Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the key characteristic of a unitary system of government?
What is the key characteristic of a unitary system of government?
- Constitutional provisions guarantee regional autonomy.
- A single, sovereign government controls all aspects. (correct)
- Multiple governments coexist with equal sovereignty.
- Sovereignty is divided among different levels of government.
In a federal system, how is sovereignty structured?
In a federal system, how is sovereignty structured?
- Sovereignty is absolute in the local government.
- Sovereignty is shared between the central and regional governments. (correct)
- Sovereignty is centralized in the regional governments.
- Sovereignty exists only at the national level.
Which of the following best represents the term 'devolution' in governance?
Which of the following best represents the term 'devolution' in governance?
- The establishment of new separate states from a central government.
- The elimination of all governmental tiers except the central government.
- The complete transfer of sovereignty to local governments.
- The process where power is transferred from a central government to regional governments. (correct)
What does the 'continuum of centralization' illustrate?
What does the 'continuum of centralization' illustrate?
What role do regional governments play in a federal system?
What role do regional governments play in a federal system?
Which of the following types of government does NOT have constituent governments?
Which of the following types of government does NOT have constituent governments?
Which type of government maintains a central government with regard to regional autonomy?
Which type of government maintains a central government with regard to regional autonomy?
Which of the following accurately describes a confederation?
Which of the following accurately describes a confederation?
Which of the following is NOT a feature of federalism?
Which of the following is NOT a feature of federalism?
What is typically the primary reason for implementing a federal system of government?
What is typically the primary reason for implementing a federal system of government?
In terms of checks on government power, which entity coordinates local representation?
In terms of checks on government power, which entity coordinates local representation?
What does the abbreviation P.O.G.G. stand for in the context of Canadian federalism?
What does the abbreviation P.O.G.G. stand for in the context of Canadian federalism?
Which of the following powers are not explicitly mentioned under federal powers?
Which of the following powers are not explicitly mentioned under federal powers?
According to James Madison in Federalist 10, what is a primary concern of factions in government?
According to James Madison in Federalist 10, what is a primary concern of factions in government?
What is the significance of James Madison's Federalist 10 in relation to government responsibility?
What is the significance of James Madison's Federalist 10 in relation to government responsibility?
What does the 'Peace, Order and Good Government' (P.O.G.G) principle imply in Canadian federalism?
What does the 'Peace, Order and Good Government' (P.O.G.G) principle imply in Canadian federalism?
Which statement accurately reflects the nature of checks on government power in Canadian federalism?
Which statement accurately reflects the nature of checks on government power in Canadian federalism?
What primary concern arises from the complexities of federalism as mentioned in the content?
What primary concern arises from the complexities of federalism as mentioned in the content?
What distinguishes a federal system from a unitary system regarding sovereignty?
What distinguishes a federal system from a unitary system regarding sovereignty?
Which option best describes the term 'devolution' in the context of government structure?
Which option best describes the term 'devolution' in the context of government structure?
In a unitary government system, how are the powers of regional governments characterized?
In a unitary government system, how are the powers of regional governments characterized?
What is the role of regional governments in a federal system according to constitutional law?
What is the role of regional governments in a federal system according to constitutional law?
During which phase does the concept of 'integration' occur within the continuum of centralization?
During which phase does the concept of 'integration' occur within the continuum of centralization?
What is a common characteristic of both unitary and federal systems concerning government structure?
What is a common characteristic of both unitary and federal systems concerning government structure?
Which statement accurately describes the nature of sovereignty in a confederation?
Which statement accurately describes the nature of sovereignty in a confederation?
What is primarily illustrated by the 'continuum of centralization' in terms of governance?
What is primarily illustrated by the 'continuum of centralization' in terms of governance?
What is a significant complexity associated with federalism?
What is a significant complexity associated with federalism?
What characterizes the political conflict mentioned in the content?
What characterizes the political conflict mentioned in the content?
Which of the following is an example of civil disobedience?
Which of the following is an example of civil disobedience?
Which group is described as an extreme left wing and anti-democratic organization?
