Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following protozoal diseases is more prevalent in the UK due to immunosuppression?
Which of the following protozoal diseases is more prevalent in the UK due to immunosuppression?
- Malaria
- Trypanosoma
- Giardia
- Toxoplasma (correct)
Malaria is caused by which genus of protozoa?
Malaria is caused by which genus of protozoa?
- Plasmodium (correct)
- Toxoplasma
- Cryptosporidium
- Entamoeba
Which species of Plasmodium is NOT responsible for causing malaria?
Which species of Plasmodium is NOT responsible for causing malaria?
- P. vivax
- P. malariae
- P. falciparum
- P. gondii (correct)
Which of the following areas is NOT a major region where malaria is endemic?
Which of the following areas is NOT a major region where malaria is endemic?
What is the mode of transmission for Toxoplasmosis?
What is the mode of transmission for Toxoplasmosis?
Which of these diseases is caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii?
Which of these diseases is caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii?
What is the first step in treating water to remove pathogens?
What is the first step in treating water to remove pathogens?
What makes the detection of cysts in water difficult?
What makes the detection of cysts in water difficult?
Which of the following diseases does not respond to antibiotics?
Which of the following diseases does not respond to antibiotics?
What is the drug of choice for treating pneumocystosis?
What is the drug of choice for treating pneumocystosis?
How is pneumocystosis primarily spread?
How is pneumocystosis primarily spread?
Which population is most commonly affected by pneumocystosis in central Europe?
Which population is most commonly affected by pneumocystosis in central Europe?
What is the definitive host for Toxoplasma gondii?
What is the definitive host for Toxoplasma gondii?
Which group is NOT considered at-risk for toxoplasmosis?
Which group is NOT considered at-risk for toxoplasmosis?
What is a potential effect of congenital toxoplasmosis if contracted in early pregnancy?
What is a potential effect of congenital toxoplasmosis if contracted in early pregnancy?
How many cases of acquired toxoplasmosis were reported to the HPA in 2008?
How many cases of acquired toxoplasmosis were reported to the HPA in 2008?
Which symptom is NOT associated with acquired toxoplasmosis?
Which symptom is NOT associated with acquired toxoplasmosis?
Which is NOT true about Cryptosporidium parvum?
Which is NOT true about Cryptosporidium parvum?
Which treatment is NOT recommended for congenital toxoplasmosis?
Which treatment is NOT recommended for congenital toxoplasmosis?
Which method is effective but not routinely used in the UK to kill Cryptosporidium parvum cysts in water?
Which method is effective but not routinely used in the UK to kill Cryptosporidium parvum cysts in water?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
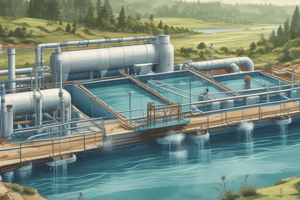
Contamination of Drinking Water
- Giardia and cryptosporidium are major concerns for the water industry, as they can cause significant problems.
- These pathogens enter water sources through human or animal faeces or runoff from slaughterhouses.
- Filtration is the primary treatment method, which should remove all pathogens, but many outbreaks occur due to failures in this stage.
- Chlorination is the secondary treatment method, but it does not kill the cysts.
- Cysts are present in small numbers and are difficult to detect, requiring large volumes of water (1m³) to be tested.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnosis requires invasive techniques such as broncho-alveolar lavage or open lung biopsy.
- The organism can be detected using silver or immunofluorescent stains in these samples.
- Cotrimoxazole (sulphamethoxazole plus trimethoprim) is the drug of choice for treatment.
- Pentamidine can be used as an alternative.
Diseases
- Atypical interstitial cell pneumonia (pneumocystosis) is a type of pneumonia that does not respond to antibiotics.
- It is spread by droplet infection and close contact, commonly affecting infants in crowded institutions.
- An estimated 85% of AIDS patients will become infected.
- Low levels of antibodies in healthy adults suggest that sub-clinical infection is common, and disease may result from reactivation rather than new infection.
Protozoa
- Protozoa are important due to the diseases they cause, which are generally not common in the UK but prevalent in the Third World due to poverty and survival of vectors.
- Some infections have become more prevalent in the UK associated with immunosuppression, such as toxoplasma, pneumocystis, and cryptosporidium.
Plasmodium
- Plasmodium causes malaria in areas where mosquito vectors can breed, primarily in the tropics between 60°N and 40°S latitude.
- There are four species of plasmodium: P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. malariae, and P. ovale.
- The complex life cycle involves liver and blood cells, with several different stages of parasites.
Toxoplasmosis
- Toxoplasmosis is caused by the common parasite Toxoplasma gondii, which can infect all mammal and bird species worldwide.
- The parasite is only passed on if it enters the food chain.
- Up to one billion people worldwide are infected with T. gondii.
- The definitive host is the domestic cat, with mammals acting as reservoirs.
- 75% of feline population has antibodies, and 25% of human population has antibodies.
- Between 7-34% of people in the UK have been infected, with the majority being asymptomatic or experiencing flu-like symptoms.
- A latent infection can be reactivated later in life if predisposing conditions arise.
- There are two main at-risk groups: immunosuppressed individuals and pregnant women.
Congenital Toxoplasmosis
- If contracted during pregnancy, the infection can cross the placenta and infect the foetus.
- The severity of disease depends on the stage of pregnancy.
- Infection in early pregnancy can lead to miscarriage, stillbirth, and birth defects, while infection in the last 28 weeks rarely leads to problems at birth, but symptoms may develop later in life.
- Pregnant women can be tested by looking for a rising titre of antibodies.
- Education about the risks is important, encouraging prevention of infection.
Acquired Toxoplasmosis
- Acquired toxoplasmosis can be lethal to immunosuppressed individuals.
- Low numbers of infection occur in England and Wales, with symptoms including fever, headaches, fatigue, and swelling of lymph glands.
- Infection can also occur in the brain, lung, heart, and liver.
Cryptosporidium parvum
- Cryptosporidium parvum causes cryptosporidosis.
- In healthy adults, the disease causes mild gastrointestinal upset and is self-limiting.
- It is potentially lethal to immunosuppressed individuals.
- There is no effective chemotherapy.
- About 6,000 cases occur per year, mainly associated with drinking water.
Treatment
- All congenital cases should be treated with pyrimethane plus sulphadiazine.
- Pyrimethane is teratogenic and should not be used in the first trimester.
- Spiramycin is effective but not licensed in the UK for this use.
- If treatment fails, termination may be considered.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.