Questions and Answers
Which hormone do the kidneys release that stimulates the production of red blood cells?
What is the primary function of the ureters?
Which layer of the urinary bladder is responsible for its contraction during urine release?
What is the primary function of the glomerulus in the kidney?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of aldosterone in relation to kidney function?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure collects liquid waste that has been filtered out of the blood?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following structures controls the voluntary release of urine?
Signup and view all the answers
Which function of the kidneys is essential for maintaining the acid-base balance in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
Where does most reabsorption occur in the nephron?
Signup and view all the answers
Which substance is primarily secreted into the filtrate to maintain pH balance?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do the peritubular capillaries play in kidney function?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements about the renal cortex and medulla is true?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of waste is primarily secreted into the filtrate from the blood?
Signup and view all the answers
How many nephrons are approximately present in each kidney?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
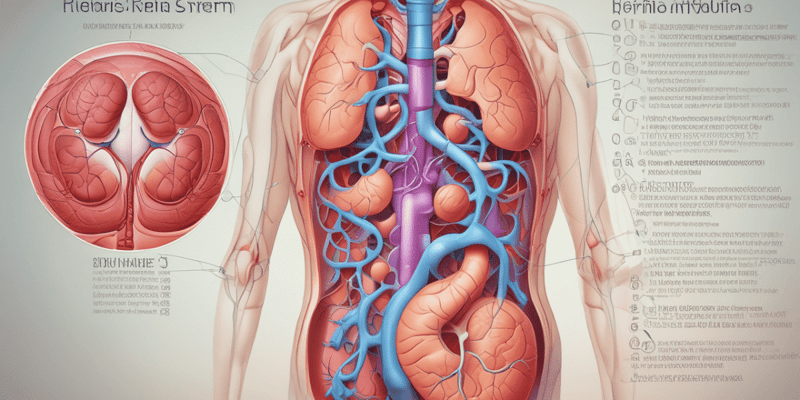
Parts and Main Functions of the Renal System
- Responsible for waste removal from blood, excreting it as urine.
- The primary liquid excreted is yellow urine.
Anatomy of the Kidney
- Renal Cortex: The outer region of the kidney.
- Renal Medulla: Inner section containing renal pyramids and nephrons.
- Renal Pelvis: Collecting tube for urine.
- Medullary Pyramids: Triangular tissue regions in the medulla where nephrons are located.
Nephrons
- Structural and functional units of the kidneys, with about 1 million in each kidney.
- Main components include the glomerulus and renal tubule.
Glomerulus
- Key role in blood filtration, preventing blood cells from entering filtrate.
- Composed of a specialized capillary bed connected to afferent and efferent arterioles.
- Bowman’s Capsule: Collects filtered liquid waste.
Renal Tubule
- Functions in reabsorption and secretion.
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule: Primary site for reabsorption of water, glucose, salts, and ions.
- Secretion: Process of transferring waste molecules (such as urea and medications) from blood to filtrate.
- Collecting Duct: Transports urine to the renal pelvis.
Other Functions of the Kidney
- Urine formation and excretion of waste products.
- Regulation of electrolytes and acid-base balance (H+/HCO3).
- Control of water balance and osmolarity, aided by the secretion of renin and aldosterone.
- Regulation of red blood cell production through erythropoietin stimulation of bone marrow.
- Synthesis of active form of Vitamin D for calcium balance and bone health.
- Regulation of calcium and phosphorus levels, as well as secretion of prostaglandins.
The Ureters
- One ureter per kidney, connecting kidneys to the bladder.
- Long, smooth muscle tubes facilitating urine movement via peristalsis.
- Enter the bladder at an angle to prevent backflow.
The Urinary Bladder
- Smooth muscular sac for temporary urine storage, with a capacity of 1.5-2 liters.
- Walls consist of four layers:
- Adventitia (outer connective tissue)
- Detrusor (smooth muscle)
- Submucosal layer (loose connective tissue)
- Mucosal lining (inner layer, impermeable to water).
The Urethra
- Thin-walled tube transporting urine from bladder to the outside.
- Urine release regulated by two sphincters:
- Internal urethral sphincter (involuntary control).
- External urethral sphincter (voluntary control).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers the essential components of the urinary system including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It explores their anatomy and physiological functions such as filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Test your knowledge on how the renal system contributes to waste removal from the body.