Podcast
Questions and Answers
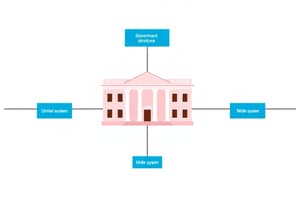
What characterizes a unitary system of government?
What characterizes a unitary system of government?
- Regional governments possess equal sovereignty as the central government.
- Power is shared between the central government and regional governments.
- A single, sovereign government controls all aspects of the country. (correct)
- Sovereignty is divided among multiple independent states.
In a federal system, where is the sovereignty of regional governments established?
In a federal system, where is the sovereignty of regional governments established?
- Via agreements made at the local level.
- Within the nation's constitution. (correct)
- Through the decisions of the central government.
- In the framework set by international treaties.
Which of the following is NOT an example of a level of government in a federal system?
Which of the following is NOT an example of a level of government in a federal system?
- Central Government
- Local Government
- Regional Government
- Supreme Government (correct)
What does devolution refer to in a unitary government system?
What does devolution refer to in a unitary government system?
Which statement best describes the continuum of centralization?
Which statement best describes the continuum of centralization?
What is a key feature of a confederation in relation to sovereign states?
What is a key feature of a confederation in relation to sovereign states?
Which of the following would best illustrate the concept of federalism?
Which of the following would best illustrate the concept of federalism?
In which governance model would 'administrative divisions' retain limited powers?
In which governance model would 'administrative divisions' retain limited powers?
What is an implication of federalism for the relationship between central and regional governments?
What is an implication of federalism for the relationship between central and regional governments?
What mechanism is primarily used for checking the power of the federal government by provinces?
What mechanism is primarily used for checking the power of the federal government by provinces?
Which section grants provinces control over their natural resources?
Which section grants provinces control over their natural resources?
Which of the following is not explicitly stated as a federal power under s.91?
Which of the following is not explicitly stated as a federal power under s.91?
What does 'P.O.G.G.' stand for in the context of federalism?
What does 'P.O.G.G.' stand for in the context of federalism?
In what year was the last use of disallowance recorded?
In what year was the last use of disallowance recorded?
Which section provides the federal government with power over criminal law?
Which section provides the federal government with power over criminal law?
Which section of the Constitution involves the administration of justice in the province?
Which section of the Constitution involves the administration of justice in the province?
Which group is empowered to raise revenue for its operations according to provincial powers?
Which group is empowered to raise revenue for its operations according to provincial powers?
What does s.92 allow provinces to legislate on?
What does s.92 allow provinces to legislate on?
What is a consequence of the complexities of federalism in Canada?
What is a consequence of the complexities of federalism in Canada?
What is a key distinction between unitary and federal systems of government?
What is a key distinction between unitary and federal systems of government?
Which of the following best describes the nature of devolution in a unitary government?
Which of the following best describes the nature of devolution in a unitary government?
In the context of the continuum of centralization, which form represents complete centralization?
In the context of the continuum of centralization, which form represents complete centralization?
What is the primary characteristic of a federal system regarding the constitution?
What is the primary characteristic of a federal system regarding the constitution?
Which of the following statements about regional governments in federal systems is accurate?
Which of the following statements about regional governments in federal systems is accurate?
What defines the governance model of a confederation?
What defines the governance model of a confederation?
Which characteristic is common to both unitary and federal systems of government?
Which characteristic is common to both unitary and federal systems of government?
What is commonly emphasized in discussions about the complexities of federalism?
What is commonly emphasized in discussions about the complexities of federalism?
Which of the following concepts is essential to understanding decentralized governance?
Which of the following concepts is essential to understanding decentralized governance?
How does the concept of 'administrative divisions' function within a unitary government?
How does the concept of 'administrative divisions' function within a unitary government?
What does section 92 of the Constitution primarily address?
What does section 92 of the Constitution primarily address?
Which of the following is a significant aspect of federalism as highlighted in the content?
Which of the following is a significant aspect of federalism as highlighted in the content?
What can be inferred about the complexities of federalism in Canada?
What can be inferred about the complexities of federalism in Canada?
What is the purpose of the 'peace, order and good government' (P.O.G.G.) clause?
What is the purpose of the 'peace, order and good government' (P.O.G.G.) clause?
Which section of the Constitution allows federal control over currency and coinage?
Which section of the Constitution allows federal control over currency and coinage?
Which statement accurately reflects the concept of federalism according to the provided content?
Which statement accurately reflects the concept of federalism according to the provided content?
What has historically been true about the federal government's power in Canada?
What has historically been true about the federal government's power in Canada?
What was the last year disallowance was used according to the historical context provided?
What was the last year disallowance was used according to the historical context provided?
What is indicated by the concept of residual power in the context of federalism?
What is indicated by the concept of residual power in the context of federalism?
Which of the following attaches to the specific matters given to the provinces as outlined in the content?
Which of the following attaches to the specific matters given to the provinces as outlined in the content?
What distinguishes guerrilla violence from other forms of political violence?
What distinguishes guerrilla violence from other forms of political violence?
Which of the following best describes counter-insurgency strategies?
Which of the following best describes counter-insurgency strategies?
Which type of terrorism is defined by an individual adopting the aims of a terrorist group without formal ties to it?
Which type of terrorism is defined by an individual adopting the aims of a terrorist group without formal ties to it?
Which revolution is not classified as a significant global revolution in the 18th or 19th century?
Which revolution is not classified as a significant global revolution in the 18th or 19th century?
What is a characteristic feature of spontaneous violence in political contexts?
What is a characteristic feature of spontaneous violence in political contexts?
Which aspect of political violence is most directly associated with the use of physical force to achieve specific political goals?
Which aspect of political violence is most directly associated with the use of physical force to achieve specific political goals?
Which type of revolution led to the establishment of a communist state in the 20th century?
Which type of revolution led to the establishment of a communist state in the 20th century?
During which revolution did the overthrow of the monarchy play a critical role in political change?
During which revolution did the overthrow of the monarchy play a critical role in political change?
Which of the following tactics are commonly associated with guerrilla warfare?
Which of the following tactics are commonly associated with guerrilla warfare?
What challenge is commonly faced in counter-insurgency operations?
What challenge is commonly faced in counter-insurgency operations?
What distinguishes 'civil disobedience' from other forms of protest?
What distinguishes 'civil disobedience' from other forms of protest?
What is typically a primary goal of unconventional politics?
What is typically a primary goal of unconventional politics?
In the context of political conflict, which is often a direct cause for protests?
In the context of political conflict, which is often a direct cause for protests?
Transnational political protest typically involves what distinct characteristic?
Transnational political protest typically involves what distinct characteristic?
Which of the following groups is characterized as extreme left wing and anti-democratic?
Which of the following groups is characterized as extreme left wing and anti-democratic?
What role do 'opportunity structures' play in protests?
What role do 'opportunity structures' play in protests?
What common tactic is associated with protests aimed at creating social change?
What common tactic is associated with protests aimed at creating social change?
Which of the following categories best describes the main types of violence in unconventional politics?
Which of the following categories best describes the main types of violence in unconventional politics?
What is a notable feature of groups like the alt-right?
What is a notable feature of groups like the alt-right?
Which of the following protests specifically addresses racial justice?
Which of the following protests specifically addresses racial justice?
What is the primary objective of regime violence in the context of political violence?
What is the primary objective of regime violence in the context of political violence?
Which characteristic is NOT typically associated with guerrilla insurgency tactics?
Which characteristic is NOT typically associated with guerrilla insurgency tactics?
What is a key challenge in counter-insurgency strategies?
What is a key challenge in counter-insurgency strategies?
In what way does lone wolf terrorism differ from organized terrorism?
In what way does lone wolf terrorism differ from organized terrorism?
Which revolution is noted for its significant impact on the establishment of modern democratic ideals?
Which revolution is noted for its significant impact on the establishment of modern democratic ideals?
What distinguishes protracted guerrilla warfare from other military engagements?
What distinguishes protracted guerrilla warfare from other military engagements?
Which of the following is commonly classified as a type of terrorism that relies on psychological tactics of fear?
