Answering the following 3 questions according to the image attached. Question 1: In the problem depicted in the image above, please describe the start state, the goal state, and th... Answering the following 3 questions according to the image attached. Question 1: In the problem depicted in the image above, please describe the start state, the goal state, and the operators involved. Question 2: Looking at the solution to the problem in the image above, which of the problem-solving approaches we learned about in class/the textbook would you say best describes the approach needed in order to solve the problem? What are the two key steps described by that approach that would lead you to a solution to the problem? Question 3: Would you describe the problem in the image above as well-defined or ill-defined? Knowledge-rich or knowledge-lean? Adversarial or non-adversarial? For each answer, please explain your reasoning to get the full points.
Understand the Problem
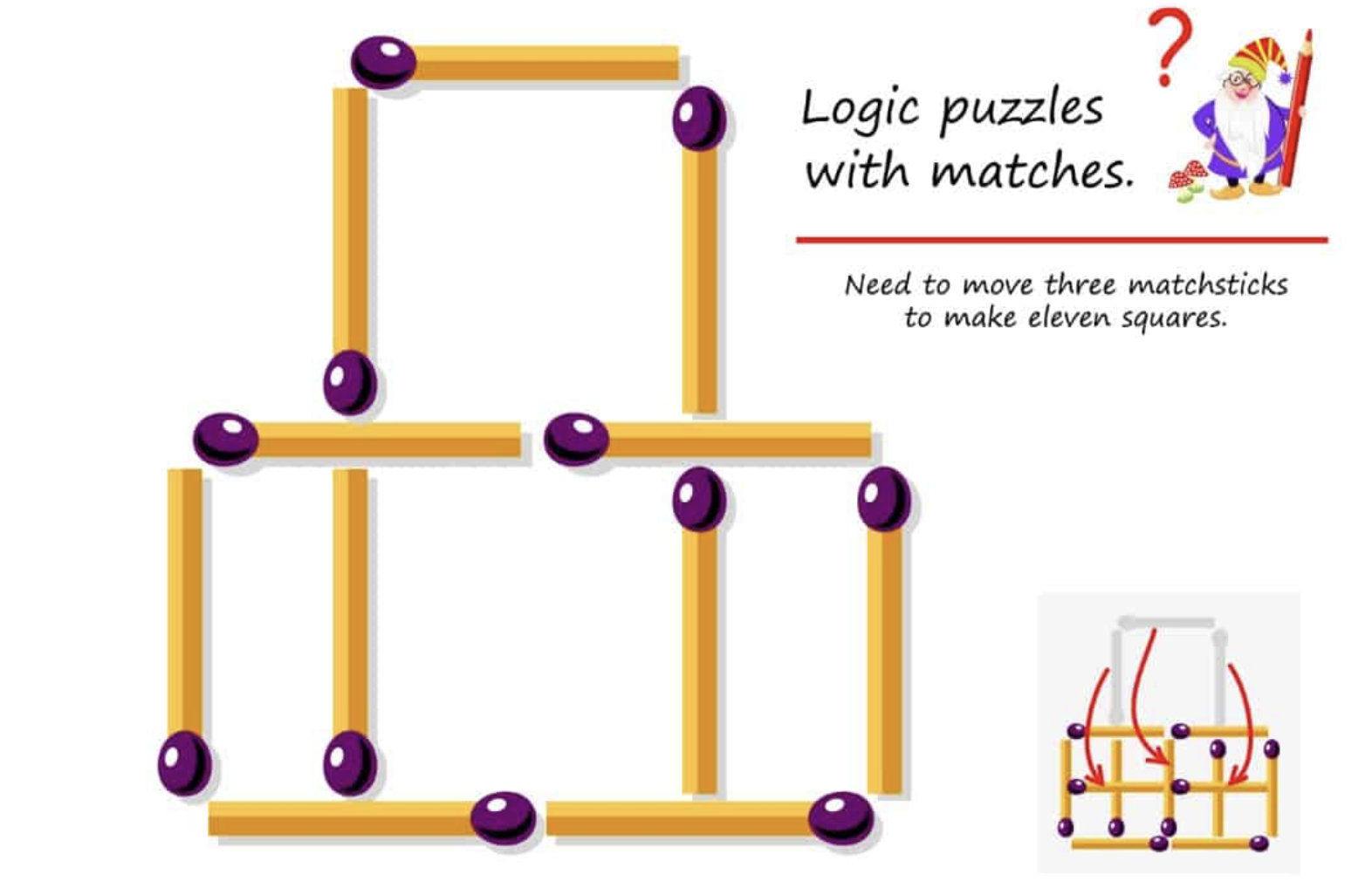
The questions are centered around a logic puzzle involving matchsticks. The user is asked to analyze the problem's state, describe the problem-solving approach utilized, and categorize it based on specific criteria. This involves understanding the initial and goal states of the puzzle, identifying the methods applied to solve it, and classifying its nature.
Answer
1. Initial squares, goal is eleven squares. Move sticks. 2. Trial and error. Key: hypothesize, test moves. 3. Well-defined, knowledge-lean, non-adversarial.
-
Start state: Matchsticks form initial squares as shown. Goal state: Form eleven squares by moving three matchsticks. Operators: Move allowed matchsticks.
-
Best approach: Trial and error, involving hypothesizing and testing moves. Key steps: Identify alternative configurations, evaluate effectiveness.
-
The problem is well-defined, knowledge-lean, and non-adversarial. It has clear rules and objectives, relies on cognitive thinking, and lacks competitive elements.
Answer for screen readers
-
Start state: Matchsticks form initial squares as shown. Goal state: Form eleven squares by moving three matchsticks. Operators: Move allowed matchsticks.
-
Best approach: Trial and error, involving hypothesizing and testing moves. Key steps: Identify alternative configurations, evaluate effectiveness.
-
The problem is well-defined, knowledge-lean, and non-adversarial. It has clear rules and objectives, relies on cognitive thinking, and lacks competitive elements.
More Information
Matchstick puzzles enhance spatial reasoning and problem-solving skills by challenging one to visualize transformations.
Tips
A common mistake is not considering all possible configurations, leading to premature conclusions.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information