Podcast
Questions and Answers
What event defines syngamy in the context of embryogenesis?
What event defines syngamy in the context of embryogenesis?
- The fusion of the male and female pronuclei. (correct)
- The development of anatomical form in the embryo.
- The formation of extra-embryonic membranes.
- The attachment of the conceptus to the uterine wall.
Why is the term 'conceptus' used to describe the developing embryo?
Why is the term 'conceptus' used to describe the developing embryo?
- It is limited to the period before the formation of the placenta.
- It refers specifically to the stage where organogenesis is complete.
- It describes the embryo's genetic contribution exclusively.
- It broadly encompasses the embryo during early development, extra-embryonic membranes, allantois and the fetus. (correct)
What is the primary role of the zona pellucida during pre-attachment development?
What is the primary role of the zona pellucida during pre-attachment development?
- Preventing polyspermy immediately following fertilization.
- Facilitating nutrient exchange with the maternal environment.
- Protecting the developing embryo during cleavage. (correct)
- Providing structural rigidity to the developing morula.
Which of the following best explains the necessity of the 'hatching' process in blastocyst development?
Which of the following best explains the necessity of the 'hatching' process in blastocyst development?
What three key factors govern the hatching of the blastocyst?
What three key factors govern the hatching of the blastocyst?
What is the critical role of histotroph ('uterine milk') following the hatching of the blastocyst?
What is the critical role of histotroph ('uterine milk') following the hatching of the blastocyst?
How do extra-embryonic membranes support successful attachment of the embryo to the uterus?
How do extra-embryonic membranes support successful attachment of the embryo to the uterus?
From which of the following embryonic germ layers do the extra-embryonic membranes originate?
From which of the following embryonic germ layers do the extra-embryonic membranes originate?
What is the role of the amnion in the development of the embryo?
What is the role of the amnion in the development of the embryo?
The allantois has which key function in the context of embryonic development?
The allantois has which key function in the context of embryonic development?
What role does allantochorion play in placentation?
What role does allantochorion play in placentation?
What are the main sources of the amniotic fluid?
What are the main sources of the amniotic fluid?
What is the role of the allantoic fluid in fetal development?
What is the role of the allantoic fluid in fetal development?
What is the significance of maternal recognition of pregnancy (MRP)?
What is the significance of maternal recognition of pregnancy (MRP)?
Why is adequate luteal function crucial during early pregnancy?
Why is adequate luteal function crucial during early pregnancy?
What determines whether a placenta is classified as 'deciduate' or 'non-deciduate'?
What determines whether a placenta is classified as 'deciduate' or 'non-deciduate'?
What is the key distinction between 'epitheliochorial,' 'endotheliochorial,' and 'hemochorial' placentae?
What is the key distinction between 'epitheliochorial,' 'endotheliochorial,' and 'hemochorial' placentae?
Which placenta type has all layers of maternal and foetal tissue preserved?
Which placenta type has all layers of maternal and foetal tissue preserved?
How do villous placentae facilitate nutrient and waste exchange?
How do villous placentae facilitate nutrient and waste exchange?
What characterizes placentation in mares and sows?
What characterizes placentation in mares and sows?
Which of the following species exhibits zonary placentation?
Which of the following species exhibits zonary placentation?
What is a placentome, and in which type of placental distribution is it found?
What is a placentome, and in which type of placental distribution is it found?
What is the key difference between maternal and fetal blood in the placenta?
What is the key difference between maternal and fetal blood in the placenta?
How does the exchange of nutrients and wastes occur between the mother and fetus?
How does the exchange of nutrients and wastes occur between the mother and fetus?
Through what structure does the fetal circulation connect to the placenta?
Through what structure does the fetal circulation connect to the placenta?
Which of the following is NOT a placental function?
Which of the following is NOT a placental function?
What is the role of binucleate giant cells in placental function?
What is the role of binucleate giant cells in placental function?
What is the role of endometrial cups in the equine placenta?
What is the role of endometrial cups in the equine placenta?
What is the luteo-placental shift?
What is the luteo-placental shift?
Why is progesterone important during pregnancy?
Why is progesterone important during pregnancy?
How does relaxin aid in parturition?
How does relaxin aid in parturition?
What is the role of placental lactogen?
What is the role of placental lactogen?
Which of the following is NOT a step required before the attachment of the embryo?
Which of the following is NOT a step required before the attachment of the embryo?
Which of the following best describes the transition from morula to blastocyst?
Which of the following best describes the transition from morula to blastocyst?
Match the placental type to the species that has that type of placenta: Epitheliochorial
Match the placental type to the species that has that type of placenta: Epitheliochorial
Match the placental type to the species that has that type of placenta: Hemochorial
Match the placental type to the species that has that type of placenta: Hemochorial
Which of the following terms best describes the cells formed during cleavage?