Which of the following is commonly classified as a type of terrorism that relies on psychological tactics of fear?
What is a fundamental aspect of spontaneous violence in political contexts?
What is a fundamental aspect of spontaneous violence in political contexts?
Which historical revolution is associated with Marxist-Leninist ideology?
Which historical revolution is associated with Marxist-Leninist ideology?
What involves combining repression and reform in actions against insurgencies?
What involves combining repression and reform in actions against insurgencies?
Which group represents the radical right wing populist movement that embraces violence?
Which group represents the radical right wing populist movement that embraces violence?
What purpose do 'opportunity structures' serve in political movements?
What purpose do 'opportunity structures' serve in political movements?
Which of the following is a tactic NOT associated with protests?
Which of the following is a tactic NOT associated with protests?
Which of the following best describes the nature of protests?
Which of the following best describes the nature of protests?
What element is NOT typically present in the definition of violence in a political context?
What element is NOT typically present in the definition of violence in a political context?
Which movement is primarily associated with civil disobedience?
Which movement is primarily associated with civil disobedience?
What describes the main opposition in political conflict?
What describes the main opposition in political conflict?
Which statement best characterizes transnational political protests?
Which statement best characterizes transnational political protests?
What is a common misconception about unconventional political movements?
What is a common misconception about unconventional political movements?
Which factor significantly enhances the influence of interest and advocacy groups?
Which factor significantly enhances the influence of interest and advocacy groups?
What is a potential drawback of interest and advocacy groups on public policy?
What is a potential drawback of interest and advocacy groups on public policy?
Which of the following is NOT considered a factor affecting the influence of interest groups?
Which of the following is NOT considered a factor affecting the influence of interest groups?
How does the perception of an interest group's impact affect its political influence?
How does the perception of an interest group's impact affect its political influence?
What is an outcome of effective leadership within an advocacy group?
What is an outcome of effective leadership within an advocacy group?
What is the primary goal of political parties in a democratic system?
What is the primary goal of political parties in a democratic system?
Which role is NOT typically associated with political parties?
Which role is NOT typically associated with political parties?
Which type of political party primarily relies on membership dues and maintains a strong organization outside the legislature?
Which type of political party primarily relies on membership dues and maintains a strong organization outside the legislature?
In which type of political party system are multiple parties able to compete for power without a clear majority winner?
In which type of political party system are multiple parties able to compete for power without a clear majority winner?
What is a distinguishing feature of ideological parties?
What is a distinguishing feature of ideological parties?
What strategy is primarily employed by interest groups to influence government action?
What strategy is primarily employed by interest groups to influence government action?
What describes the purpose of social movements in the political context?
What describes the purpose of social movements in the political context?
Which of the following best represents a cadre party's characteristics?
Which of the following best represents a cadre party's characteristics?
Which type of political party primarily aims for electoral success through the use of experts to market their ideals?
Which type of political party primarily aims for electoral success through the use of experts to market their ideals?
What characteristic distinguishes brokerage parties from other political parties?
What characteristic distinguishes brokerage parties from other political parties?
Which characteristic best distinguishes movement parties from traditional political parties?
Which characteristic best distinguishes movement parties from traditional political parties?
In a one-party dominant system, what is typically true about the opposition parties?
In a one-party dominant system, what is typically true about the opposition parties?
Which type of party is most likely to offer voters clear ideological choices and intensify political divisions?
Which type of party is most likely to offer voters clear ideological choices and intensify political divisions?
Which political system is characterized by two primary parties that contest elections, often leading to greater stability?
Which political system is characterized by two primary parties that contest elections, often leading to greater stability?
What is a defining trait of personalistic parties?
What is a defining trait of personalistic parties?
Which statement accurately describes the nature of programmatic/ideological parties?
Which statement accurately describes the nature of programmatic/ideological parties?
What challenge is commonly faced by governments in multi-party systems?
What challenge is commonly faced by governments in multi-party systems?
What motivates interest parties primarily as they transform from advocacy groups to political parties?
What motivates interest parties primarily as they transform from advocacy groups to political parties?
Which example best illustrates a one-party system?
Which example best illustrates a one-party system?
What is a primary concern about party representation in many political systems?
What is a primary concern about party representation in many political systems?
How do pragmatic/electoral-professional parties generally differ in their approach to policies compared to ideological parties?
How do pragmatic/electoral-professional parties generally differ in their approach to policies compared to ideological parties?
Which of the following statements is true about two-party plus systems?
Which of the following statements is true about two-party plus systems?
Which political party type would be considered least focused on electoral gains and more on adherence to ideological principles?
Which political party type would be considered least focused on electoral gains and more on adherence to ideological principles?
What is a key feature of cadre parties in their organizational structure?
What is a key feature of cadre parties in their organizational structure?
What factor may lead to more frequent changes of government in multi-party systems?
What factor may lead to more frequent changes of government in multi-party systems?
What common approach distinguishes brokerage parties in the electoral landscape?
What common approach distinguishes brokerage parties in the electoral landscape?
Which of the following accurately describes a key feature of one-party systems?
Which of the following accurately describes a key feature of one-party systems?
What distinguishes public interest groups from self-interest groups?
What distinguishes public interest groups from self-interest groups?
Which type of advocacy group is characterized by a formal structure and paid staff?
Which type of advocacy group is characterized by a formal structure and paid staff?
Which of the following best describes the role of lobby groups?
Which of the following best describes the role of lobby groups?
What factor has contributed to the increased influence of interest groups in recent years?
What factor has contributed to the increased influence of interest groups in recent years?
Which of the following is an example of a self-interest group?
Which of the following is an example of a self-interest group?
In what way do associational advocacy groups differ from institutional groups?
In what way do associational advocacy groups differ from institutional groups?
What is a characteristic of issue-oriented or spontaneous advocacy groups?
What is a characteristic of issue-oriented or spontaneous advocacy groups?
Which scenario best illustrates the influence of advocacy groups due to declining political party affiliation?
Which scenario best illustrates the influence of advocacy groups due to declining political party affiliation?
What is the main purpose of self-interest groups within the context of advocacy?
What is the main purpose of self-interest groups within the context of advocacy?
Which example best represents an institutional advocacy group?
Which example best represents an institutional advocacy group?
What is a primary function of political parties in a democratic system?
What is a primary function of political parties in a democratic system?
Which type of political party primarily relies on membership dues and features a strong organization outside the legislature?
Which type of political party primarily relies on membership dues and features a strong organization outside the legislature?
In a multi-party system, what is a likely outcome regarding political representation?
In a multi-party system, what is a likely outcome regarding political representation?
What role do interest groups primarily serve in the political system?
What role do interest groups primarily serve in the political system?
Which of the following distinguishes social movements from political parties?
Which of the following distinguishes social movements from political parties?
What is a characteristic of a pragmatic party in a political system?
What is a characteristic of a pragmatic party in a political system?
In terms of political party systems, what is a challenge associated with a one-party system?
In terms of political party systems, what is a challenge associated with a one-party system?
Which function of political parties involves assessing and proposing alternatives to existing policies?
Which function of political parties involves assessing and proposing alternatives to existing policies?
What is a significant factor affecting the influence of interest groups?
What is a significant factor affecting the influence of interest groups?
Which factor is critical for an interest group to successfully mobilize members?
Which factor is critical for an interest group to successfully mobilize members?
How does public perception of an issue impact an interest group's influence?
How does public perception of an issue impact an interest group's influence?
What can lead to disproportionate influence within advocacy groups?
What can lead to disproportionate influence within advocacy groups?
Which problem may arise from the activities of interest groups?
Which problem may arise from the activities of interest groups?
What distinguishes pragmatic/electoral-professional parties from programmatic/ideological parties?
What distinguishes pragmatic/electoral-professional parties from programmatic/ideological parties?
Which characteristic is most associated with brokerage parties?
Which characteristic is most associated with brokerage parties?
What is the primary goal of interest parties as distinct from interest groups?
What is the primary goal of interest parties as distinct from interest groups?
Which statement best describes the function of personalistic parties?