Which group is described as an extreme left wing and anti-democratic organization?
What are 'opportunity structures' in the context of unconventional politics?
What are 'opportunity structures' in the context of unconventional politics?
What term refers to the violent strategies used by groups seeking political change?
What term refers to the violent strategies used by groups seeking political change?
Which of the following is NOT mentioned as a form of protest?
Which of the following is NOT mentioned as a form of protest?
Which statement best reflects the role of marginalized actors in protests?
Which statement best reflects the role of marginalized actors in protests?
How do radical right wing populists present themselves according to the content?
How do radical right wing populists present themselves according to the content?
Which term is associated with a form of political protest that operates beyond formal political channels?
Which term is associated with a form of political protest that operates beyond formal political channels?
What does the term 'transnational political protest' refer to?
What does the term 'transnational political protest' refer to?
What best describes the approach of counter-insurgency as outlined in the content?
What best describes the approach of counter-insurgency as outlined in the content?
Which characteristic is most associated with guerrilla warfare?
Which characteristic is most associated with guerrilla warfare?
In the context of political violence, how is 'terrorism' primarily categorized?
In the context of political violence, how is 'terrorism' primarily categorized?
What is a defining feature of spontaneous political violence?
What is a defining feature of spontaneous political violence?
Which type of terrorism is characterized by individuals adopting the goals of a group without formal affiliation?
Which type of terrorism is characterized by individuals adopting the goals of a group without formal affiliation?
What challenge is often faced by counter-insurgency operations?
What challenge is often faced by counter-insurgency operations?
Which of the following aspects is least likely to be a goal of regime/government violence?
Which of the following aspects is least likely to be a goal of regime/government violence?
What is a hallmark of protracted political violence?
What is a hallmark of protracted political violence?
Which category of interest/advocacy groups is primarily characterized by formal organizations with established memberships and aims to advance long-term interests?
Which category of interest/advocacy groups is primarily characterized by formal organizations with established memberships and aims to advance long-term interests?
What is the primary function of political parties in a democratic context?
What is the primary function of political parties in a democratic context?
Which type of political party is characterized by drawing support from regular dues-paying members?
Which type of political party is characterized by drawing support from regular dues-paying members?
What is a significant factor contributing to the increased influence of interest/advocacy groups?
What is a significant factor contributing to the increased influence of interest/advocacy groups?
Which of the following is NOT a role of political parties in government?
Which of the following is NOT a role of political parties in government?
Which type of interest group primarily advocates for specific interests of its members rather than for the broader community?
Which type of interest group primarily advocates for specific interests of its members rather than for the broader community?
What distinguishes a mass political party from other types of parties?
What distinguishes a mass political party from other types of parties?
How do institutional interest groups primarily distinguish themselves?
How do institutional interest groups primarily distinguish themselves?
Which of the following best defines an issue-oriented advocacy group?
Which of the following best defines an issue-oriented advocacy group?
Which political party system includes more than two dominant parties competing for power?
Which political party system includes more than two dominant parties competing for power?
In what way do interest groups differ from political parties?
In what way do interest groups differ from political parties?
What is a notable distinction between interest/advocacy groups and political parties?
What is a notable distinction between interest/advocacy groups and political parties?
What is a primary characteristic of cadre parties?
What is a primary characteristic of cadre parties?
Which type of political party is characterized by a flexible approach to principles, often borrowing proposals from others?
Which type of political party is characterized by a flexible approach to principles, often borrowing proposals from others?
Programmatic parties primarily focus on what aspect of their political agenda?
Programmatic parties primarily focus on what aspect of their political agenda?
What do interest parties primarily seek to achieve?
What do interest parties primarily seek to achieve?
Which of the following best describes personalistic parties?
Which of the following best describes personalistic parties?
In the context of brokerage parties, what is a significant strategy they employ?
In the context of brokerage parties, what is a significant strategy they employ?
What is one limitation often encountered by programmatic parties?
What is one limitation often encountered by programmatic parties?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of electoral-professional parties?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of electoral-professional parties?
