Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the typical range for the length of an adult kidney?
What is the typical range for the length of an adult kidney?
- 14-15 cm
- 11-12 cm (correct)
- 16-17 cm
- 8-9 cm
Which of the following structures is NOT part of a nephron?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of a nephron?
- Renal calyx (correct)
- Glomerulus
- Collecting duct
- Renal tubule
At what approximate level of the vertebral column do the kidneys typically extend?
At what approximate level of the vertebral column do the kidneys typically extend?
- L3 to S1
- T6 to T10
- S1 to S4
- T12 to L3 (correct)
The renal arteries normally originate from which major vessel?
The renal arteries normally originate from which major vessel?
Which of the following best describes the anatomical relationship of the right kidney to the liver?
Which of the following best describes the anatomical relationship of the right kidney to the liver?
What is the approximate glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
What is the approximate glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
Which of the following is NOT part of the surrounding layers of the kidney?
Which of the following is NOT part of the surrounding layers of the kidney?
What is the typical length of an adult ureter?
What is the typical length of an adult ureter?
Where do the ureters enter the bladder?
Where do the ureters enter the bladder?
In males, what anatomical structure does the ureter pass under?
In males, what anatomical structure does the ureter pass under?
In females, the ureter passes under which artery?
In females, the ureter passes under which artery?
Which arteries supply the upper part of the ureters?
Which arteries supply the upper part of the ureters?
What is the term for the triangular area defined by the two ureteric openings and the internal urethral opening in the bladder?
What is the term for the triangular area defined by the two ureteric openings and the internal urethral opening in the bladder?
What is the name of the muscle that makes up the wall of the bladder?
What is the name of the muscle that makes up the wall of the bladder?
Which of the following is the approximate length of the female urethra?
Which of the following is the approximate length of the female urethra?
What is the approximate length of the adult male urethra?
What is the approximate length of the adult male urethra?
Flashcards
Nephron
Nephron
The functional unit of the kidney, responsible for filtering blood and producing urine.
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
The rate at which fluid is filtered from the blood through the glomerulus in the kidney.
Renal artery
Renal artery
The main blood supply to the kidneys, originating from the abdominal aorta.
Renal pelvis
Renal pelvis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureter
Ureter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bladder
Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra
Urethra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate
Prostate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureter's Path Through bladder
Ureter's Path Through bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureter Blood Supply
Ureter Blood Supply
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bladder Location and Anatomy
Bladder Location and Anatomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigone of the Bladder
Trigone of the Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Detrusor Muscle of Bladder
Detrusor Muscle of Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neck of the Bladder
Neck of the Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra in Males and Females
Urethra in Males and Females
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apex of the Bladder
Apex of the Bladder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Urology Module - Semester 4
-
Lecture name: Anatomy of the Urinary System
-
Lecturer: Dr. Salam Abdulameer Almosawi
-
Credentials: F.I.C.M.S.(URO)
-
Contact: [email protected]
Objectives
- Understand the gross structure of the urinary system in both males and females
- Learn the overall functions of the urinary system
- Identify the anatomical position of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and prostate, along with their relationships
- Detail the blood supply, venous drainage, and lymphatics of the urinary system
Anatomy of the Urinary System
- The urinary system consists of:
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Bladder
- Urethra
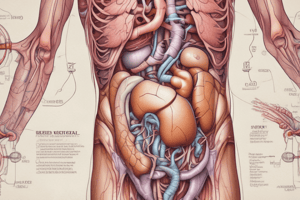
The Kidneys
- Bean-shaped, retroperitoneal, located on either side of the vertebral column
- Extend from T12 to L3
- Right kidney typically positioned slightly more caudally
- Dimensions: approximately 11-12 cm in length, 5-7.5 cm in width, and 2.5-3.0 cm in thickness.
- Surrounded by:
- Tough fibrous capsule
- Perirenal fat
- Gerotas fascia
- Para-renal fat
- Functional unit: nephron
- Nephron structure: glomerulus, renal tubule, and collecting duct
- Filtration:
- Occurs in specialized leaky capillaries (glomeruli) within the kidney cortex.
- High pressure in glomeruli forces water and small molecules out of the plasma at a rate of 125 ml/min or 180 L per day, known as glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Blood Supply of the Kidneys
- Usually supplied by a single renal artery branching from the abdominal aorta at the level of L1.
- Accessory renal arteries are sometimes present.
- Renal artery enters the kidney through the hilum, typically dividing into anterior and posterior branches.
- Abnormal arterial supply can originate from the superior mesenteric, suprarenal, testicular or ovarian arteries.
Relationships of the Kidneys
- Right Kidney:
- Superior: adrenal gland, liver
- Posterior: posterior abdominal wall (psoas major muscle)
- Anterior: liver, adrenal gland, duodenum, and colon
- Left Kidney:
- Superior: adrenal gland, spleen
- Posterior: posterior abdominal wall (psoas major muscle)
- Anterior: adrenal gland, spleen, stomach, pancreas, small bowel and colon
The Ureters
- Originate from the renal pelvis
- Length: 25-30 cm in adults
- Course:
- In abdomen, runs along anterior aspect of transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae
- Crosses pelvic brim at the sacroiliac joint, anterior to the bifurcation of common iliac artery
- Runs posterolaterally along bladder wall before entering the bladder obliquely
- Male: passes under vas deferens, superiorly to seminal vesicle
- Female: descends posterior to ovary and into the broad ligament, passing under the uterine artery.
Blood Supply of the Ureters
- The upper part is supplied by renal arteries.
- The middle and lower parts are supplied by common iliac and internal iliac arteries.
- The lower part receives blood from uterine (female) or inferior vesical (male) arteries.
- Corresponding veins drain the ureters.
The Bladder
- Position: posterior to pubic bones and symphysis.
- Shape: empty - lies entirely within true pelvic cavity. Full – becomes spherical and can reach above the umbilicus
- Surfaces:
- Base (posterior surface)
- One superior surface
- Two anterolateral surfaces
- Trigone (internal structure): triangular area defined internally by two ureteric openings and the internal urethral opening, including the interureteric ridge
- Neck: area where the base and inferolateral surfaces meet, inferiorly
The Urethra
- Female: 4-5 cm long, straight
- Male: 20 cm long, divided into
- Posterior part (5 cm): prostatic and membranous
- Anterior part (15 cm): bulbus and penile
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.