Which statement best describes the function of personalistic parties?
What is a significant trait of programmatic/ideological parties?
What is a significant trait of programmatic/ideological parties?
What often differentiates electoral-professional parties from cadre parties?
What often differentiates electoral-professional parties from cadre parties?
Which term best describes parties that seek to intensify political divisions rather than reconcile them?
Which term best describes parties that seek to intensify political divisions rather than reconcile them?
What is a common critique of pragmatic/electoral-professional parties?
What is a common critique of pragmatic/electoral-professional parties?
What characterizes the strategies of interest parties compared to traditional political parties?
What characterizes the strategies of interest parties compared to traditional political parties?
What is a defining characteristic of a movement party?
What is a defining characteristic of a movement party?
Which of the following is an example of a one-party system?
Which of the following is an example of a one-party system?
What is a characteristic of a two-party plus system?
What is a characteristic of a two-party plus system?
Which statement best explains the nature of multi-party systems?
Which statement best explains the nature of multi-party systems?
What factor complicates government formation in multi-party systems?
What factor complicates government formation in multi-party systems?
Which political party is an example of a one-party dominant system?
Which political party is an example of a one-party dominant system?
What is a major criticism of party representation in political systems?
What is a major criticism of party representation in political systems?
What does a one-party system guarantee regarding party existence?
What does a one-party system guarantee regarding party existence?
Which of the following challenges is commonly associated with multi-party systems?
Which of the following challenges is commonly associated with multi-party systems?
What characterizes a two-party system in political contexts?
What characterizes a two-party system in political contexts?
What is primarily the goal of public interest groups?
What is primarily the goal of public interest groups?
What distinguishes self-interest groups from other types of interest groups?
What distinguishes self-interest groups from other types of interest groups?
Which of the following is an example of an institutional interest group?
Which of the following is an example of an institutional interest group?
What factor has contributed to the increased influence of advocacy groups in recent years?
What factor has contributed to the increased influence of advocacy groups in recent years?
Which characteristic best describes associational interest groups?
Which characteristic best describes associational interest groups?
In what way are interest groups primarily distinct from political parties?
In what way are interest groups primarily distinct from political parties?
Which of the following is a notable reason for self-interest groups to influence local governments?
Which of the following is a notable reason for self-interest groups to influence local governments?
What describes the nature of issue-oriented or spontaneous advocacy groups?
What describes the nature of issue-oriented or spontaneous advocacy groups?
Which of the following exemplifies the decline in political party affiliation’s effect on advocacy groups?
Which of the following exemplifies the decline in political party affiliation’s effect on advocacy groups?
What best describes a characteristic of institutional interest groups?
What best describes a characteristic of institutional interest groups?
What is a key characteristic that differentiates totalitarianism from traditional authoritarianism?
What is a key characteristic that differentiates totalitarianism from traditional authoritarianism?
Which type of authoritarianism is exemplified by a government using legal means to undermine opposition?
Which type of authoritarianism is exemplified by a government using legal means to undermine opposition?
What is a common feature of traditional authoritarian regimes?
What is a common feature of traditional authoritarian regimes?
In what way does authoritarianism differ from autocracy?
In what way does authoritarianism differ from autocracy?
Which of the following types of authoritarianism specifically involves a theocratic governance structure?
Which of the following types of authoritarianism specifically involves a theocratic governance structure?
What is a characteristic of modern authoritarian regimes compared to traditional ones?
What is a characteristic of modern authoritarian regimes compared to traditional ones?
Which political system is often characterized by a significant role of military personnel in governance?
Which political system is often characterized by a significant role of military personnel in governance?
Which combination of features best describes hybrid authoritarian systems?
Which combination of features best describes hybrid authoritarian systems?
What is a significant downside of diminished political pluralism in authoritarian regimes?
What is a significant downside of diminished political pluralism in authoritarian regimes?
Which type of authoritarianism primarily relies on legal and constitutional frameworks to suppress opposition?
Which type of authoritarianism primarily relies on legal and constitutional frameworks to suppress opposition?
What was a major focus of South Korea's military regime from 1961 to 1988 in terms of economic planning?
What was a major focus of South Korea's military regime from 1961 to 1988 in terms of economic planning?
What characterizes traditional authoritarianism in relation to political participation?
What characterizes traditional authoritarianism in relation to political participation?
Which of the following accurately reflects the role of the military in traditional authoritarian regimes?
Which of the following accurately reflects the role of the military in traditional authoritarian regimes?
What is a common feature of transformational authoritarian regimes?
What is a common feature of transformational authoritarian regimes?
What often happens regarding political pluralism in transformational authoritarian regimes?
What often happens regarding political pluralism in transformational authoritarian regimes?
In what manner do authoritarian regimes often control the economy?
In what manner do authoritarian regimes often control the economy?
What ideological approach is typically associated with the official ideology of many transformational authoritarian regimes?
What ideological approach is typically associated with the official ideology of many transformational authoritarian regimes?
Which type of authoritarianism is characterized as potentially revolutionary and may include theocratic elements?
Which type of authoritarianism is characterized as potentially revolutionary and may include theocratic elements?
What is a significant practical limitation faced by transformational authoritarian regimes in achieving their transformative goals?
What is a significant practical limitation faced by transformational authoritarian regimes in achieving their transformative goals?
What is one of the main reasons authoritarian governments limit political mobilization?
What is one of the main reasons authoritarian governments limit political mobilization?
What management strategy did Qaddafi implement regarding oil extraction?
What management strategy did Qaddafi implement regarding oil extraction?
In transformational authoritarianism, what often facilitates ideological conformity?
In transformational authoritarianism, what often facilitates ideological conformity?
Which statement accurately describes a feature of totalitarianism?
Which statement accurately describes a feature of totalitarianism?
Which term best defines a government system led by an all-powerful leader with a 'cult of personality'?
Which term best defines a government system led by an all-powerful leader with a 'cult of personality'?
What is a characteristic of pseudo-democratic rule in totalitarian regimes?
What is a characteristic of pseudo-democratic rule in totalitarian regimes?
Which element is NOT typically associated with centralized economic planning in totalitarian systems?
Which element is NOT typically associated with centralized economic planning in totalitarian systems?
What was an action undertaken by totalitarian states towards traditional institutions?
What was an action undertaken by totalitarian states towards traditional institutions?
How does control of communications function in totalitarian regimes?
How does control of communications function in totalitarian regimes?
What is the role of police in transformational authoritarian systems?
What is the role of police in transformational authoritarian systems?
What common feature of totalitarianism is associated with a single party reaching into all aspects of society?
What common feature of totalitarianism is associated with a single party reaching into all aspects of society?
What was a significant aspect of South Korea's military regime from 1961 to 1988?
What was a significant aspect of South Korea's military regime from 1961 to 1988?
What characteristic of traditional authoritarianism involves the role of the military in governance?
What characteristic of traditional authoritarianism involves the role of the military in governance?
Under traditional authoritarianism, how is economic direction often described?
Under traditional authoritarianism, how is economic direction often described?
Which of the following best describes transformational authoritarianism?
Which of the following best describes transformational authoritarianism?
What is a common characteristic of leaders in transformational authoritarian regimes?
What is a common characteristic of leaders in transformational authoritarian regimes?
How do transformational authoritarian regimes typically restrict political pluralism?
How do transformational authoritarian regimes typically restrict political pluralism?
What ideological characteristic is commonly associated with transformational authoritarian regimes?
What ideological characteristic is commonly associated with transformational authoritarian regimes?
Which factor often leads to limited political mobilization in traditional authoritarian regimes?
Which factor often leads to limited political mobilization in traditional authoritarian regimes?
What consequence arises from the practical limitations faced by transformational authoritarian regimes?
What consequence arises from the practical limitations faced by transformational authoritarian regimes?
What role does the military often play in the governance of countries under traditional authoritarianism?
What role does the military often play in the governance of countries under traditional authoritarianism?
Which leadership style is often associated with totalitarian regimes, marked by a strong 'cult of personality'?
Which leadership style is often associated with totalitarian regimes, marked by a strong 'cult of personality'?
