Podcast
Questions and Answers
What percentage of premature births is accounted for by placentation issues?
What percentage of premature births is accounted for by placentation issues?
- 10%
- 20%
- 5%
- 15% (correct)
Which artery is responsible for delivering oxygenated maternal blood to the intervillous space?
Which artery is responsible for delivering oxygenated maternal blood to the intervillous space?
- Umbilical arteries
- Spiral arteries (correct)
- Endometrial arteries
- Uterine veins
What drains the blood from the intervillous space in the placental circulation?
What drains the blood from the intervillous space in the placental circulation?
- Endometrial arteries
- Umbilical vein
- Uterine veins (correct)
- Spiral arteries
In the context of placental circulation, what does the umbilical cord consist of?
In the context of placental circulation, what does the umbilical cord consist of?
Which component is NOT part of the maternal side of placental circulation?
Which component is NOT part of the maternal side of placental circulation?
What is the primary role of the maternal portion of the placenta?
What is the primary role of the maternal portion of the placenta?
Which component is primarily responsible for nutrient and gas exchange in the placenta?
Which component is primarily responsible for nutrient and gas exchange in the placenta?
What structure forms from the fusion of the chorion and the decidua during placentation?
What structure forms from the fusion of the chorion and the decidua during placentation?
In the context of monozygotic twins, what is the result of their separation after implantation?
In the context of monozygotic twins, what is the result of their separation after implantation?
Which of the following is considered an endocrine function of the placenta?
Which of the following is considered an endocrine function of the placenta?
Which part of the placenta is responsible for the formation of the villous chorion?
Which part of the placenta is responsible for the formation of the villous chorion?
What issue can arise concerning the amniotic fluid balance during early placental development?
What issue can arise concerning the amniotic fluid balance during early placental development?
What is the primary change that occurs to cytotrophoblasts during the 2nd trimester?
What is the primary change that occurs to cytotrophoblasts during the 2nd trimester?
What components make up the placental barrier later in gestation?
What components make up the placental barrier later in gestation?
What role do anchoring villi play in placentation?
What role do anchoring villi play in placentation?
What happens to cytotrophoblasts within anchoring villi?
What happens to cytotrophoblasts within anchoring villi?
Which layer acts as the 'floor' of the placenta?
Which layer acts as the 'floor' of the placenta?
How do extravillous trophoblasts contribute to placentation?
How do extravillous trophoblasts contribute to placentation?
In which location is the majority of the fetal cytotrophoblast present?
In which location is the majority of the fetal cytotrophoblast present?
What is the significance of the thinning of the placental barrier?
What is the significance of the thinning of the placental barrier?
What type of tissue is primarily involved in forming the columns of anchoring villi?
What type of tissue is primarily involved in forming the columns of anchoring villi?
Which of the following best describes the functional importance of the placental barrier?
Which of the following best describes the functional importance of the placental barrier?
What is established by the end of week 3 in the development of the placenta?
What is established by the end of week 3 in the development of the placenta?
Which component of the primitive placenta consists of differentiated endometrium?
Which component of the primitive placenta consists of differentiated endometrium?
What forms when the capillaries in the tertiary chorionic stem villi fuse?
What forms when the capillaries in the tertiary chorionic stem villi fuse?
Which of the following best describes the embryonic component of the primitive placenta?
Which of the following best describes the embryonic component of the primitive placenta?
What type of blood flow begins slowly through the capillaries of the tertiary chorionic stem villi?
What type of blood flow begins slowly through the capillaries of the tertiary chorionic stem villi?
What role do decidual cells have in the developing placenta?
What role do decidual cells have in the developing placenta?
Which structure directly connects the embryonic heart to the developing placenta?
Which structure directly connects the embryonic heart to the developing placenta?
Which of the following statements about the decidua is true?
Which of the following statements about the decidua is true?
Which fetal structure is primarily responsible for the exchange of nutrients and waste?
Which fetal structure is primarily responsible for the exchange of nutrients and waste?
At week 4 of development, how has the embryo, amniotic cavity, and chorionic cavity changed with respect to the uterine cavity?
At week 4 of development, how has the embryo, amniotic cavity, and chorionic cavity changed with respect to the uterine cavity?
What is a notable feature of the implanted embryo at week 4 regarding the placenta?
What is a notable feature of the implanted embryo at week 4 regarding the placenta?
What is indicated by the term 'decidua' in relation to the week 4 embryo?
What is indicated by the term 'decidua' in relation to the week 4 embryo?
Which of the following statements is accurate for the condition of the embryo at week 4?
Which of the following statements is accurate for the condition of the embryo at week 4?
Which structure is primarily associated with the implantation seen in week 4?
Which structure is primarily associated with the implantation seen in week 4?
Which statement correctly captures the relationship between the implanted embryo and the uterine endometrium at week 4?
Which statement correctly captures the relationship between the implanted embryo and the uterine endometrium at week 4?
What happens to the chorionic and amniotic cavities by week 4?
What happens to the chorionic and amniotic cavities by week 4?
Which of the following describes the anatomical characteristics of the implanting embryo at week 4?
Which of the following describes the anatomical characteristics of the implanting embryo at week 4?
In which publication is the diagram of the sagittal section of an implanted embryo referenced?
In which publication is the diagram of the sagittal section of an implanted embryo referenced?
What major milestone in embryonic development is highlighted at week 4?
What major milestone in embryonic development is highlighted at week 4?