Which of the following terms best describes the cells formed during cleavage?
Following its formation, what is the immediate developmental event that the zygote undergoes?
Following its formation, what is the immediate developmental event that the zygote undergoes?
How does the blastocyst facilitate the process of 'hatching'?
How does the blastocyst facilitate the process of 'hatching'?
What key characteristic defines the period after the blastocyst has undergone hatching?
What key characteristic defines the period after the blastocyst has undergone hatching?
How do extra-embryonic membranes facilitate the attachment of the embryo to the uterus?
How do extra-embryonic membranes facilitate the attachment of the embryo to the uterus?
From which key germ layers are extra-embryonic membranes primarily derived?
From which key germ layers are extra-embryonic membranes primarily derived?
How does the amnion contribute to the protection of the developing fetus?
How does the amnion contribute to the protection of the developing fetus?
What is the primary role of the allantois during early embryonic development?
What is the primary role of the allantois during early embryonic development?
What is the ultimate fate of the allantois during placental development in many species?
What is the ultimate fate of the allantois during placental development in many species?
Which fluid component primarily contributes to protecting the foetus from mechanical shock?
Which fluid component primarily contributes to protecting the foetus from mechanical shock?
What is the key role of the allantoic fluid in supporting the developing foetus?
What is the key role of the allantoic fluid in supporting the developing foetus?
What major physiological change must occur in the mother to support the requirements for a developing embryo?
What major physiological change must occur in the mother to support the requirements for a developing embryo?
Why is sufficient luteal function essential for early pregnancy maintenance?
Why is sufficient luteal function essential for early pregnancy maintenance?
What is the primary basis for classifying placentae as either 'deciduate' or 'non-deciduate'?
What is the primary basis for classifying placentae as either 'deciduate' or 'non-deciduate'?
In epitheliochorial placentation, which tissues are preserved?
In epitheliochorial placentation, which tissues are preserved?
Considering the histological classification of the placenta, what is the defining characteristic of a hemochorial placenta?
Considering the histological classification of the placenta, what is the defining characteristic of a hemochorial placenta?
How do villous placentae optimize the exchange of nutrients and waste between fetal and maternal blood?
How do villous placentae optimize the exchange of nutrients and waste between fetal and maternal blood?
What type of placental distribution is typical for mares and sows?
What type of placental distribution is typical for mares and sows?
In the context of placentation, what is the functional role of the allantochorion?
In the context of placentation, what is the functional role of the allantochorion?
In species exhibiting cotyledonary placentation, how are the fetal and maternal sides of the placentome characterized?
In species exhibiting cotyledonary placentation, how are the fetal and maternal sides of the placentome characterized?
How does the structure of the placenta ensure the separation of maternal and fetal blood?
How does the structure of the placenta ensure the separation of maternal and fetal blood?
What role does the umbilical cord play in fetal circulation?
What role does the umbilical cord play in fetal circulation?
In ruminants, binucleate giant cells migrate from the foetal to the maternal side. What is a key function of these binucleate giant cells?
In ruminants, binucleate giant cells migrate from the foetal to the maternal side. What is a key function of these binucleate giant cells?
What is the main role of endometrial cups in equine placentation?
What is the main role of endometrial cups in equine placentation?
Flashcards
Syngamy
Syngamy
Fusion of the male and female pronuclei.
Embryo
Embryo
Organism in early development, before recognizable species form.
Conceptus
Conceptus
Product of conception, including embryo, membranes, fetus, and placenta.
Placenta
Placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Steps before attachment
Steps before attachment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ootid
Ootid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zygote
Zygote
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cleavage
Cleavage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blastomeres
Blastomeres
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morula
Morula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blastocyst
Blastocyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
ICM
ICM
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blastocoele
Blastocoele
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trophoblast
Trophoblast
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hatching
Hatching
Signup and view all the flashcards
Forces for hatching
Forces for hatching
Signup and view all the flashcards
Survival requirements after hatching
Survival requirements after hatching
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extra-embryonic membranes
Extra-embryonic membranes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Origin of extra-embryonic membranes
Origin of extra-embryonic membranes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Yolk sac
Yolk sac
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amnion
Amnion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allantois
Allantois
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allantochorion
Allantochorion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amniotic fluid
Amniotic fluid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allantoic fluid
Allantoic fluid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adequate Luteal Function
Adequate Luteal Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goal of MRP
Goal of MRP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type of placental attachment
Type of placental attachment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-deciduate placenta
Non-deciduate placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deciduate placenta
Deciduate placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Histological characteristics of placenta
Histological characteristics of placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epitheliochorial Placenta
Epitheliochorial Placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epitheliochorial species
Epitheliochorial species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endotheliochorial placenta
Endotheliochorial placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endotheliochorial species
Endotheliochorial species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemochorial placenta
Hemochorial placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemochorial species
Hemochorial species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placental membrane apposition
Placental membrane apposition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Villous
Villous
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chorionic villi distribution
Chorionic villi distribution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffuse placentation
Diffuse placentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffuse species
Diffuse species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zonary placentation
Zonary placentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zonary species
Zonary species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Discoid placentation
Discoid placentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Discoid species
Discoid species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cotyledonary placentation
Cotyledonary placentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cotyledonary species
Cotyledonary species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placentation
Placentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal/Maternal Blood
Fetal/Maternal Blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Embryogenesis and Placentation are the topics for the lecture VSC262 202530.