What feature is characteristic of pseudo-democratic rule in totalitarian systems?
What feature is characteristic of pseudo-democratic rule in totalitarian systems?
What type of control is essential to maintain power in a transformational authoritarian regime?
What type of control is essential to maintain power in a transformational authoritarian regime?
Which of the following describes the relationship between one-party states and traditional institutions in totalitarianism?
Which of the following describes the relationship between one-party states and traditional institutions in totalitarianism?
What factor significantly limits centralized economic planning in authoritarian regimes?
What factor significantly limits centralized economic planning in authoritarian regimes?
Which feature is common to totalitarian regimes regarding communication control?
Which feature is common to totalitarian regimes regarding communication control?
In the context of totalitarianism, what role do terroristic police forces play?
In the context of totalitarianism, what role do terroristic police forces play?
What is a primary characteristic of the official ideology in totalitarian regimes?
What is a primary characteristic of the official ideology in totalitarian regimes?
Which of the following describes the method of political recruitment in transformational authoritarianism?
Which of the following describes the method of political recruitment in transformational authoritarianism?
Who or what typically enforces police control in a totalitarian regime?
Who or what typically enforces police control in a totalitarian regime?
What best defines an autocratic system of governance?
What best defines an autocratic system of governance?
Which aspect distinguishes totalitarianism from authoritarianism?
Which aspect distinguishes totalitarianism from authoritarianism?
Which of the following is a characteristic of traditional authoritarianism?
Which of the following is a characteristic of traditional authoritarianism?
What term best describes governments that maintain power through corruption and electoral fraud?
What term best describes governments that maintain power through corruption and electoral fraud?
Which form of authoritarianism is commonly associated with religious principles?
Which form of authoritarianism is commonly associated with religious principles?
What is a key feature of the system of governance under military authoritarianism?
What is a key feature of the system of governance under military authoritarianism?
What generalization can be made about authoritarian regimes?
What generalization can be made about authoritarian regimes?
In traditional authoritarian regimes, how is political pluralism typically managed?
In traditional authoritarian regimes, how is political pluralism typically managed?
Which description accurately reflects the nature of authoritarianism?
Which description accurately reflects the nature of authoritarianism?
What can be inferred about the ideology of traditional authoritarian regimes?
What can be inferred about the ideology of traditional authoritarian regimes?
Which essential condition for democratic elections emphasizes the importance of citizens having the right to vote regardless of their background?
Which essential condition for democratic elections emphasizes the importance of citizens having the right to vote regardless of their background?
In what way do autocratic elections differ fundamentally from democratic elections?
In what way do autocratic elections differ fundamentally from democratic elections?
Which electoral system type is characterized by the winning party receiving more votes than any other candidate in a single-member district?
Which electoral system type is characterized by the winning party receiving more votes than any other candidate in a single-member district?
What is a common feature of plurality/majority electoral systems?
What is a common feature of plurality/majority electoral systems?
Which aspect is crucial for ensuring that candidates are accessible and able to compete in elections?
Which aspect is crucial for ensuring that candidates are accessible and able to compete in elections?
What defines the nature of voter support in democratic elections?
What defines the nature of voter support in democratic elections?
Which electoral system can include both proportional elements and single-member districts?
Which electoral system can include both proportional elements and single-member districts?
What characteristic is often present in elections characterized as 'free and fair'?
What characteristic is often present in elections characterized as 'free and fair'?
Which of the following is NOT considered an essential condition for democratic elections?
Which of the following is NOT considered an essential condition for democratic elections?
Which type of electoral system allows voters to express preferences for multiple candidates, potentially changing the order of preference based on later counts?
Which type of electoral system allows voters to express preferences for multiple candidates, potentially changing the order of preference based on later counts?
How can a political party receive more votes but win fewer seats in an election?
How can a political party receive more votes but win fewer seats in an election?
What is a potential effect of a winner-takes-all electoral system?
What is a potential effect of a winner-takes-all electoral system?
What issue arises from the underrepresentation of certain parties in electoral systems?
What issue arises from the underrepresentation of certain parties in electoral systems?
Which example illustrates a disparity between votes received and seats won in Canadian elections?
Which example illustrates a disparity between votes received and seats won in Canadian elections?
What is one consequence of landslide victories in elections under majority systems?
What is one consequence of landslide victories in elections under majority systems?
In the context of electoral systems, how might 'thinly spread' votes affect party representation?
In the context of electoral systems, how might 'thinly spread' votes affect party representation?
What does the term 'majority systems' encompass in the context of electoral systems?
What does the term 'majority systems' encompass in the context of electoral systems?
Which political phenomenon can be caused by a party receiving a greater share of votes yet fewer seats?
Which political phenomenon can be caused by a party receiving a greater share of votes yet fewer seats?
How might a concentration of votes influence a political party's success in an electoral system?
How might a concentration of votes influence a political party's success in an electoral system?
What was the percentage change in the number of seats for the party with the highest representation in the 1984 federal election compared to 1980?
What was the percentage change in the number of seats for the party with the highest representation in the 1984 federal election compared to 1980?
Which party experienced the largest percentage decrease in seats in the 1993 federal election compared to 1988?
Which party experienced the largest percentage decrease in seats in the 1993 federal election compared to 1988?
In a majority run-off system, what happens if no candidate achieves a majority in the first round?
In a majority run-off system, what happens if no candidate achieves a majority in the first round?
What distinguishes the majority-plurality system from a traditional run-off voting system?
What distinguishes the majority-plurality system from a traditional run-off voting system?
What was the overall percentage of seats for the party that had the largest share of votes in the 1993 election?
What was the overall percentage of seats for the party that had the largest share of votes in the 1993 election?
What is the total number of seats contested in the 1993 federal election?
What is the total number of seats contested in the 1993 federal election?
How does the alternative/preferential vote system operate when a candidate does not achieve a majority?
How does the alternative/preferential vote system operate when a candidate does not achieve a majority?
What significant change occurred in the distribution of seats for the party that went from 32 seats to 30 in the 1984 election?
What significant change occurred in the distribution of seats for the party that went from 32 seats to 30 in the 1984 election?
In the 1984 federal election, what was the percentage of the overall vote received by the party with 40 seats?
In the 1984 federal election, what was the percentage of the overall vote received by the party with 40 seats?
What is a characteristic feature of a majority run-off system as observed in specific countries?
What is a characteristic feature of a majority run-off system as observed in specific countries?
What is a significant advantage of using an Alternative/Preferential Ballot in electoral systems?
What is a significant advantage of using an Alternative/Preferential Ballot in electoral systems?
In a system of Proportional Representation, how are the candidates elected from a party's list determined?
In a system of Proportional Representation, how are the candidates elected from a party's list determined?
Which characteristic of proportional representation systems often leads to coalition governments?
Which characteristic of proportional representation systems often leads to coalition governments?
What is a common feature of the Single-Transferable Vote (STV) system?
What is a common feature of the Single-Transferable Vote (STV) system?
Which of the following describes the Mixed-Member Proportional (MMP) system?
Which of the following describes the Mixed-Member Proportional (MMP) system?
What is a unique element of the Highest Average method in proportional representation?
What is a unique element of the Highest Average method in proportional representation?
What can often result from the increased number of parties in proportional representation systems?
What can often result from the increased number of parties in proportional representation systems?
What is the principal feature of a corrective system in mixed electoral systems?
What is the principal feature of a corrective system in mixed electoral systems?
Which statement accurately reflects the function of a quota in the context of proportional representation systems?
Which statement accurately reflects the function of a quota in the context of proportional representation systems?
What fundamental principle does liberal/constitutional democracy emphasize regarding individual rights?
What fundamental principle does liberal/constitutional democracy emphasize regarding individual rights?
Which characteristic refers to the ability of individuals to engage in the political process?
Which characteristic refers to the ability of individuals to engage in the political process?
What concept is essential to prevent the majority from oppressing minority views in a democracy?
What concept is essential to prevent the majority from oppressing minority views in a democracy?
Which historical limitation did the right to vote initially impose in Canada according to the content?
Which historical limitation did the right to vote initially impose in Canada according to the content?