Which of the following accurately describes a one-party dominant system in a political context?
Which of the following accurately describes a one-party dominant system in a political context?
What is a primary characteristic of movement parties as described?
What is a primary characteristic of movement parties as described?
Which of the following statements about multi-party systems is true?
Which of the following statements about multi-party systems is true?
What key feature distinguishes a two-party plus system from a standard two-party system?
What key feature distinguishes a two-party plus system from a standard two-party system?
Which of the following best describes the challenges of coalition governance in multi-party systems?
Which of the following best describes the challenges of coalition governance in multi-party systems?
In which type of political party system does a single party exist legally without permission for others?
In which type of political party system does a single party exist legally without permission for others?
What defines party representation in relation to member demographics?
What defines party representation in relation to member demographics?
Which of the following scenarios is an example of a two-party system?
Which of the following scenarios is an example of a two-party system?
What aspect of traditional authoritarianism contributes to limited political mobilization?
What aspect of traditional authoritarianism contributes to limited political mobilization?
In transformational authoritarianism, political pluralism is primarily restricted due to which factor?
In transformational authoritarianism, political pluralism is primarily restricted due to which factor?
Which of the following best describes the role of the military in traditional authoritarian regimes?
Which of the following best describes the role of the military in traditional authoritarian regimes?
Which of the following is NOT typically associated with the official ideology of transformational authoritarianism?
Which of the following is NOT typically associated with the official ideology of transformational authoritarianism?
What is a common characteristic of the economic strategy employed in traditional authoritarian states?
What is a common characteristic of the economic strategy employed in traditional authoritarian states?
What is often a major reason for authoritarian regimes to revert to civilian governance?
What is often a major reason for authoritarian regimes to revert to civilian governance?
Which term best describes the characteristic of centralized economic planning in transformational authoritarianism?
Which term best describes the characteristic of centralized economic planning in transformational authoritarianism?
What is a common feature of a totalitarian regime as described in the content?
What is a common feature of a totalitarian regime as described in the content?
Which aspect differentiates transformational authoritarianism from totalitarianism?
Which aspect differentiates transformational authoritarianism from totalitarianism?
In the context of totalitarianism, what does 'pseudo-democratic rule' imply?
In the context of totalitarianism, what does 'pseudo-democratic rule' imply?
Which feature is crucial to understanding the concept of a one-party state in totalitarian regimes?
Which feature is crucial to understanding the concept of a one-party state in totalitarian regimes?
What role does police control play in transformational authoritarian regimes?
What role does police control play in transformational authoritarian regimes?
Which characteristic most accurately describes 'cult of personality' in totalitarian systems?
Which characteristic most accurately describes 'cult of personality' in totalitarian systems?
Which of the following statements best captures the economic control within totalitarian regimes?
Which of the following statements best captures the economic control within totalitarian regimes?
How does the role of foreign workers in Qaddafi's regime contrast with typical approaches in fully authoritarian systems?
How does the role of foreign workers in Qaddafi's regime contrast with typical approaches in fully authoritarian systems?
Which of the following best describes the function of terroristic police control in totalitarian regimes?
Which of the following best describes the function of terroristic police control in totalitarian regimes?
What impact does controlled communication have in a totalitarian state?
What impact does controlled communication have in a totalitarian state?
What distinguishes totalitarianism from authoritarianism?
What distinguishes totalitarianism from authoritarianism?
Which type of authoritarianism is typically associated with military influence?
Which type of authoritarianism is typically associated with military influence?
What method describes government power maintained through dubious electoral practices?
What method describes government power maintained through dubious electoral practices?
What is a common characteristic of traditional authoritarianism?
What is a common characteristic of traditional authoritarianism?
How does hybrid authoritarianism typically maintain its power?
How does hybrid authoritarianism typically maintain its power?
What is the role of the military in traditional authoritarian systems?
What is the role of the military in traditional authoritarian systems?
What aspect of totalitarianism is most distinct from other forms of governance?
What aspect of totalitarianism is most distinct from other forms of governance?
Which feature is least likely to be present in authoritarian regimes?
