Podcast
Questions and Answers
What role does aldosterone play in maintaining blood pressure?
What role does aldosterone play in maintaining blood pressure?
- Promoting the retention of potassium
- Promoting the retention of sodium (correct)
- Promoting the excretion of sodium
- Promoting the excretion of potassium
What is the consequence of aldosterone deficiency in CAH?
What is the consequence of aldosterone deficiency in CAH?
- Weakness and fatigue
- Accelerated bone maturation
- Life-threatening dehydration (correct)
- Low blood sugar
Which hormone deficiency can result in symptoms like weakness, fatigue, and nausea?
Which hormone deficiency can result in symptoms like weakness, fatigue, and nausea?
- Cortisol (correct)
- Testosterone
- Aldosterone
- Androgens
What consequences can excessive androgens have in CAH?
What consequences can excessive androgens have in CAH?
In CAH, what is the most common form that affects cortisol and aldosterone production?
In CAH, what is the most common form that affects cortisol and aldosterone production?
Which enzyme is essential for cortisol and aldosterone synthesis in 17-Alpha Hydroxylase Deficiency CAH?
Which enzyme is essential for cortisol and aldosterone synthesis in 17-Alpha Hydroxylase Deficiency CAH?
Which gene mutation is responsible for causing 11-Beta Hydroxylase Deficiency CAH?
Which gene mutation is responsible for causing 11-Beta Hydroxylase Deficiency CAH?
What is a common symptom seen in individuals affected by 3-Beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Deficiency CAH?
What is a common symptom seen in individuals affected by 3-Beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Deficiency CAH?
Which type of CAH is associated with reduced libido and erectile dysfunction in adolescents and adults?
Which type of CAH is associated with reduced libido and erectile dysfunction in adolescents and adults?
Which enzyme deficiency leads to increased cortisol precursors and the accumulation of 11-deoxycorticosterone (DOC) in 11-Beta Hydroxylase Deficiency CAH?
Which enzyme deficiency leads to increased cortisol precursors and the accumulation of 11-deoxycorticosterone (DOC) in 11-Beta Hydroxylase Deficiency CAH?
Which hormone produced by the placenta is responsible for the preparation of the mother's body for lactation and contributing to the growth and development of the fetus?
Which hormone produced by the placenta is responsible for the preparation of the mother's body for lactation and contributing to the growth and development of the fetus?
Which hormone aids in loosening the ligaments around the pelvis, facilitating childbirth during delivery?
Which hormone aids in loosening the ligaments around the pelvis, facilitating childbirth during delivery?
During early pregnancy, which hormone is responsible for maintaining the corpus luteum and producing essential progesterone for pregnancy maintenance?
During early pregnancy, which hormone is responsible for maintaining the corpus luteum and producing essential progesterone for pregnancy maintenance?
What is the role of uterine secretions in the earliest stages of life?
What is the role of uterine secretions in the earliest stages of life?
How is the production of uterine milk and uterine secretions regulated?
How is the production of uterine milk and uterine secretions regulated?
Why is uterine milk considered essential for the growth and development of the embryo?
Why is uterine milk considered essential for the growth and development of the embryo?
What is the role of oxytocin during implantation?
What is the role of oxytocin during implantation?
Which hormone is responsible for inhibiting uterine contractions during implantation?
Which hormone is responsible for inhibiting uterine contractions during implantation?
What are common signs of successful implantation?
What are common signs of successful implantation?
When does the zona pellucida degenerate?
When does the zona pellucida degenerate?
Which of the following correctly matches blood supply to the endometrial layers?
Which of the following correctly matches blood supply to the endometrial layers?
What role does the decidua basalis primarily play in pregnancy?
What role does the decidua basalis primarily play in pregnancy?
During early pregnancy, which type of decidua thickens to prepare for implantation?
During early pregnancy, which type of decidua thickens to prepare for implantation?