Which aspect of liberal democracy emphasizes the role of the people in governance?
Which aspect of liberal democracy emphasizes the role of the people in governance?
What is a significant potential issue that can arise in liberal democracies?
What is a significant potential issue that can arise in liberal democracies?
Which term best describes a political system that combines liberalism and democracy while adhering to constitutional principles?
Which term best describes a political system that combines liberalism and democracy while adhering to constitutional principles?
Which of the following rights is fundamental to the practice of political participation in a liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which of the following rights is fundamental to the practice of political participation in a liberal/constitutional democracy?
What is the primary concept that liberalism highlights within the framework of liberal/constitutional democracy?
What is the primary concept that liberalism highlights within the framework of liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which factor does political freedom ensure in the context of liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which factor does political freedom ensure in the context of liberal/constitutional democracy?
What is the primary function of liberalism within liberal/constitutional democracy?
What is the primary function of liberalism within liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which of the following best defines the problem of the 'tyranny of the majority' in a liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which of the following best defines the problem of the 'tyranny of the majority' in a liberal/constitutional democracy?
What does 'political freedom' primarily refer to in the context of liberal/constitutional democracy?
What does 'political freedom' primarily refer to in the context of liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which characteristic most directly ensures 'equality of political rights' in a liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which characteristic most directly ensures 'equality of political rights' in a liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which aspect of political participation is most relevant to the concept of liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which aspect of political participation is most relevant to the concept of liberal/constitutional democracy?
What does the inclusion of 'constitutional constraints' imply in a liberal/constitutional democracy?
What does the inclusion of 'constitutional constraints' imply in a liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which group historically faced initial restrictions in exercising political rights in liberal democracies?
Which group historically faced initial restrictions in exercising political rights in liberal democracies?
How does individualism contribute to the framework of liberal/constitutional democracy?
How does individualism contribute to the framework of liberal/constitutional democracy?
What has historically limited the right to vote in liberal democracies?
What has historically limited the right to vote in liberal democracies?
Which of the following statements reflects the principle of self-government in liberal democracies?
Which of the following statements reflects the principle of self-government in liberal democracies?
What is the primary characteristic of populism as defined in the content?
What is the primary characteristic of populism as defined in the content?
Which of the following political figures is associated with right-wing populism in the United States?
Which of the following political figures is associated with right-wing populism in the United States?
In Canada, which political party emerged as a response to the dissatisfaction of farmers post-World War I?
In Canada, which political party emerged as a response to the dissatisfaction of farmers post-World War I?
How does populism typically challenge the status quo regarding institutions?
How does populism typically challenge the status quo regarding institutions?
Which party in the United States was primarily formed in response to agrarian discontent during the 1890s?
Which party in the United States was primarily formed in response to agrarian discontent during the 1890s?
What ideological stance does Bernie Sanders represent within the populism spectrum?
What ideological stance does Bernie Sanders represent within the populism spectrum?
Which institution is most often challenged by populist movements due to their perceived elite status?
Which institution is most often challenged by populist movements due to their perceived elite status?
Which of the following best describes the ideological spectrum position of populism?
Which of the following best describes the ideological spectrum position of populism?
Which aspect of populism often leads to a rejection of outside influences?
Which aspect of populism often leads to a rejection of outside influences?
Which historical figure is most commonly associated with amplifying racist sentiments within the context of populism?
Which historical figure is most commonly associated with amplifying racist sentiments within the context of populism?
What is a defining characteristic of populism?
What is a defining characteristic of populism?
Which political figure is associated with right-wing populism in the United States?
Which political figure is associated with right-wing populism in the United States?
How did the United Farmers Association (UFA) contribute to populism in Canada?
How did the United Farmers Association (UFA) contribute to populism in Canada?
Which of the following best explains the ideological spectrum of populism?
Which of the following best explains the ideological spectrum of populism?
What was one potential criticism of Richard Nixon's involvement in populism?
What was one potential criticism of Richard Nixon's involvement in populism?
Which historical party in the United States emerged from the discontent of farmers during the 1890s?
Which historical party in the United States emerged from the discontent of farmers during the 1890s?
Which aspect did the Reform Party in Canada emphasize?
Which aspect did the Reform Party in Canada emphasize?
What was a significant stance of George Wallace as a populist leader?
What was a significant stance of George Wallace as a populist leader?
What strategy do populists typically use to challenge established elites?
What strategy do populists typically use to challenge established elites?
Which populist leader is identified with a leftist ideology opposing corporate greed?
Which populist leader is identified with a leftist ideology opposing corporate greed?
What primary focus differentiates anthropocentric ideologies from biocentric ideologies in environmentalism?
What primary focus differentiates anthropocentric ideologies from biocentric ideologies in environmentalism?
What is the primary goal of tradable pollution quotas in emissions trading?
What is the primary goal of tradable pollution quotas in emissions trading?
Which international agreement specifically focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions?
Which international agreement specifically focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions?
Which principle is inherent to deep ecology as opposed to shallow ecology?
Which principle is inherent to deep ecology as opposed to shallow ecology?
Deep ecology emphasizes the worth of which of the following?
Deep ecology emphasizes the worth of which of the following?
What significant movement influenced human welfare ecology as indicated by the content?
What significant movement influenced human welfare ecology as indicated by the content?
What does conservationism prioritize in its approach to environmental management?
What does conservationism prioritize in its approach to environmental management?
What is an example of ecological sabotage in the context of deep ecology?
What is an example of ecological sabotage in the context of deep ecology?
Green parties prioritize which of the following principles?
Green parties prioritize which of the following principles?
Which aspect of human welfare ecology is directly associated with Rachel Carson's concerns?
Which aspect of human welfare ecology is directly associated with Rachel Carson's concerns?
What inherent value does ecocentrism attribute to natural environments?
What inherent value does ecocentrism attribute to natural environments?
Which initiative is likely to involve community-based action for environmental advocacy?
Which initiative is likely to involve community-based action for environmental advocacy?
Which organization is best known for its global advocacy against environmental degradation?
Which organization is best known for its global advocacy against environmental degradation?
What does ecocentrism emphasize compared to technocentrism in environmental discussions?
What does ecocentrism emphasize compared to technocentrism in environmental discussions?
What is the relationship between deep ecology and animal rights as presented by Peter Singer?
What is the relationship between deep ecology and animal rights as presented by Peter Singer?
What kind of political expression is commonly linked to deep ecology?
What kind of political expression is commonly linked to deep ecology?
Which ecological philosophy argues that moral obligations to the environment arise from our responsibilities to future generations?
Which ecological philosophy argues that moral obligations to the environment arise from our responsibilities to future generations?
In proportional representation systems, which factor is likely to hinder the success of Green parties?
In proportional representation systems, which factor is likely to hinder the success of Green parties?
Which of the following is an action taken by advocacy groups like the Canadian Parks & Wilderness Society?
Which of the following is an action taken by advocacy groups like the Canadian Parks & Wilderness Society?
What era's significant legislation serves as a prime historical example of conservationism in practice?
What era's significant legislation serves as a prime historical example of conservationism in practice?
Which of the following pollutants is estimated by the World Health Organization to have caused the highest number of premature deaths worldwide?
Which of the following pollutants is estimated by the World Health Organization to have caused the highest number of premature deaths worldwide?
What concept describes the challenge of maintaining common spaces due to a lack of ownership and responsibility?
What concept describes the challenge of maintaining common spaces due to a lack of ownership and responsibility?
According to the content, what does sustainable development emphasize?
According to the content, what does sustainable development emphasize?
Which of the following is an implication of climate change as outlined in the content?
Which of the following is an implication of climate change as outlined in the content?
What problem does free market environmentalism aim to address?
What problem does free market environmentalism aim to address?
According to the content, which region experienced the greatest number of premature deaths due to air pollution?
According to the content, which region experienced the greatest number of premature deaths due to air pollution?
What does the shrinking of ice sheets and glacial retreat signify in relation to climate change?
What does the shrinking of ice sheets and glacial retreat signify in relation to climate change?