Which feature is least likely to be present in authoritarian regimes?
What is a significant characteristic of right-wing authoritarianism?
What is a significant characteristic of right-wing authoritarianism?
What typically occurs under traditional authoritarian regimes regarding political opposition?
What typically occurs under traditional authoritarian regimes regarding political opposition?
What is a key benefit of using an alternative/preferential ballot system?
What is a key benefit of using an alternative/preferential ballot system?
Which statement accurately describes the impact of proportional representation on political parties?
Which statement accurately describes the impact of proportional representation on political parties?
How does the single-transferable vote (STV) system determine election winners?
How does the single-transferable vote (STV) system determine election winners?
In a mixed-member proportional (MMP) system, what is the purpose of the second ballot?
In a mixed-member proportional (MMP) system, what is the purpose of the second ballot?
What is a characteristic feature of the highest average method in proportional representation systems?
What is a characteristic feature of the highest average method in proportional representation systems?
Which feature is essential for elections to be considered democratic?
Which feature is essential for elections to be considered democratic?
What distinguishes a mixed electoral system from purely plurality/majority or proportional systems?
What distinguishes a mixed electoral system from purely plurality/majority or proportional systems?
In autocratic elections, what is the primary role of voters?
In autocratic elections, what is the primary role of voters?
Which of these is NOT a component of universal adult suffrage?
Which of these is NOT a component of universal adult suffrage?
Which electoral system allows voters to rank candidates in order of preference?
Which electoral system allows voters to rank candidates in order of preference?
What is a common challenge faced by voters in newly established democracies?
What is a common challenge faced by voters in newly established democracies?
Which condition does NOT promote accountability in democratic elections?
Which condition does NOT promote accountability in democratic elections?
Which electoral system is associated with receiving more votes than any other candidate in a constituency?
Which electoral system is associated with receiving more votes than any other candidate in a constituency?
Which electoral system was used in the majority run-off system?
Which electoral system was used in the majority run-off system?
How does the alternative/preferential vote system operate during elections?
How does the alternative/preferential vote system operate during elections?
What characterizes the majority-plurality system in elections?
What characterizes the majority-plurality system in elections?
What is a potential effect of majority electoral systems on the relationship between votes and seats?
What is a potential effect of majority electoral systems on the relationship between votes and seats?
What leads to the persistent underrepresentation of specific parties in a majority electoral system?
What leads to the persistent underrepresentation of specific parties in a majority electoral system?
What phenomenon does overrepresentation in election outcomes often indicate?
What phenomenon does overrepresentation in election outcomes often indicate?
What was the outcome for the Green Party in relation to their percentage of votes and seats?
What was the outcome for the Green Party in relation to their percentage of votes and seats?
What problem might arise due to the winner-take-all feature of electoral systems?
What problem might arise due to the winner-take-all feature of electoral systems?
What impact does a landslide victory have on political representation?
What impact does a landslide victory have on political representation?
What is a significant characteristic of the representation of minority parties in a majority electoral system?
What is a significant characteristic of the representation of minority parties in a majority electoral system?
What is a characteristic feature of totalitarian regimes?
What is a characteristic feature of totalitarian regimes?
Which statement accurately describes the police control in authoritarian regimes?
Which statement accurately describes the police control in authoritarian regimes?
What does the term 'pseudo-democratic rule' often refer to in totalitarian systems?
What does the term 'pseudo-democratic rule' often refer to in totalitarian systems?
Which of the following best captures the role of the leader in totalitarian regimes?
Which of the following best captures the role of the leader in totalitarian regimes?
What is the approach to economic planning in authoritarian states?
What is the approach to economic planning in authoritarian states?
What economic strategy was commonly used by South Korea's military regime between 1961 and 1988?
What economic strategy was commonly used by South Korea's military regime between 1961 and 1988?
Which of the following describes the nature of political mobilization in traditional authoritarian regimes?
Which of the following describes the nature of political mobilization in traditional authoritarian regimes?
What role does the military typically play in traditional authoritarian regimes?
What role does the military typically play in traditional authoritarian regimes?
