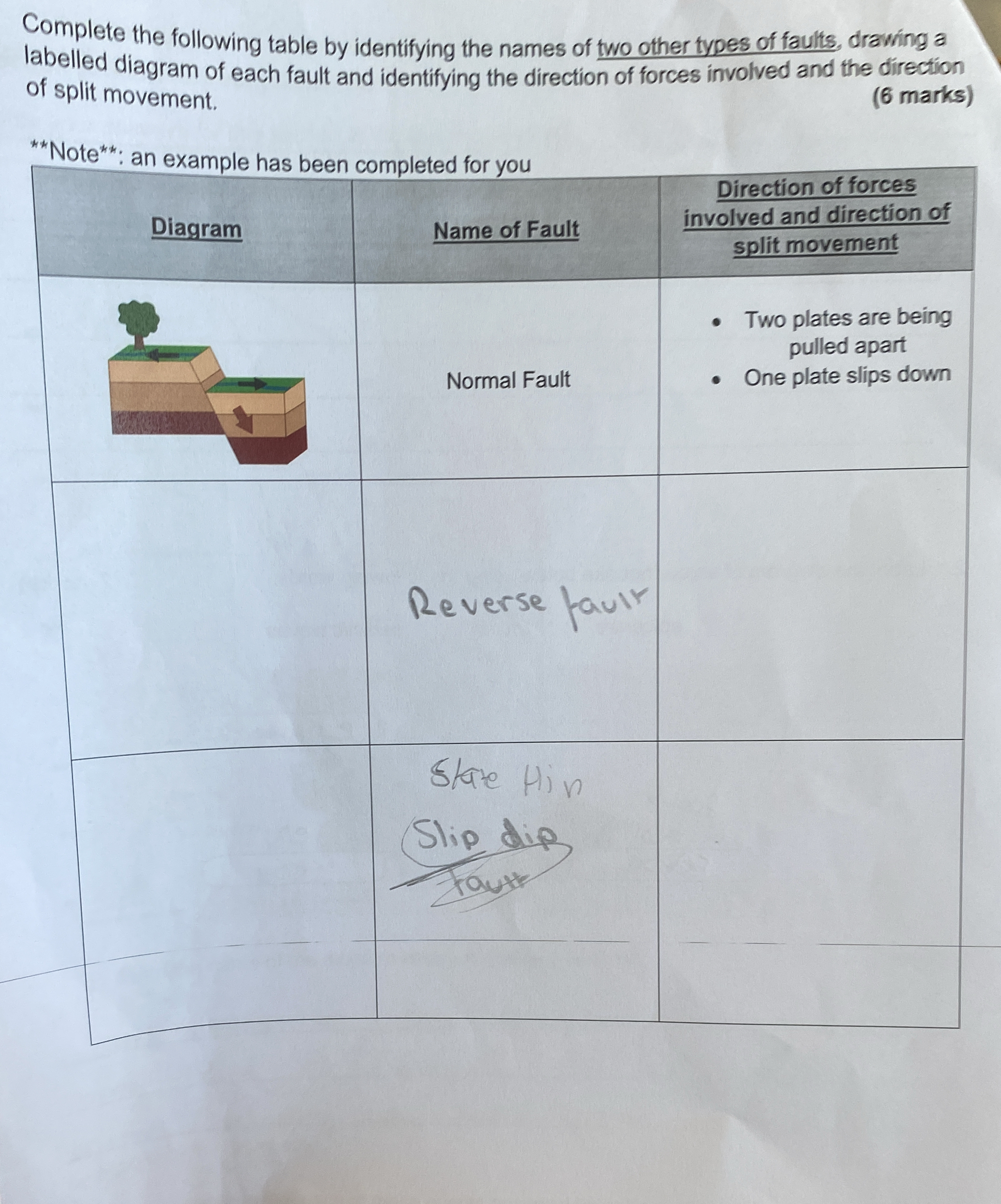
Complete the following table by identifying the names of two other types of faults, drawing a labelled diagram of each fault and identifying the direction of forces involved and th... Complete the following table by identifying the names of two other types of faults, drawing a labelled diagram of each fault and identifying the direction of forces involved and the direction of split movement.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to complete a table with information about two types of geological faults, including diagrams, names, and the direction of forces involved. It involves identifying faults beyond the provided example of a normal fault.
Answer
Reverse Fault: Compressive forces, upward movement. Strike-slip Fault: Lateral forces, horizontal movement.
The other two types of faults are the Reverse Fault and the Strike-slip Fault. In a Reverse Fault, compressive forces push the hanging wall upward. In a Strike-slip Fault, lateral forces cause horizontal movement along the fault plane.
Answer for screen readers
The other two types of faults are the Reverse Fault and the Strike-slip Fault. In a Reverse Fault, compressive forces push the hanging wall upward. In a Strike-slip Fault, lateral forces cause horizontal movement along the fault plane.
More Information
Faults are fractures in the Earth's crust. Reverse faults occur where compressive forces push rocks upwards, while strike-slip faults involve lateral sliding along the fault plane. Each type of fault has unique characteristics and movement patterns.
Tips
Common mistakes include confusing the directions of movement and mixing up types of faults.
Sources
- 3 Types of Faults: Normal, Reverse and Strike-Slip - Earth How - earthhow.com
- Fault and Types of Faults - Geology Science - geologyscience.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information