What aspect of governance does the UN Brundtland Commission Report emphasize?
What aspect of governance does the UN Brundtland Commission Report emphasize?
Which challenge is associated with the phenomenon of overpopulation according to the content?
Which challenge is associated with the phenomenon of overpopulation according to the content?
What is the primary concern relating to biodiversity as highlighted by the IUCN Red List?
What is the primary concern relating to biodiversity as highlighted by the IUCN Red List?
What significant ruling did the Supreme Court of Canada make in 1928 regarding women's status?
What significant ruling did the Supreme Court of Canada make in 1928 regarding women's status?
Which event marked the beginning of the second wave of feminism?
Which event marked the beginning of the second wave of feminism?
What is the percentage of women who hold executive positions compared to men moving from middle management?
What is the percentage of women who hold executive positions compared to men moving from middle management?
What notable achievement did Agnes Macphail accomplish in Canadian politics?
What notable achievement did Agnes Macphail accomplish in Canadian politics?
What did the term 'micropolitics of gender equality' refer to in the context of the third and fourth waves of feminism?
What did the term 'micropolitics of gender equality' refer to in the context of the third and fourth waves of feminism?
What percentage of STEM degree holders are women, according to the content provided?
What percentage of STEM degree holders are women, according to the content provided?
Which racial group of women earned a notably lower percentage of men's earnings in 2018?
Which racial group of women earned a notably lower percentage of men's earnings in 2018?
Which group of women did gain the right to vote in the federal election in Canada by 1940?
Which group of women did gain the right to vote in the federal election in Canada by 1940?
What is the educational attainment of women in law school as mentioned?
What is the educational attainment of women in law school as mentioned?
What was one of the focuses during the activism of the second wave of feminism?
What was one of the focuses during the activism of the second wave of feminism?
In which year did women obtain the right to vote federally in Canada?
In which year did women obtain the right to vote federally in Canada?
What percentage of judges are women according to the provided statistics?
What percentage of judges are women according to the provided statistics?
Which category encompasses a wide range of genders and sexual minorities?
Which category encompasses a wide range of genders and sexual minorities?
What was a major consequence of women entering the workforce during World War II?
What was a major consequence of women entering the workforce during World War II?
In what capacity do women of color occupy management positions?
In what capacity do women of color occupy management positions?
Which women's rights issue was not addressed during the first wave of feminism?
Which women's rights issue was not addressed during the first wave of feminism?
How much do women earn compared to men in terms of wage ratio as stated in the content?
How much do women earn compared to men in terms of wage ratio as stated in the content?
Who were the Famous Five?
Who were the Famous Five?
What percentage of practicing, licensed engineers are women?
What percentage of practicing, licensed engineers are women?
Which of the following statements reflects the relevance of feminism today?
Which of the following statements reflects the relevance of feminism today?
What is the primary aim of feminism as defined in the content?
What is the primary aim of feminism as defined in the content?
Which wave of feminism primarily focused on legal rights and women's suffrage?
Which wave of feminism primarily focused on legal rights and women's suffrage?
What is one of the major philosophical assertions of the First Wave of feminism?
What is one of the major philosophical assertions of the First Wave of feminism?
In the context of feminist theory, what does 'patriarchy' refer to?
In the context of feminist theory, what does 'patriarchy' refer to?
Which of the following feminist theories does not fit within the traditional ideological spectrum?
Which of the following feminist theories does not fit within the traditional ideological spectrum?
What does Lorraine Code suggest as part of the feminist theoretical project?
What does Lorraine Code suggest as part of the feminist theoretical project?
Which historical figure is associated with advocating for women's rights in the 18th century?
Which historical figure is associated with advocating for women's rights in the 18th century?
Which of the following best describes the Second Wave of feminism?
Which of the following best describes the Second Wave of feminism?
How does radical feminism differentiate itself within feminist thought?
How does radical feminism differentiate itself within feminist thought?
In which period is the Third Wave of feminism said to have occurred?
In which period is the Third Wave of feminism said to have occurred?
What is the primary focus of ethnic nationalism?
What is the primary focus of ethnic nationalism?
Which of the following best describes the concept of irredentism?
Which of the following best describes the concept of irredentism?
What outcome is a potential manifestation of tyranny of the majority?
What outcome is a potential manifestation of tyranny of the majority?
Which concept suggests an individual's loyalty to the nation-state over group interests?
Which concept suggests an individual's loyalty to the nation-state over group interests?
What aspect does civic nationalism primarily emphasize?
What aspect does civic nationalism primarily emphasize?
Which nation is associated with the practice of imperialism during the time between World Wars?
Which nation is associated with the practice of imperialism during the time between World Wars?
How can protectionism manifest in a nationalist context?
How can protectionism manifest in a nationalist context?
Which ideology is most strongly connected to the belief in self-determination?
Which ideology is most strongly connected to the belief in self-determination?
Which of the following would NOT typically be considered a manifestation of nationalism?
Which of the following would NOT typically be considered a manifestation of nationalism?
What is a possible result of limiting internet access in the context of nationalism?
What is a possible result of limiting internet access in the context of nationalism?
Which ideological belief is primarily associated with Nazism?
Which ideological belief is primarily associated with Nazism?
What is a defining characteristic of totalitarian regimes as described?
What is a defining characteristic of totalitarian regimes as described?
Which aspect is NOT typically associated with fascist regimes?
Which aspect is NOT typically associated with fascist regimes?
Which term describes the economic structure proposed by Mussolini?
Which term describes the economic structure proposed by Mussolini?
What does neo-fascism predominantly advocate for?
What does neo-fascism predominantly advocate for?
What purpose does the symbol of fasces serve in nationalist ideologies?
What purpose does the symbol of fasces serve in nationalist ideologies?
Which characteristic is common to both nationalism and totalitarian governance?
Which characteristic is common to both nationalism and totalitarian governance?
What is a common feature of the radical right/neo-fascism movements?
What is a common feature of the radical right/neo-fascism movements?
Which statement best captures Albert Einstein's view on nationalism?
Which statement best captures Albert Einstein's view on nationalism?
What role does the 'cult of personality' play in totalitarian regimes?
What role does the 'cult of personality' play in totalitarian regimes?
Which of the following statements best characterizes the rise of nationalism after WWII?
Which of the following statements best characterizes the rise of nationalism after WWII?
What ideological tension is associated with nationalism according to the provided content?
What ideological tension is associated with nationalism according to the provided content?
Which event is a significant marker of the emergence of smaller, homogenous states in Europe?
Which event is a significant marker of the emergence of smaller, homogenous states in Europe?
Which groups were involved in movements for nationhood during the 19th century?
Which groups were involved in movements for nationhood during the 19th century?
What was a significant aspect of national self-determination that emerged after the decline of the USSR?
What was a significant aspect of national self-determination that emerged after the decline of the USSR?
Which characteristic is associated with the reaction of nationalism towards imperialism?
Which characteristic is associated with the reaction of nationalism towards imperialism?
In what context did conservatism connect with nationalism?
In what context did conservatism connect with nationalism?
Which of the following outcomes can be attributed to the establishment of the United Nations post-WWII?
Which of the following outcomes can be attributed to the establishment of the United Nations post-WWII?
Marx's perspective on nationalism differed from that of other ideologies because he believed in which of the following?
Marx's perspective on nationalism differed from that of other ideologies because he believed in which of the following?
What resulted from the nationalist movements in Eastern Europe following the decline of the USSR?
What resulted from the nationalist movements in Eastern Europe following the decline of the USSR?
Flashcards
Unitary System
Unitary System
A system of government where a single, supreme central government holds all authority and power. Administrative divisions may exist, but they derive their power from the central government.
Federal System
Federal System
A political system where power is divided between a central government and regional governments (provinces, states). Regional governments have significant autonomy.
Central Government
Central Government
The highest level of government in a country, responsible for national policies and affairs. Examples include the Government of Canada or the Federal Republic of Germany.