What is the significance of the decidua parietalis in pregnancy?
What is the significance of the decidua parietalis in pregnancy?
Which trimesters are crucial for the decidua in maintaining a healthy pregnancy?
Which trimesters are crucial for the decidua in maintaining a healthy pregnancy?
What distinguishes decidua vera from decidua basalis and decidua parietalis?
What distinguishes decidua vera from decidua basalis and decidua parietalis?
What is the primary role of trophoblast invasion in the intermediate trophoblastic phase of pregnancy?
What is the primary role of trophoblast invasion in the intermediate trophoblastic phase of pregnancy?
During which phase of fetal nutrition does the trophoblast invasion and consumption of the uterine decidua significantly contribute?
During which phase of fetal nutrition does the trophoblast invasion and consumption of the uterine decidua significantly contribute?
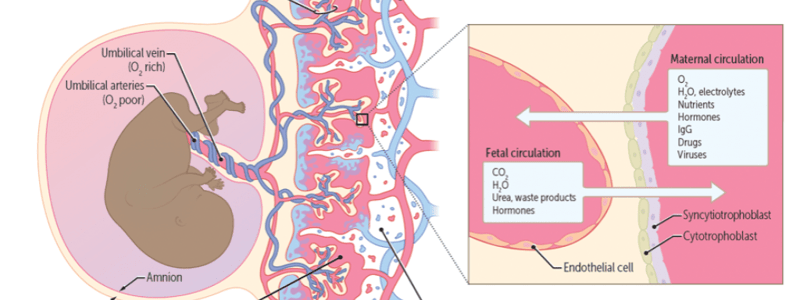
What is the key function of the placental villi in pregnancy?
What is the key function of the placental villi in pregnancy?
What is the primary function of syncytiotrophoblast cells in pregnancy?
What is the primary function of syncytiotrophoblast cells in pregnancy?
What is the significance of trophoblast differentiation from cytotrophoblast to syncytiotrophoblast cells?
What is the significance of trophoblast differentiation from cytotrophoblast to syncytiotrophoblast cells?
How do trophoblast cells contribute to immune tolerance during pregnancy?
How do trophoblast cells contribute to immune tolerance during pregnancy?
What can abnormally high levels of hCG during pregnancy indicate?
What can abnormally high levels of hCG during pregnancy indicate?
How do low hCG levels in early pregnancy potentially signal a problem?
How do low hCG levels in early pregnancy potentially signal a problem?
In terms of doubling patterns, when do hCG levels typically begin to slow down during early pregnancy?
In terms of doubling patterns, when do hCG levels typically begin to slow down during early pregnancy?
Which of the following could lead to higher than normal hCG?
Which of the following could lead to higher than normal hCG?
What is a potential limitation of using methotrexate for treating ectopic pregnancy?
What is a potential limitation of using methotrexate for treating ectopic pregnancy?
In what scenario would laparoscopic surgery be preferred over methotrexate for treating ectopic pregnancy?
In what scenario would laparoscopic surgery be preferred over methotrexate for treating ectopic pregnancy?
What makes laparoscopic surgery more invasive compared to methotrexate for treating ectopic pregnancy?
What makes laparoscopic surgery more invasive compared to methotrexate for treating ectopic pregnancy?
What is one of the most common ultrasound findings in molar pregnancies?
What is one of the most common ultrasound findings in molar pregnancies?
What is a classic sign of a hydatidiform mole on ultrasound imaging?
What is a classic sign of a hydatidiform mole on ultrasound imaging?
What is the primary purpose of surgical removal in the management of hydatidiform moles?
What is the primary purpose of surgical removal in the management of hydatidiform moles?
What is a unique characteristic of choriocarcinoma related to metastases?
What is a unique characteristic of choriocarcinoma related to metastases?
How can choriocarcinoma metastases affect the lung's surface?
How can choriocarcinoma metastases affect the lung's surface?
