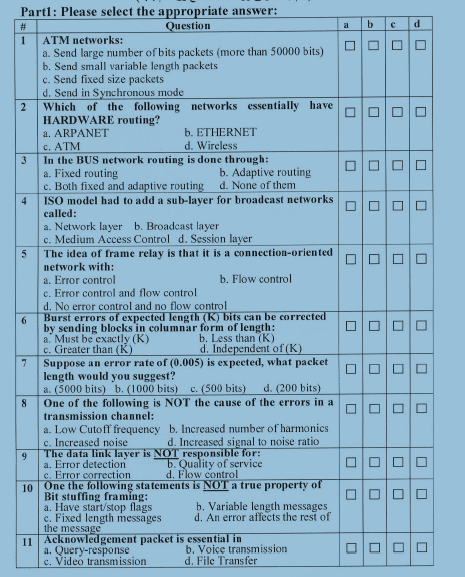
1. ATM networks: a. Send a large number of bits packets (more than 50000 bits) b. Send small variable length packets c. Send fixed size packets d. Send in synchronous mode 2. Which... 1. ATM networks: a. Send a large number of bits packets (more than 50000 bits) b. Send small variable length packets c. Send fixed size packets d. Send in synchronous mode 2. Which of the following networks essentially have HARDWARE routing? a. ARPANET b. ETHERNET c. ATM d. Wireless 3. In the BUS network routing is done through: a. Fixed routing b. Adaptive routing c. Both fixed and adaptive routing d. None of them 4. ISO model had to add a sub-layer for broadcast networks called: a. Network layer b. Broadcast layer c. Medium Access Control d. Session layer 5. The idea of frame relay is that it is a connection-oriented network with: a. Error control b. Flow control c. Error control and flow control d. No error control and no flow control 6. Burst errors of expected length (K) bits can be corrected by sending blocks in columnar form of length: a. Must be exactly (K) b. Less than (K) c. Independent of (K) d. Greater than (K) 7. Suppose an error rate of (0.005) is expected, what packet length would you suggest? a. (500 bits) b. (1000 bits) c. (500 bits) d. (200 bits) 8. One of the following is NOT the cause of the errors in a transmission channel: a. Low Cutoff frequency b. Increased number of harmonics c. Increased noise d. Increased signal to noise ratio 9. The data link layer is NOT responsible for: a. Error detection b. Quality of service c. Error correction d. Flow control 10. One of the following statements is NOT a true property of bit stuffing framing: a. Have start/stop flags b. Variable length messages c. Fixed length messages d. An error affects the rest of the message 11. Encapsulated packet is essential in: a. Video-response b. Streaming c. Video transmission d. File transfer
Understand the Problem
The question is presenting a multiple-choice quiz related to networking concepts, specifically focusing on ATM networks, various types of network routing, and the ISO model. It is asking for the correct answers to several questions.
Answer
["1: c, 2: c, 3: a, 4: c, 5: d, 6: d, 7: d, 8: d, 9: b, 10: c, 11: d"]
["ATM networks use fixed size packets (c).","ATM networks essentially have HARDWARE routing (c).","In BUS networks, routing is done through fixed routing (a).","ISO model added a sub-layer for broadcast networks called the Medium Access Control (c).","Frame relay is a connection-oriented network with no error control and no flow control (d).","Burst errors of expected length (K) can be corrected by sending blocks in columnar form of length greater than (K) (d).","For an expected error rate of 0.005, a packet length of 200 bits is suggested (d).","Increased signal to noise ratio is NOT the cause of transmission errors (d).","The data link layer is NOT responsible for Quality of service (b).","Bit stuffing framing does not have fixed length messages (c).","Encapsulated packet is essential in file transfer (d)."]
Answer for screen readers
["ATM networks use fixed size packets (c).","ATM networks essentially have HARDWARE routing (c).","In BUS networks, routing is done through fixed routing (a).","ISO model added a sub-layer for broadcast networks called the Medium Access Control (c).","Frame relay is a connection-oriented network with no error control and no flow control (d).","Burst errors of expected length (K) can be corrected by sending blocks in columnar form of length greater than (K) (d).","For an expected error rate of 0.005, a packet length of 200 bits is suggested (d).","Increased signal to noise ratio is NOT the cause of transmission errors (d).","The data link layer is NOT responsible for Quality of service (b).","Bit stuffing framing does not have fixed length messages (c).","Encapsulated packet is essential in file transfer (d)."]
More Information
ATM's use of fixed-size cells allows for predictable, efficient processing; the lack of inherent error control in Frame Relay is offset by its ability to support high-speed data transmission.
Tips
A common mistake when working with ATM is assuming variable packet sizes like in IP networks, but ATM consistently uses fixed 53-byte cells.
Sources
- Solved Past Exam Questions - Chegg - chegg.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information