What is a characteristic feature of transformational authoritarian regimes?
What is a characteristic feature of transformational authoritarian regimes?
What is the common element of official ideologies observed in transformational authoritarian governments?
What is the common element of official ideologies observed in transformational authoritarian governments?
Which type of political structure is characterized by restricted political pluralism?
Which type of political structure is characterized by restricted political pluralism?
What is a significant challenge faced by transformational authoritarian regimes in pursuing their goals?
What is a significant challenge faced by transformational authoritarian regimes in pursuing their goals?
Which of the following is NOT a tactic used by transformational authoritarian regimes?
Which of the following is NOT a tactic used by transformational authoritarian regimes?
What is the main characteristic of authoritarianism?
What is the main characteristic of authoritarianism?
Which of the following is a feature of traditional authoritarianism?
Which of the following is a feature of traditional authoritarianism?
Which term refers to governments that maintain their power through electoral fraud and legal tactics?
Which term refers to governments that maintain their power through electoral fraud and legal tactics?
What distinguishes totalitarianism from other forms of government?
What distinguishes totalitarianism from other forms of government?
How does traditional authoritarianism typically view political pluralism?
How does traditional authoritarianism typically view political pluralism?
Which of the following is NOT a variety of authoritarianism?
Which of the following is NOT a variety of authoritarianism?
What best describes the underlying ideology in traditional authoritarianism?
What best describes the underlying ideology in traditional authoritarianism?
Which form of authoritarianism is known for its religious basis?
Which form of authoritarianism is known for its religious basis?
Which condition is NOT essential for democratic elections?
Which condition is NOT essential for democratic elections?
What is a characteristic of autocratic elections?
What is a characteristic of autocratic elections?
Which type of electoral system involves the concept of 'First Past the Post'?
Which type of electoral system involves the concept of 'First Past the Post'?
Which of the following describes a mixed electoral system?
Which of the following describes a mixed electoral system?
What is often a consequence of electoral systems that utilize majority-runoff elections?
What is often a consequence of electoral systems that utilize majority-runoff elections?
Which of the following is characteristic of proportional electoral systems?
Which of the following is characteristic of proportional electoral systems?
Which aspect does NOT support the legitimacy of elections?
Which aspect does NOT support the legitimacy of elections?
What key factor impacts voter support in elections?
What key factor impacts voter support in elections?
What is a primary advantage of using the alternative/preferential ballot in electoral systems?
What is a primary advantage of using the alternative/preferential ballot in electoral systems?
Which statement accurately describes proportional representation systems?
Which statement accurately describes proportional representation systems?
In a list system, how are candidates elected?
In a list system, how are candidates elected?
What does the Single-Transferable Vote (STV) system aim to achieve?
What does the Single-Transferable Vote (STV) system aim to achieve?
What is a characteristic of mixed systems in electoral representation?
What is a characteristic of mixed systems in electoral representation?
In proportional representation systems, what typically happens when a voter's first choice candidate has already secured a seat?
In proportional representation systems, what typically happens when a voter's first choice candidate has already secured a seat?
What does a quota/largest remainder system rely on for candidates to secure seats?
What does a quota/largest remainder system rely on for candidates to secure seats?
How are coalition governments typically formed in proportional representation systems?
How are coalition governments typically formed in proportional representation systems?
What issue can arise from a majority electoral system in elections with multiple candidates?
What issue can arise from a majority electoral system in elections with multiple candidates?
In the British Columbia election of 1996, which outcome was observed regarding votes and seats?
In the British Columbia election of 1996, which outcome was observed regarding votes and seats?
Which of the following describes a problem with majority electoral systems?
Which of the following describes a problem with majority electoral systems?
How does the distribution of seats based on votes typically manifest under majority systems?
How does the distribution of seats based on votes typically manifest under majority systems?
Which party in the context provided presented a contrast with representation despite vote percentages?
Which party in the context provided presented a contrast with representation despite vote percentages?
What characteristic of majority systems can undermine democratic legitimacy?
