Balance the following redox reaction under acidic aqueous conditions using the smallest whole-number coefficients possible. What is the coefficient of HSO3-? MnO4-(aq) + HSO3-(aq)... Balance the following redox reaction under acidic aqueous conditions using the smallest whole-number coefficients possible. What is the coefficient of HSO3-? MnO4-(aq) + HSO3-(aq) → Mn2+(aq) + SO4^2-(aq)
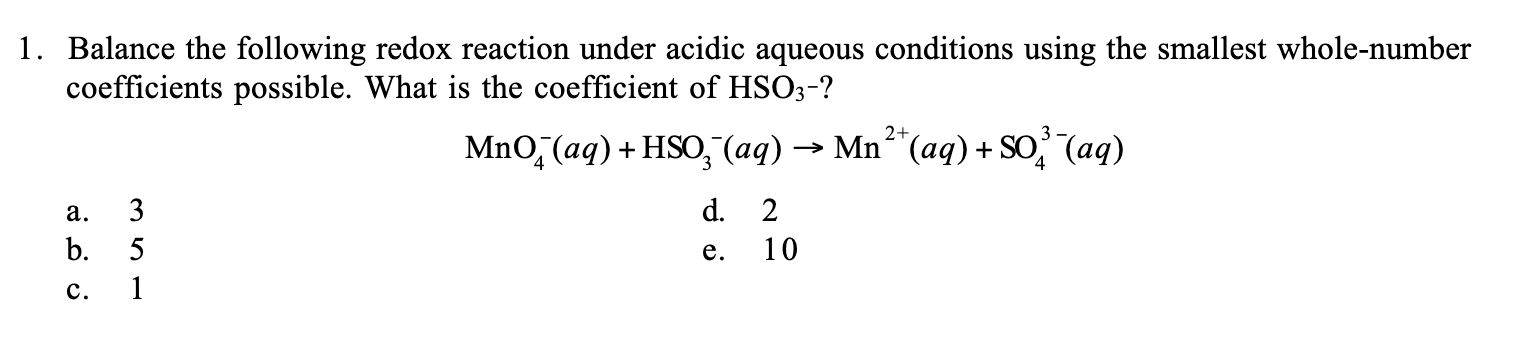
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to balance a redox reaction in acidic aqueous conditions and find the coefficient of HSO3- in the balanced equation.
Answer
5
Answer for screen readers
The coefficient of $HSO_3^-$ is 5.
Steps to Solve
-
Identify Redox Components The half-reactions need to be identified. The reduction reaction involves the conversion of $MnO_4^-$ to $Mn^{2+}$ and the oxidation reaction involves the conversion of $HSO_3^-$ to $SO_4^{2-}$.
-
Determine Oxidation States Determine the changes in oxidation states for the redox components:
- In $MnO_4^-$, Mn is in the +7 oxidation state, and it is reduced to +2 in $Mn^{2+}$.
- In $HSO_3^-$, sulfur is in the +4 oxidation state and is oxidized to +6 in $SO_4^{2-}$.
-
Write the Half-Reactions Write the half-reactions based on the oxidation states:
- Reduction: $$ MnO_4^- + 8H^+ + 5e^- \rightarrow Mn^{2+} + 4H_2O $$
- Oxidation: $$ HSO_3^- + H_2O \rightarrow SO_4^{2-} + 2H^+ + 2e^- $$
-
Balance Electrons To balance the number of electrons lost and gained, multiply the oxidation half-reaction by 5 and the reduction half-reaction by 2:
- Reduction: $$ 2MnO_4^- + 16H^+ + 10e^- \rightarrow 2Mn^{2+} + 8H_2O $$
- Oxidation: $$ 5HSO_3^- + 5H_2O \rightarrow 5SO_4^{2-} + 10H^+ + 10e^- $$
-
Combine the Half-Reactions Add the two half-reactions together, ensuring all components are balanced: $$ 2MnO_4^- + 5HSO_3^- + 6H^+ \rightarrow 2Mn^{2+} + 5SO_4^{2-} + 3H_2O $$
-
Determine the Coefficient of $HSO_3^-$ The coefficient of $HSO_3^-$ in the balanced equation is 5.
The coefficient of $HSO_3^-$ is 5.
More Information
In redox reactions, balancing the oxidation and reduction half-reactions is crucial to ensure conservation of mass and charge. The process often involves adjusting coefficients until electron transfers are equivalent.
Tips
- Forgetting to balance hydrogen and oxygen atoms after balancing electrons.
- Not correctly identifying oxidation states can lead to incorrect half-reactions.
- Not multiplying the half-reactions to ensure electron balance.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information