What can cause cannonball metastases in choriocarcinoma?
What can cause cannonball metastases in choriocarcinoma?
Which symptom of ectopic pregnancy can be indicative of low blood pressure due to internal bleeding?
Which symptom of ectopic pregnancy can be indicative of low blood pressure due to internal bleeding?
What imaging technique is commonly used to visualize the location of an ectopic pregnancy?
What imaging technique is commonly used to visualize the location of an ectopic pregnancy?
Which treatment option for ectopic pregnancies involves dissolving tissue and preventing further bleeding?
Which treatment option for ectopic pregnancies involves dissolving tissue and preventing further bleeding?
What is a potential risk of ectopic pregnancy related to damage to the fallopian tubes?
What is a potential risk of ectopic pregnancy related to damage to the fallopian tubes?
How can the risk of ectopic pregnancy be reduced through preventive measures?
How can the risk of ectopic pregnancy be reduced through preventive measures?
A 25-year-old woman (AFAB) presents for evaluation of amenorrhea. She has not had a menstrual period for 2 months. On physical examination, her uterus is enlarged. Serum levels of human chorionic gonadotropin are elevated. This hormone most likely derives from which of the following locations?
A 25-year-old woman (AFAB) presents for evaluation of amenorrhea. She has not had a menstrual period for 2 months. On physical examination, her uterus is enlarged. Serum levels of human chorionic gonadotropin are elevated. This hormone most likely derives from which of the following locations?
What is one of the primary roles of amniotic fluid in fetal development?
What is one of the primary roles of amniotic fluid in fetal development?
How does the composition of amniotic fluid change during pregnancy?
How does the composition of amniotic fluid change during pregnancy?
Why is monitoring the volume and composition of amniotic fluid important during pregnancy?
Why is monitoring the volume and composition of amniotic fluid important during pregnancy?
What is the primary function of the chorionic membrane in protecting the developing fetus?
What is the primary function of the chorionic membrane in protecting the developing fetus?
Which hormone is primarily secreted by the chorionic membrane to maintain the early stages of pregnancy?
Which hormone is primarily secreted by the chorionic membrane to maintain the early stages of pregnancy?
How do chorionic villi contribute to the establishment of the placental connection between the mother and the fetus?
How do chorionic villi contribute to the establishment of the placental connection between the mother and the fetus?
What is a potential complication often seen in monochorionic diamniotic (MCDA) twins?
What is a potential complication often seen in monochorionic diamniotic (MCDA) twins?
Why is close monitoring crucial in monochorionic monoamniotic (MoMA) twin pregnancies?
Why is close monitoring crucial in monochorionic monoamniotic (MoMA) twin pregnancies?
What distinguishes dichorionic diamniotic (DCDA) twins from MCDA twins?
What distinguishes dichorionic diamniotic (DCDA) twins from MCDA twins?
Which complication is commonly associated with monochorionic twins but not dichorionic twins?
Which complication is commonly associated with monochorionic twins but not dichorionic twins?
Why is delivery often performed by cesarean section in monochorionic twins?
Why is delivery often performed by cesarean section in monochorionic twins?
How does hPL contribute to fetal growth and development?
How does hPL contribute to fetal growth and development?
What is one of the implications of hPL-induced insulin resistance in the mother?
What is one of the implications of hPL-induced insulin resistance in the mother?
Which factor influences the regulation of hPL secretion in addition to placental and maternal hormones?
Which factor influences the regulation of hPL secretion in addition to placental and maternal hormones?
What role does human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) play during the luteal-placental transition in pregnancy?
What role does human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) play during the luteal-placental transition in pregnancy?
Which hormone undergoes a reduction during the luteal-placental transition as the placenta takes over its production?
Which hormone undergoes a reduction during the luteal-placental transition as the placenta takes over its production?
What is the significance of the luteal-placental transition for successful pregnancy continuation?
What is the significance of the luteal-placental transition for successful pregnancy continuation?