What characteristic of majority systems can undermine democratic legitimacy?
Which electoral system modification requires only a plurality to win in the second round?
Which electoral system modification requires only a plurality to win in the second round?
Which electoral system allows voters to rank their preferences?
Which electoral system allows voters to rank their preferences?
Which voting method is typically used in France's presidential elections?
Which voting method is typically used in France's presidential elections?
What is the primary function of liberalism within liberal/constitutional democracy?
What is the primary function of liberalism within liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which of the following characteristics is NOT typically associated with liberal/constitutional democracy?
Which of the following characteristics is NOT typically associated with liberal/constitutional democracy?
In the context of liberal/constitutional democracy, what does 'political participation' primarily refer to?
In the context of liberal/constitutional democracy, what does 'political participation' primarily refer to?
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between majority rule and individual rights in a liberal democracy?
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between majority rule and individual rights in a liberal democracy?
What challenge does 'conformism' present in a liberal democracy?
What challenge does 'conformism' present in a liberal democracy?
Which principle ensures that every individual's vote carries the same weight in a liberal democracy?
Which principle ensures that every individual's vote carries the same weight in a liberal democracy?
Which historical limitation has characterized the right to vote in liberal democracies?
Which historical limitation has characterized the right to vote in liberal democracies?
In a liberal/constitutional democracy, what is a major concern related to 'tyranny of the majority'?
In a liberal/constitutional democracy, what is a major concern related to 'tyranny of the majority'?
What is the primary role of the President regarding foreign policy?
What is the primary role of the President regarding foreign policy?
Which action can a Prime Minister NOT take without support?
Which action can a Prime Minister NOT take without support?
Under what condition can the President's veto be overridden?
Under what condition can the President's veto be overridden?
What institutional limit affects the President's effectiveness in governance?
What institutional limit affects the President's effectiveness in governance?
What characterizes the President's power to make appointments?
What characterizes the President's power to make appointments?
How many electoral college votes are needed for a presidential candidate to win the election?
How many electoral college votes are needed for a presidential candidate to win the election?
Which states have a unique method for distributing electoral college votes?
Which states have a unique method for distributing electoral college votes?
What is the maximum number of terms a president can serve in the U.S.?
What is the maximum number of terms a president can serve in the U.S.?
Which body is responsible for holding a trial if a president is impeached?
Which body is responsible for holding a trial if a president is impeached?
What must happen for a Prime Minister to be removed from office?
What must happen for a Prime Minister to be removed from office?
In presidential elections, what is defined as 'down ballot races'?
In presidential elections, what is defined as 'down ballot races'?
Which of the following best describes the electoral college's function?
Which of the following best describes the electoral college's function?
What determines the number of electoral college votes assigned to each state?
What determines the number of electoral college votes assigned to each state?
What is a key characteristic of a parliamentary system compared to a presidential system?
What is a key characteristic of a parliamentary system compared to a presidential system?
How is a Prime Minister usually selected in a parliamentary system?
How is a Prime Minister usually selected in a parliamentary system?
What describes the separation of powers in a presidential system?
What describes the separation of powers in a presidential system?
Which of the following accurately reflects the nature of power in a presidential system?
Which of the following accurately reflects the nature of power in a presidential system?
In the context of party nominations for the presidency, what is a significant part of the process?
In the context of party nominations for the presidency, what is a significant part of the process?
What happens if a party forms a minority government in a parliamentary system?
What happens if a party forms a minority government in a parliamentary system?
What role does the judiciary play in a presidential system?
What role does the judiciary play in a presidential system?
How frequently do presidential elections typically occur?
How frequently do presidential elections typically occur?
What is a primary characteristic of populism?
What is a primary characteristic of populism?
Which of the following leaders is associated with right-wing populism in the United States?
Which of the following leaders is associated with right-wing populism in the United States?
Which political party in Canada was formed in response to the discontent of farmers post WW1?
Which political party in Canada was formed in response to the discontent of farmers post WW1?
Which political ideology is positioned on the left of the populism spectrum?
Which political ideology is positioned on the left of the populism spectrum?