Flashcards
Placenta
Placenta
The structure that facilitates nutrient and gas exchange between the developing fetus and the mother.
Lacunar Blood Network
Lacunar Blood Network
A system of interconnected spaces filled with maternal blood, formed by the erosion of maternal capillaries by the syncytiotrophoblast.
Chorionic Villi
Chorionic Villi
Finger-like projections of the trophoblast that grow into the lacunae, increasing the surface area for exchange.
Primitive Placenta
Primitive Placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua Basalis
Decidua Basalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Villous Chorion
Villous Chorion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placentation
Placentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Villous arteriocapillary networks
Villous arteriocapillary networks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua
Decidua
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidual cells
Decidual cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chorion
Chorion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryonic blood flow in the placenta
Embryonic blood flow in the placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Establishment of the primitive placenta
Establishment of the primitive placenta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decidua
Decidua
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intervillous Space
Intervillous Space
Signup and view all the flashcards
Umbilical Cord
Umbilical Cord
Signup and view all the flashcards
Syncytiotrophoblast
Syncytiotrophoblast
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Plate
Basal Plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anchoring Villi
Anchoring Villi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrium (Decidua)
Endometrium (Decidua)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amniotic Cavity
Amniotic Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Floating Villi
Floating Villi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chorionic Cavity
Chorionic Cavity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Placental Barrier
Placental Barrier
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Capillaries
Fetal Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extravillous Trophoblasts
Extravillous Trophoblasts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implantation
Implantation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryonic Period
Embryonic Period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cytotrophoblastic Columns
Cytotrophoblastic Columns
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cytotrophoblastic Shell
Cytotrophoblastic Shell
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Period
Fetal Period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryogenesis
Embryogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Viability
Viability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Placentation Lecture Learning Objectives
- Describe the formation of the primitive placenta
- Describe the formation of the lacunar blood network
- Describe the formation of chorionic villi
- Describe the formation of the primitive placenta
- Describe the development of the early placenta
- Describe the decidua during the first trimester
- Compare and contrast the three regions of the decidua
- Describe the chorion during the first trimester
- Compare and contrast the two regions of the chorion
- Describe the structure of the placenta at the end of the first trimester
- Describe the organization and structure of the placenta
- Describe the fetal portion of the placenta, the villous chorion
- Describe the maternal portion of the placenta, the decidua basalis
- Describe the interaction of the chorionic villi with the intervillous space and the basal plate
- Describe chorionic villi
- Describe the changes in chorionic villi structure during gestation
- Describe the placental barrier, where maternal and fetal circulations exchange
- Describe the components of the basal plate
- Describe anchoring villi
- Describe extravillous trophoblasts
- Describe the role of extravillous trophoblasts in placental structure and pathophysiology
- Describe the maternal-fetal circulation of the placenta
- Describe how the placental barrier is crossed by gases, nutrients, waste, antibodies, and drugs
- Describe the endocrine functions of the placenta
- Describe the structure and function of the amniotic cavity
- Describe the structure and function of the amniochorionic membrane
- Describe the source(s) of amniotic fluid and its flow in the fetus
- Describe the functions of amniotic fluid
- Describe the consequences of problems with amniotic fluid balance
- Describe oligohydramnios, including its cause
- Describe polyhydramnios, including its cause
- Describe the appearance of the term placenta
- Describe the placenta and membranes of twins
- Describe the placenta of dizygotic twins
- Describe the placenta of monozygotic twins
- Describe the placenta of monozygotic twins that separate before blastocyst formation
- Describe the placenta of monozygotic twins that separate during blastocyst formation
- Describe the placenta of monozygotic twins that separate after implantation
Review of the Primitive Placenta
- Formation of Lacunar Blood Network
- Formation of Chorionic Villi
- Formation of Primitive Placenta
Development of Early Placenta
- Decidua during the first trimester
- Chorion during the first trimester
- Placenta at the end of the first trimester
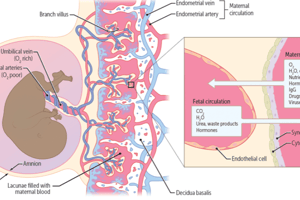
Organization and Structure of the Placenta
- Fetal Portion: Villous Chorion (Chorion Frondosum)
- Maternal Portion: Decidua Basalis
- Chorionic Villi (floating or branching villi)
- Basal Plate and Anchoring Villi
- Extravillous Trophoblasts
- Placental Circulation
- Placental Transport
Amniotic Cavity
- Amniochorionic Membrane
- Amniotic Fluid
- Functions of Amniotic Fluid
- Problems with Amniotic Fluid Balance
- Oligohydramnios
- Polyhydramnios
Term Placenta
- Placenta at Birth
- Appearance of term placenta
- Fetal Side of placenta
- Maternal Side of Placenta
Placenta and Membranes of Twins
- Dizygotic Twins (non-identical)
- Monozygotic Twins (identical)
- Dizygotic vs Monozygotic
Additional Notes
- Implantation site of the embryo in the uterine wall is called the decidua.
- Three regions of the decidua can be distinguished
- Decidua Basalis
- Decidua Capsularis
- Decidua Parietalis
- The chorion changes from chorion frondosum to chorion laeve.
- The primitive placenta develops into the true placenta.
- Fetal and maternal components form the true placenta.
- The placental barrier separates maternal and fetal blood. The components of the barrier change as gestation progresses.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.