Learning Objectives
- Discuss embryo growth from conception to parturition.
- Briefly describe why and how Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy (MRP) is necessary.
- Discuss placental formation, classification, and function.
- Discuss placentation similarities and differences in domestic species.
Terminology
- Syngamy is the fusion of male and female pronuclei.
- An embryo is an organism in early development, without anatomical form or organogenesis, and unrecognizable as a species.
- Conceptus is the product of conception, including the embryo during early development, extra-embryonic membranes, fetus, and placenta.
Placenta Formation
- The placenta provides attachment between fetal and maternal tissues.
- Placenta functions include exchanging nutrients and wastes between mother and fetus.
- The placenta aids in hormone production.
- The placenta may act as a "shock absorber" to protect the developing conceptus.
Steps Before Attachment
- Development within the zona pellucida (cleavage).
- Hatching of the embryo.
- Maternal recognition of pregnancy.
- Formation of extra-embryonic membranes.
Pre-Attachment Embryo Development
- Ootid is the oocyte after fertilization but before nuclear fusion.
- Male and Female Pronuclei are the genetic components of the ootid.
- The first and second polar bodies are expelled during meiosis.
- Syngamy is the fusion of pronuclei.
- A zygote undergoes cleavage, resulting in daughter cells also known as "Blastomeres".
- The embryo changes from 4 cells, to 8 cells to a morula.
- Morula then becomes a Blastocyst.
- Blastocyst consists of the Inner Cell Mass (ICM), Blastocoele and Trophoblast.
Hatching of the Blastocyst
- Hatching is governed by growth and fluid accumulation in the blastocyst.
- Enzymes produced by trophoblastic cells weaken the zona pellucida.
- Contraction of trophoblastic cells causes intermittent pressure, rupturing the zona pellucida.
Post-Hatching
- The embryo is free-floating and subject to the uterine environment.
- Survival requires adequate luteal function.
- Survival requires adequate progesterone synthesis.
- The uterus needs to be progesterone responsive.
- Uterine "milk" histotroph is a nutrient-rich secretion.
Extra-Embryonic Membranes
- The pre-attachment period is long, and rapid embryonic growth is due to the formation of extra-embryonic membranes.
- Formation of extra-embryonic membranes is essential for embryo attachment to the uterus.
- Membranes originate from the mesoderm, endoderm, and trophoblast.
Amnion
- The yolk sac regresses in size as the conceptus develops; it is transient.
- Primitive germ cells that migrate to the genital ridge are attributed to the yolk sac.
- The amnion encloses the fetus in a fluid-filled cavity for hydraulic protection and also provides an anti-adhesion material.
Allantois and Allantochorion
- The allantois is a fluid-filled sac that collects liquid waste from the embryo.
- Allantois eventually fuses with the chorion to make the allanto-chorion.
- The allantois contains vessels that connect the fetus with placental circulation.
- The Allantochorion is the fetal contribution to the placenta that provides a surface for attachment (chorionic villi).
Amnionic and Allantoic Fluids
- Amnionic fluid is secreted from the respiratory tract and mouth and amnion itself.
- Amnionic Fluid protects the fetus from external shock and prevents adhesions.
- Amnionic Fluid assists in dilating and lubricating birth passages.
- Allantoic fluid is fetal urine and a secretory activity of the allantoic membrane.
- Apposition of allantochorion with the endometrium helps maintain osmotic pressure of fetal plasma.
- The Allantoic Fluid stores foetal wastes that are not transferable back to the mother.
Maternal Recognition of Pregnancy (MRP)
- MRP prevents oestrus and overt signs of cyclicity, whilst survival also requires adequate luteal function.
- MRP Survival requires adequate progesterone synthesis and cervix closure.
- Survival requires a progesterone-responsive uterus with a quiescent myometrium.
- Uterine "milk" histotroph promotes survival
- Anti-inflammatory helps survival.