What tactic is commonly utilized by populist leaders to gain support?
What tactic is commonly utilized by populist leaders to gain support?
Which Canadian populist party is known for its opposition to Eastern banks and business interests?
Which Canadian populist party is known for its opposition to Eastern banks and business interests?
How do populist movements typically view globalization?
How do populist movements typically view globalization?
What is a key characteristic of populism?
What is a key characteristic of populism?
In the context of populism, the term 'elites' typically refers to which of the following?
In the context of populism, the term 'elites' typically refers to which of the following?
Which political movement in Canada is linked to prairie populism post-World War I?
Which political movement in Canada is linked to prairie populism post-World War I?
What form of political mechanism is commonly associated with populist movements?
What form of political mechanism is commonly associated with populist movements?
Which statement best reflects the ideological spectrum associated with populism?
Which statement best reflects the ideological spectrum associated with populism?
What does the term 'drain the swamp' signify in the context of populism?
What does the term 'drain the swamp' signify in the context of populism?
Which aspect of tradable pollution quotas is aimed at encouraging companies to reduce emissions?
Which aspect of tradable pollution quotas is aimed at encouraging companies to reduce emissions?
What does deep ecology primarily emphasize as a justification for reducing natural diversity?
What does deep ecology primarily emphasize as a justification for reducing natural diversity?
What challenge do green parties commonly face in gaining legislative representation?
What challenge do green parties commonly face in gaining legislative representation?
Which of the following is a significant action advocated by deep ecology proponents?
Which of the following is a significant action advocated by deep ecology proponents?
Which organization is known for its activism against oil sands development?
Which organization is known for its activism against oil sands development?
What is the primary focus of conservationism within environmentalism?
What is the primary focus of conservationism within environmentalism?
Which of the following embodies the principles of deep ecology?
Which of the following embodies the principles of deep ecology?
What significant challenge is posed by the concept of the 'Tragedy of the Commons' in environmental protection?
What significant challenge is posed by the concept of the 'Tragedy of the Commons' in environmental protection?
Which statement best characterizes human welfare ecology as represented by Rachel Carson?
Which statement best characterizes human welfare ecology as represented by Rachel Carson?
Which pollutant is estimated to have caused the most premature deaths according to WHO statistics?
Which pollutant is estimated to have caused the most premature deaths according to WHO statistics?
What does sustainable development primarily emphasize?
What does sustainable development primarily emphasize?
What distinguishes anthropocentric ideology from biocentric ideology?
What distinguishes anthropocentric ideology from biocentric ideology?
Which of the following best describes a significant outcome of climate change?
Which of the following best describes a significant outcome of climate change?
Which ecological approach is characterized by its emphasis on deep ecological principles?
Which ecological approach is characterized by its emphasis on deep ecological principles?
According to the IUCN Red List, what is a critical global issue related to biodiversity?
According to the IUCN Red List, what is a critical global issue related to biodiversity?
What is considered a central tenet of deep ecology?
What is considered a central tenet of deep ecology?
What factor does free market environmentalism seek to address?
What factor does free market environmentalism seek to address?
Which of these actions is commonly associated with conservationism?
Which of these actions is commonly associated with conservationism?
Which ideology underscores the belief that the environment possesses intrinsic value independent of human interests?
Which ideology underscores the belief that the environment possesses intrinsic value independent of human interests?
Which significant consequence is associated with climate change?
Which significant consequence is associated with climate change?
What is a key consideration for addressing climate change according to the discussed principles?
What is a key consideration for addressing climate change according to the discussed principles?
What significant legal decision did the Supreme Court of Canada make in 1928 regarding women?
What significant legal decision did the Supreme Court of Canada make in 1928 regarding women?
What was a primary focus of activism during the Second Wave of feminism?
What was a primary focus of activism during the Second Wave of feminism?
Which milestone event in women's history occurred in 1929 in Canada?
Which milestone event in women's history occurred in 1929 in Canada?
What was a result of women's participation in the workforce during World War II?
What was a result of women's participation in the workforce during World War II?
