Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the end product of purine metabolism?
What is the end product of purine metabolism?
- Hypoxanthine
- Xanthine
- Uric Acid (correct)
- Inosine monophosphate
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of hypoxanthine to xanthine?
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of hypoxanthine to xanthine?
- Urate oxidase
- IMP dehydrogenase
- Ribose-5-phosphate
- Xanthine oxidase (correct)
What happens to uric acid in most mammals?
What happens to uric acid in most mammals?
- It is excreted through the kidney.
- It is excreted through the gastrointestinal tract.
- It is converted to allantoate by urate oxidase. (correct)
- It is converted to xanthine by xanthine oxidase.
Why do humans have higher serum UA concentrations compared to most other mammals?
Why do humans have higher serum UA concentrations compared to most other mammals?
How is approximately one-third of uric acid removed from the body?
How is approximately one-third of uric acid removed from the body?
What condition is characterized by plaque buildup within blood vessel walls?
What condition is characterized by plaque buildup within blood vessel walls?
Which of the following has been linked to increased UA levels and MSU crystal formation?
Which of the following has been linked to increased UA levels and MSU crystal formation?
What has been proposed as a potential therapeutic to manage diseases related to dysregulated UA metabolism?
What has been proposed as a potential therapeutic to manage diseases related to dysregulated UA metabolism?
What is crucial for appreciating the impact of uric acid metabolism on human health?
What is crucial for appreciating the impact of uric acid metabolism on human health?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Uric acid (UA) metabolism is a crucial process in maintaining overall health in humans. As the end product of purine metabolism, UA plays a vital role in various biological functions, acting as an antioxidant and contributing to the development of certain diseases. This article will explore the pathways involved in UA metabolism and discuss the implications of dysregulated UA levels on health, focusing on the relationship between UA metabolism and metabolic syndrome components such as atherosclerosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Purine Metabolism and Uric Acid Generation
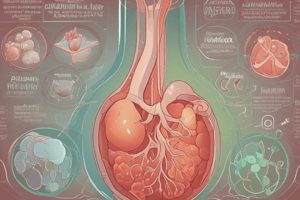
Inosine monophosphate (IMP), a key intermediate in purine metabolism, is derived from de novo purine synthesis and purine salvage pathways. Hypoxanthine, formed from IMP via ribose-5-phosphate, is then catalyzed to xanthine and ultimately to uric acid by xanthine oxidase (XO) (Figure 1). Humans lack the ability to convert UA to the more soluble allantoate due to the absence of urate oxidase or uricase, leading to higher serum UA concentrations compared to most other mammals. Approximately two-thirds of UA is excreted through the kidney, while one-third is removed through the gastrointestinal tract.
Relationship Between Uric Acid Metabolism and Disease
Recent research has highlighted the potential consequences of impaired UA metabolism and the associated inflammatory responses on various health issues. For example, elevated UA levels have been linked to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by plaque buildup within blood vessel walls. Similarly, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a form of liver damage, has been associated with increased UA levels and the subsequent formation of monosodium urate (MSU) crystals. These findings suggest that UA metabolism plays a significant role in maintaining cardiovascular health and liver function.
Therapeutic Implications
Inhibitors of xanthine oxidase have been proposed as potential therapeutics to manage diseases related to dysregulated UA metabolism. For instance, these inhibitors have shown promise in reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and NASH through their ability to modulate UA levels and associated inflammation. However, further research is needed to fully understand the molecular mechanisms underlying these effects and to optimize treatment strategies.
In summary, understanding the intricacies of uric acid metabolism is crucial for appreciating its impact on various aspects of human health. The identification of key pathways and the development of targeted therapies can potentially lead to improved management of conditions such as atherosclerosis and NASH.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.