Regional Government
Regional Government
Signup and view all the flashcards
Local Government
Local Government
Signup and view all the flashcards
Devolution
Devolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Continuum of Centralization
Continuum of Centralization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shared Sovereignty
Shared Sovereignty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sovereignty of Regional Governments
Sovereignty of Regional Governments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benefits of Federalism
Benefits of Federalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Federalism in Canada
Federalism in Canada
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explicit Powers (s.91)
Explicit Powers (s.91)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Provincial Powers (s. 92)
Provincial Powers (s. 92)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disallowance (s. 56)
Disallowance (s. 56)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reservation (s. 90)
Reservation (s. 90)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Declaratory Power (s. 92(10)(c))
Declaratory Power (s. 92(10)(c))
Signup and view all the flashcards
Residual Power
Residual Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peace, Order and Good Government (POGG)
Peace, Order and Good Government (POGG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Checks on Government Power
Checks on Government Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
Local Representation
Local Representation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disallowance
Disallowance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Declaratory Power
Declaratory Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
Federalism
Federalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Provincial Powers
Provincial Powers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explicit Powers
Explicit Powers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Constitutional provisions vs political practice
Constitutional provisions vs political practice
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unconventional Politics
Unconventional Politics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Opportunity Structures
Opportunity Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political Protest
Political Protest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Civil Disobedience
Civil Disobedience
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radical Right and Left
Radical Right and Left
Signup and view all the flashcards
Terrorism
Terrorism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insurgency
Insurgency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Guerilla Warfare
Guerilla Warfare
Signup and view all the flashcards
Civil Rights Movement
Civil Rights Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political Violence
Political Violence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regime Violence
Regime Violence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spontaneous Violence
Spontaneous Violence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Counter-Insurgency
Counter-Insurgency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Suicide Terrorism
Suicide Terrorism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lone Wolf Terrorism
Lone Wolf Terrorism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Revolutionary Process
Revolutionary Process
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radical Right and Left Groups
Radical Right and Left Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cadre Party
Cadre Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mass Party
Mass Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pragmatic Party
Pragmatic Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ideological Party
Ideological Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interest Party
Interest Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Personal Party
Personal Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Movement Party
Movement Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
One-Party System
One-Party System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single-Party System
Single-Party System
Signup and view all the flashcards
One-Party Dominant System
One-Party Dominant System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multi-Party System
Multi-Party System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parties for marginalized groups
Parties for marginalized groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
National Independence Parties
National Independence Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coalitions
Coalitions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Government Instability
Government Instability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interest/Advocacy Groups
Interest/Advocacy Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Self-Interest Groups
Self-Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Public Interest Groups
Public Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Associational Interest Groups
Associational Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-associational/Latent Groups
Non-associational/Latent Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Institutional Interest Groups
Institutional Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Issue-Oriented/Spontaneous/Anomic Groups
Issue-Oriented/Spontaneous/Anomic Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Parties
Populist Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Factors Affecting Influence of Interest Groups
Factors Affecting Influence of Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Social Movements
Social Movements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decline in Party Affiliation
Decline in Party Affiliation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Influence of Technology
Influence of Technology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benefits and Problems of Interest Groups
Benefits and Problems of Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Growing Influence of Interest Groups
Growing Influence of Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pragmatic/Electoral-Professional Party
Pragmatic/Electoral-Professional Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Programmatic/Ideological/Interest Party
Programmatic/Ideological/Interest Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interest Party (from interest group)
Interest Party (from interest group)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Personal/Personalistic Party
Personal/Personalistic Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pragmatic Party: Program Focus
Pragmatic Party: Program Focus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pragmatic Party: Electoral Focus
Pragmatic Party: Electoral Focus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brokerage Party
Brokerage Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Programmatic/Ideological/Interest Party: Impact on Voters
Programmatic/Ideological/Interest Party: Impact on Voters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Programmatic/Ideological/Interest Party: Effect on Society
Programmatic/Ideological/Interest Party: Effect on Society
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political Parties: Their Role
Political Parties: Their Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interest Groups: Aim & Actions
Interest Groups: Aim & Actions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Social Movements: Goal & Methods
Social Movements: Goal & Methods
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cadre Party: Definition
Cadre Party: Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mass Party: Definition
Mass Party: Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pragmatic Party: Definition
Pragmatic Party: Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ideological Party: Definition
Ideological Party: Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interest Party: Definition
Interest Party: Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-associational/Latent Interest Groups
Non-associational/Latent Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Factors Affecting Group Influence
Factors Affecting Group Influence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decline in Party Affiliation and Rise of Interest Groups
Decline in Party Affiliation and Rise of Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autocracy
Autocracy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Authoritarianism
Authoritarianism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Totalitarianism
Totalitarianism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hybrid Regime
Hybrid Regime
Signup and view all the flashcards
Traditional Authoritarianism
Traditional Authoritarianism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Personal Dictatorship
Personal Dictatorship
Signup and view all the flashcards
Military Dictatorship
Military Dictatorship
Signup and view all the flashcards
Religious/Theocratic Dictatorship
Religious/Theocratic Dictatorship
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diminished Political Pluralism
Diminished Political Pluralism
Signup and view all the flashcards
No Developed, Transformative Ideology
No Developed, Transformative Ideology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transformational Authoritarianism
Transformational Authoritarianism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Statism
Statism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Military involvement in Authoritarian regimes
Military involvement in Authoritarian regimes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ideological Conformity
Ideological Conformity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Military as a tool of intimidation
Military as a tool of intimidation
Signup and view all the flashcards
All-powerful leader
All-powerful leader
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudo-democratic rule
Pseudo-democratic rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Control of communications
Control of communications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Terroristic police control
Terroristic police control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central control and direction of the economy
Central control and direction of the economy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bribery and corruption
Bribery and corruption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Controlled political mobilization
Controlled political mobilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Restricted Political Pluralism
Restricted Political Pluralism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Official Ideology
Official Ideology
Signup and view all the flashcards
State Repression
State Repression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Armed Insurgency
Armed Insurgency
Signup and view all the flashcards
First Past the Post (FPP)
First Past the Post (FPP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Majority System
Majority System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Less than Majority
Less than Majority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Winner-Take-All
Winner-Take-All
Signup and view all the flashcards
Overrepresentation
Overrepresentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regional Concentration
Regional Concentration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Underrepresentation of Minorities
Underrepresentation of Minorities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Majority Systems: Problems
Majority Systems: Problems
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single-Member District
Single-Member District
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proportional Representation
Proportional Representation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Majority Run-off System
Majority Run-off System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Majority-Plurality System
Majority-Plurality System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alternative/Preferential Vote System
Alternative/Preferential Vote System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disproportionate Shift in Seats
Disproportionate Shift in Seats
Signup and view all the flashcards
Landslide Shift in Seats
Landslide Shift in Seats
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proportional Seats
Proportional Seats
Signup and view all the flashcards
Democratic Elections
Democratic Elections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autocratic Elections
Autocratic Elections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mixed Electoral Systems
Mixed Electoral Systems
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elections and Legitimacy
Elections and Legitimacy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elections and Peaceful Transfers of Power
Elections and Peaceful Transfers of Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elections and Consent of the Governed
Elections and Consent of the Governed
Signup and view all the flashcards
Voter Considerations in Elections
Voter Considerations in Elections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Essential Conditions for Democratic Elections
Essential Conditions for Democratic Elections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alternative/Preferential Ballot
Alternative/Preferential Ballot
Signup and view all the flashcards
List System
List System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quota/Largest Remainder
Quota/Largest Remainder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Highest Average
Highest Average
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single-Transferable Vote (STV)
Single-Transferable Vote (STV)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mixed System