How does progesterone (P4) contribute to maintaining a safe environment for the growing fetus?
How does progesterone (P4) contribute to maintaining a safe environment for the growing fetus?
Which of the following statements about progesterone (P4) during pregnancy is true?
Which of the following statements about progesterone (P4) during pregnancy is true?
In the context of pregnancy, what is a key role of maintaining immune tolerance between the mother and the fetus?
In the context of pregnancy, what is a key role of maintaining immune tolerance between the mother and the fetus?
How does progesterone (P4) aid in minimizing the risk of preterm labor?
How does progesterone (P4) aid in minimizing the risk of preterm labor?
What is the effect of progesterone (P4) on endometrial decidualization in pregnancy?
What is the effect of progesterone (P4) on endometrial decidualization in pregnancy?
Which phenomenon describes the mother's immune system becoming less responsive to foreign antigens during pregnancy?
Which phenomenon describes the mother's immune system becoming less responsive to foreign antigens during pregnancy?
What is the primary role of the placenta in promoting an immune-tolerant environment during pregnancy?
What is the primary role of the placenta in promoting an immune-tolerant environment during pregnancy?
How do maternal B-cells contribute to the maternal immune system during pregnancy?
How do maternal B-cells contribute to the maternal immune system during pregnancy?
What is the main method used to diagnose preeclampsia?
What is the main method used to diagnose preeclampsia?
Which complication of preeclampsia is characterized by seizures and coma?
Which complication of preeclampsia is characterized by seizures and coma?
What can occur if the placenta detaches from the uterine wall prematurely?
What can occur if the placenta detaches from the uterine wall prematurely?
What is a key factor contributing to the development of preeclampsia as described in the text?
What is a key factor contributing to the development of preeclampsia as described in the text?
Which aspect is essential for early detection of preeclampsia according to the information provided?
Which aspect is essential for early detection of preeclampsia according to the information provided?
How does oxidative stress contribute to the development of preeclampsia based on the text?
How does oxidative stress contribute to the development of preeclampsia based on the text?
What is a key consideration for deciding when to proceed with delivery for women with HELLP syndrome?
What is a key consideration for deciding when to proceed with delivery for women with HELLP syndrome?
What is a critical aspect of emergency management for HELLP syndrome regarding blood products?
What is a critical aspect of emergency management for HELLP syndrome regarding blood products?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the emergency management strategy for HELLP syndrome according to the text?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the emergency management strategy for HELLP syndrome according to the text?
Why is pre-conception counseling recommended for women at risk of PAS?
Why is pre-conception counseling recommended for women at risk of PAS?
What is a potential consequence of severe PAS?
What is a potential consequence of severe PAS?
Why is emergency preparedness important in cases of severe PAS?
Why is emergency preparedness important in cases of severe PAS?
Which factor significantly increases the risk of abruptio placentae in pregnant women over the age of 35?
Which factor significantly increases the risk of abruptio placentae in pregnant women over the age of 35?
How can placental abnormalities contribute to the development of abruptio placentae?
How can placental abnormalities contribute to the development of abruptio placentae?
Which condition is commonly associated with an increased risk of abruptio placentae due to its effect on blood pressure and blood flow?
Which condition is commonly associated with an increased risk of abruptio placentae due to its effect on blood pressure and blood flow?
What is the most common symptom of placenta previa, often leading to the diagnosis?
What is the most common symptom of placenta previa, often leading to the diagnosis?
Which is a key aspect of placenta previa management according to the text?
Which is a key aspect of placenta previa management according to the text?
Why is a C-section delivery often necessary in cases of placenta previa?
Why is a C-section delivery often necessary in cases of placenta previa?
Where is milk synthesized and stored within the mammary gland?
Where is milk synthesized and stored within the mammary gland?
Which component of the mammary gland is responsible for carrying milk from the alveoli to the nipple?