Attachment vs. Implantation
- Implantation occurs minimally
- Attachment occurs mainly
Placental Development
- Classification is based on the type of attachment to the mother.
- Classification is based on the number of histological layers.
- Classification is based on the distribution of chorionic villi.
Classification by Type of Attachment
- Non-deciduate (adeciduate) placenta: the placenta is attached, the most common type in domestic species.
- Deciduate placenta: the placenta is implanted; found in primates, rodents, and lagomorphs.
Histological Characteristics of Placentas
- Epitheliochorial placenta
- Haemochorial placenta
- Endotheliochorial placenta
Terminology of Placental Layers
- The prefix indicates the maternal side.
- The suffix indicates the fetal side.
- Epitheliochorial includes maternal epithelio and fetal chorial layers.
- All maternal and foetal tissue layers are preserved.
Species and Placental Types
- Mare, sow, and ruminants have epitheliochorial placentas.
- Dogs and cats have endotheliochorial placentas.
- Humans, primates, and rodents have hemochorial placentas.
Placental Membrane Apposition Types of Placentas
- Folded placenta.
- Villous placenta.
- Labyrinthine placenta.
Villous Placenta
- Fetal tissues form villi that may be branched.
- Villi interdigitate with similar maternal villi.
- This increases the surface area for attachment and transfer of nutrients and wastes.
- This is the most common type found in domestic species including the horse.
Distribution of Chorionic Villi
- Diffuse: Mare and Sow.
- Zonary: Dogs and Cats.
- Discoid: Rodents and Primates.
- Cotyledonary: Ruminants.
Cotyledonary
- Fetal side: cotyledon.
- Maternal side: caruncle.
- Placentome = Cotyledon + Caruncle.
- Convex is relating to cow/giraffe, Concave is relating to sheep/goat
Placental and Embryonic Systems and Processes
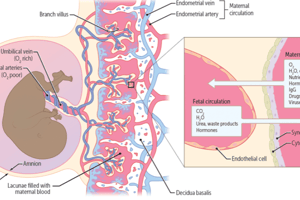
- Attachment of the outer-most fetal membrane (chorion or allantochorion) to the endometrium, known as (PLACENTATION).
- Brings the maternal & fetal blood streams as close together as possible with blood vessels in the chorioallantois.
- The maternal and fetal circulatory systems remain completely separate.
- There is NO DIRECT CONTACT between maternal & fetal blood.
- Exchange of nutrients and wastes occur between mother & fetus.
Placental Functions
- Stimulate ovarian function.
- Maintain pregnancy.
- Influence fetal growth.
- Stimulate mammary function
- Assist in parturition.
- Fetoplacental hormone production.
Endocrine Organs and Function
- Relaxin and placental lactogen are produced.
- Binucleate Giant Cells are present.
- Seen in Ruminants: Bovine - d 18-20 gestation, Ovine - d 14 gestation
- Pregnancy Specific: Protein B is produced.
- Endometrial cups, seen in horses and produce eCG, occur - d 35 gestation.
Examples of Luteo-Placental Shift
- Species where CL is responsible for full gestation progesterone maintenance: Goat, Camelids, Canid, Pig-sow.
- Species that have a luteoplacental shift to maintain gestation progesterone/progestogen: Mare (About 100 days), Cow (About 120-150 days), Ewe (About 50 days).
Hormones and Activity
- Progesterone is important in pregnancy
- Progesterone stimulates secretions from the endometrial glands.
- Progesterone is responsible for the progesterone block, which inhibits myometrial contractions.
- Progesterone is produced by the CL and the placenta.
- CL is not needed for the entire pregnancy in some species.
- Progesterone produces slight anti-inflammatory effects.
- Oestrogens are also important.
- Other placental hormones are Placental lactogen (Cows, sheep, humans, rats, and mice) and Relaxin (Humans, mares, cats, dogs, pigs, rabbits, and Monkeys).
- Placental lactogen aSimilar action to Growth Hormone which aids Mammogenesis and promote Fetal growth.
- Relaxin softens ligaments in the pelvic region and helps with dilation of the cervix during parturition.
Questions and Answers
- True or False? The aminonic fluid is made up of secretions originating from the fetal respiratory system? Ans: True
- True or False: The yolk sac develops from the primitive endoderm? Ans: True
- What type of placentation is present in the sow? Ans: Epitheliochorial and diffuse
- In the cotyledonary placentation what makes up the maternal contribution to the placentome? Ans: Caruncle
- What makes up the fetal contribution in the cotyledonary placentation? Ans: Cotyledon
- Equine chorionic gonadotrophin is produced by what structure in the equine placenta? Ans: Endometrial cups
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.