Mixed System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mixed-member Proportional (MMP)
Mixed-member Proportional (MMP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superposition System
Superposition System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Liberal/Constitutional Democracy
Liberal/Constitutional Democracy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Equality of Political Rights
Equality of Political Rights
Signup and view all the flashcards
Majority Rule
Majority Rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political Participation
Political Participation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political Freedom
Political Freedom
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tyranny of the Majority
Tyranny of the Majority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conformism
Conformism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Not Rule of the Best
Not Rule of the Best
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism
Populism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Strategy
Populist Strategy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Movements
Populist Movements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Strategy: Direct Democracy
Populist Strategy: Direct Democracy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Leaders
Populist Leaders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Targets
Populist Targets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism on the Spectrum
Populism on the Spectrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trump's Populism
Trump's Populism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Canadian Populism
Canadian Populism
Signup and view all the flashcards
European Populism
European Populism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism and Direct Democracy
Populism and Direct Democracy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism's Dual Nature
Populism's Dual Nature
Signup and view all the flashcards
Environmentalism
Environmentalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biocentrism
Biocentrism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conservationism
Conservationism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human Welfare Ecology
Human Welfare Ecology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Ecology
Deep Ecology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Technocentrism
Technocentrism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ecocentrism
Ecocentrism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intergenerational Responsibility
Intergenerational Responsibility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anthropocentrism
Anthropocentrism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political Expression of Environmentalism
Political Expression of Environmentalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tradable Pollution Quotas (Cap and Trade)
Tradable Pollution Quotas (Cap and Trade)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Government Regulation of Pollution
Government Regulation of Pollution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ecological Sabotage ('Ecotage')
Ecological Sabotage ('Ecotage')
Signup and view all the flashcards
Green Parties
Green Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Greenpeace
Greenpeace
Signup and view all the flashcards
Greta Thunberg
Greta Thunberg
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tragedy of the Commons
Tragedy of the Commons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sustainable Development
Sustainable Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
WHO Air Quality Report 2016
WHO Air Quality Report 2016
Signup and view all the flashcards
Climate Change
Climate Change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Free Market Environmentalism
Free Market Environmentalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
IUCN Red List of Threatened Species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biodiversity Loss
Biodiversity Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Market-Based Environmental Policies
Market-Based Environmental Policies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sovereignty
Sovereignty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Environmental Regulation
Environmental Regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feminism
Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feminism as a theoretical project
Feminism as a theoretical project
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patriarchy
Patriarchy
Signup and view all the flashcards
First Wave Feminism
First Wave Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Second Wave Feminism
Second Wave Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Third Wave Feminism
Third Wave Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fourth Wave Feminism
Fourth Wave Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intersectionality
Intersectionality
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radical Feminism
Radical Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ecofeminism
Ecofeminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wage Gap
Wage Gap
Signup and view all the flashcards
STEM Gap
STEM Gap
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interest Groups
Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gender fluidity
Gender fluidity
Signup and view all the flashcards
The Persons Case
The Persons Case
Signup and view all the flashcards
Agnes Macphail
Agnes Macphail
Signup and view all the flashcards
Women's Role in WWII
Women's Role in WWII
Signup and view all the flashcards
Third and Fourth Wave Feminism
Third and Fourth Wave Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Women's Suffrage
Women's Suffrage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right to Run for Office
Right to Run for Office
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right to Serve on Juries
Right to Serve on Juries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right to Own Property
Right to Own Property
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nationalism
Nationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Civic Nationalism
Civic Nationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ethnic Nationalism
Ethnic Nationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Self-Determination
Self-Determination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protectionism
Protectionism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Imperialism
Imperialism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Irredentism
Irredentism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Minority Oppression
Minority Oppression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decolonization
Decolonization
Signup and view all the flashcards
National Self-Determination
National Self-Determination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Communism
Communism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Racist Nationalism
Racist Nationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neo-Fascism
Neo-Fascism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Multiple Governments: Unitary and Federal Systems
- Unitary governments have a single, central governing body controlling all aspects of the country. Sovereignty is held by the central government, and any power delegated to regional areas is done by the central government. Regional governments act under the authority of the central government.
- Federal systems divide sovereignty between a central government and regional governments (e.g., states or provinces). Regional governments often have considerable autonomy and independent powers.
Definitions
- The continuum of centralization refers to a spectrum of government structures ranging from highly centralized (unitary) to highly decentralized (confederate). Federalism falls in the middle.
- Unitary states are governed by a single, supreme governing authority with all power concentrated at the central level.
- Federal states have power divided between a central government and constituent regional governments, with clear boundaries of responsibilities.
Levels of Government
- Central Government (National): The highest level of government, for example, the Canadian federal government.
- Regional Government: In federal systems, regional governments administer areas within the larger territory, for example, the Alberta provincial government. Provincial governments have powers delegated by the federal government. Provincial powers are usually outlined in specific sections of the constitution.
- Local Government (Municipal): The lowest level of government, such as individual cities or towns, for example, the city of Calgary. Local governments also operate under the authority of the provincial and federal governments.
Unitary System of Government
- A single, sovereign government controlling all aspects of the country.
- The central government holds supreme power.
- Power can be devolved (transferred) to lower administrative units, but the central government retains ultimate authority. This is done via statutes.
Federal System of Government
- Sovereignty is divided between a central government and regional governments (e.g., states, provinces).
- Regional governments have some self-governance over local affairs.
- The regional governments' sovereignty is often enshrined in a constitution, and explicitly outlines authorities.
- Often viewed as a union of partially self-governing regions under a central government.
Continuum of Centralization
- The spectrum depicting the centralization of power in different systems of government.
- Systems range from decentralized (e.g., confederation) to centralized (e.g., unitary).
- Federalism is in the middle of the spectrum, with shared but not equal power amongst central and regional governments.
Unitary vs. Federal Countries
- A world map visualizes the distribution of unitary and federal states geographically. Countries of various systems are identified on the map, visually illustrating their type of distributed power.
Why Federalism?
- Geography plays a role in shaping the need for federalism. A large country necessitates the distribution of power to best administer the entire territory, for example Canada's vast land mass.
- Sharing governmental responsibilities is a primary consideration of federal design.
- Cultural, linguistic, and religious divisions can influence the need for local representation and policies.
- Checks on government power promotes stability through balance of power amongst levels of government.
- Separation of powers, both vertically and horizontally, is essential for limiting potential abuses of power.
Explicit Powers (Canada)
- Specific federal powers are laid out in Sections 91 and 92 of the Constitution Act, 1867 (Canada). These sections outline the specific powers delegated and retained by federal and provincial governments. Examples for federal powers include trade, taxation, defence, and natural resources.
- Provincial powers are outlined in section 92. These sections provide a framework for the distribution of power; they outline explicit powers relating to local administration.
- Specific examples of powers, such as trade and commerce, taxation, and the administration of justice, are outlined, and explicit powers for banks, Indians, and their lands are outlined in specified sections. Specific details concerning explicit powers pertaining to health and welfare, natural resources, property and civil rights, and related topics, are included.
Complexities of Federalism
- Constitutional provisions versus political practice.
- Canada's initial design aimed for federal concentration in power, however, political practice often deviates from the constitution and the reality is often more nuanced, and power has often been redistributed amongst levels of government. Mechanisms such as the disallowance and reservation powers, and the declaratory power from section 92(10)c, are further complexities.
- National concern doctrine can be relevant in modern discussions (e.g., carbon tax).
- The US federal system aimed for a balance of power between states and the federal government.
- Examples of complexities include difficulties negotiating and implementing agreements like the Meech Lake Accord (1987), Charlottetown Accord (1992), and Quebec Referendum (1995).
Further Complexities of Federalism
- Bicameral legislatures (e.g., Canadian Senate, US Congress) help limit potential abuses of power and balance representation from different regions (e.g., the Canadian Senate). Representation within bicameral legislatures is typically based on regional representation and may vary based on the country's structure.
- Executive federalism seeks to leverage collective power of regional governments to work together on common goals, and this is evident in intergovernmental cooperation. Cooperation can occur at various levels (provincial, regional, and national).
- Asymmetrical federalism describes situations where some regional governments have more sovereignty than others. There are variations in regional autonomy across different areas within federal systems.
- Canada has experienced several historical events that impacted its federal structure, shaping the balance of power. These include the Meech Lake Accord (1987), Charlottetown Accord (1992), Quebec Referendum (1995), the Alberta Fair Deal Panel Act, and the Alberta Sovereignty Act, reflecting challenges to federal balance of power. These Acts illustrate the complicated interplay of power within a federal system.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the fundamental differences between unitary and federal systems of government. This quiz will help reinforce your understanding of governance structures, including the implications of centralized versus decentralized authority. Test your knowledge on how these systems impact the autonomy of regional governments.