Which component of the mammary gland is responsible for carrying milk from the alveoli to the nipple?
What is the main function of lobules in the mammary gland?
What is the main function of lobules in the mammary gland?
Which part of the mammary gland forms a honeycomb-like structure in breast tissue?
Which part of the mammary gland forms a honeycomb-like structure in breast tissue?
What is the role of collecting ducts in the mammary gland?
What is the role of collecting ducts in the mammary gland?
Match the following placental hormones with their role in breast development
Match the following placental hormones with their role in breast development
Match the following hormones with their role in the negative feedback on GnRH:
Match the following hormones with their role in the negative feedback on GnRH:
Match the hormone with its effect on the suppression of FSH secretion:
Match the hormone with its effect on the suppression of FSH secretion:
Match the hormone/chemical with its role in prolactin regulation in females:
Match the hormone/chemical with its role in prolactin regulation in females:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following terms with their descriptions:
Match the following scenarios with their effects on oxytocin production:
Match the following scenarios with their effects on oxytocin production:
Match the following statements with their relation to breast milk production:
Match the following statements with their relation to breast milk production:
Match the following effects of oxytocin with their descriptions:
Match the following effects of oxytocin with their descriptions:
Match the following benefits of oxytocin with their implications:
Match the following benefits of oxytocin with their implications:
Match the following oxytocin effects with their significance:
Match the following oxytocin effects with their significance:
Study Notes
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: A Deep Dive into Genetics, Hormones, and Their Impact
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, or CAH, is a genetic disorder that affects the adrenal glands, which play a vital role in producing essential hormones. Despite its name, this condition is not exclusively hyperactive but rather a result of enzyme deficiencies, primarily impacting the production of cortisol and, to a lesser extent, aldosterone. Regardless, understanding the genetics, hormones involved, and their interconnected roles provides a clearer perspective on this complex disorder.
Genetics
CAH is caused by mutations in genes responsible for producing enzymes involved in the synthesis of adrenal hormones. The most common form of CAH is due to deficiencies in the 21-hydroxylase enzyme, which affects approximately 90-95% of cases. Other, less common forms include deficiencies in 11-beta hydroxylase, 17-alpha hydroxylase, and 3-beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2.
The responsible genes, CYP21A2 for 21-hydroxylase, CYP11B1 for 11-beta hydroxylase, and CYP17A1 for 17-alpha hydroxylase, are all part of the steroidogenic acute regulatory (STAR) protein-dependent pathway. Mutations in these genes result in a multitude of potential defects and severities, from classical CAH to non-classical CAH.
Mineralocorticoids
Aldosterone, a mineralocorticoid hormone, helps regulate water and electrolyte balance. It maintains blood pressure by promoting the retention of sodium and the excretion of potassium. In CAH, aldosterone deficiency can lead to a condition called salt-wasting crisis, characterized by life-threatening dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Glucocorticoids
Cortisol, the primary glucocorticoid hormone, plays a fundamental role in stress management, maintaining blood sugar levels, and regulating immune responses. Cortisol deficiency can result in adrenal insufficiency, causing symptoms such as low blood sugar, weakness, fatigue, and nausea.
Androgens
CAH leads to overproduction of androgens, such as testosterone, which contribute to the development of ambiguous genitalia in females and premature pubarche in both males and females. Excessive androgens can also result in an early growth spurt, accelerated bone maturation, and unnecessarily rapid closure of growth plates, potentially leading to short stature in adulthood.
In summary, CAH is a genetic disorder involving enzyme deficiencies in adrenal hormone synthesis. The most common form of CAH affects cortisol and aldosterone production, leading to mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid deficiencies. Overproduction of androgens is another significant consequence of CAH, which can result in a broad range of symptoms. Understanding the complex interplay between genetics, hormones, and their roles in CAH helps medical professionals develop appropriate treatments and management strategies for affected individuals.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
H Burkin Block 3 Week 7