What is the primary focus of feminism as defined in the content?
What is the primary focus of feminism as defined in the content?
What is a characteristic of the activism seen in the Second Wave of feminism?
What is a characteristic of the activism seen in the Second Wave of feminism?
Which group was the first woman elected to the Canadian Parliament?
Which group was the first woman elected to the Canadian Parliament?
Which philosophical idea underpinned First Wave feminism?
Which philosophical idea underpinned First Wave feminism?
What did the term 'micropolitics of gender equality' in later waves of feminism refer to?
What did the term 'micropolitics of gender equality' in later waves of feminism refer to?
What distinguishes the Second Wave of feminism from the First Wave?
What distinguishes the Second Wave of feminism from the First Wave?
In what year were Chinese Canadian citizens granted the right to vote federally?
In what year were Chinese Canadian citizens granted the right to vote federally?
Which movement is NOT traditionally categorized within feminism according to the ideological spectrum provided?
Which movement is NOT traditionally categorized within feminism according to the ideological spectrum provided?
What did the First Wave primarily focus on?
What did the First Wave primarily focus on?
Who among the following thinkers contributed significantly to the early philosophical discourse on women's equality?
Who among the following thinkers contributed significantly to the early philosophical discourse on women's equality?
Which of the following characterizes the ideological context of feminism?
Which of the following characterizes the ideological context of feminism?
By what year were Japanese Canadian citizens granted the right to vote?
By what year were Japanese Canadian citizens granted the right to vote?
What best summarizes the philosophical underpinning of feminism's goal of women's emancipation?
What best summarizes the philosophical underpinning of feminism's goal of women's emancipation?
Which phrase best represents patriarchy as defined in the content?
Which phrase best represents patriarchy as defined in the content?
What is one of the key attributes of ecofeminism as mentioned in the content?
What is one of the key attributes of ecofeminism as mentioned in the content?
How does Third Wave feminism primarily differ from its predecessors?
How does Third Wave feminism primarily differ from its predecessors?
What percentage of law school graduates in Canada are female?
What percentage of law school graduates in Canada are female?
What percentage of women are represented in senior management positions within the private sector in Canada?
What percentage of women are represented in senior management positions within the private sector in Canada?
What is the female earned wage compared to male earnings in 2018?
What is the female earned wage compared to male earnings in 2018?
Which of the following categories of students has the lowest representation of women in Canada?
Which of the following categories of students has the lowest representation of women in Canada?
What percentage of practicing, licensed engineers in Canada are women?
What percentage of practicing, licensed engineers in Canada are women?
What is the percentage of judges in Canada that are women?
What is the percentage of judges in Canada that are women?
What is the representation of women of color in total management positions?
What is the representation of women of color in total management positions?
Which of the following statements best reflects the urgency of working towards gender equality?
Which of the following statements best reflects the urgency of working towards gender equality?
Which sector shows the least proportional representation of women among workers?
Which sector shows the least proportional representation of women among workers?
What is the appropriate interpretation of the 43% statistic mentioned regarding women?
What is the appropriate interpretation of the 43% statistic mentioned regarding women?
What is the primary focus of civic nationalism?
What is the primary focus of civic nationalism?
Irredentism is best described as a claim over territory based on what?
Irredentism is best described as a claim over territory based on what?
Which of the following best exemplifies ethnic nationalism?
Which of the following best exemplifies ethnic nationalism?
What can be a manifestation of nationalism when dealing with perceived threats?
What can be a manifestation of nationalism when dealing with perceived threats?
What principle does the concept of self-determination primarily focus on?
What principle does the concept of self-determination primarily focus on?
Which of the following is NOT a potential outcome of ethnic nationalism?
Which of the following is NOT a potential outcome of ethnic nationalism?
What does the tyranny of the majority imply in the context of nationalism?
What does the tyranny of the majority imply in the context of nationalism?
Which of the following reflects a protectionist measure associated with nationalism?
Which of the following reflects a protectionist measure associated with nationalism?
What is a primary characteristic of imperialism tied to nationalism?
What is a primary characteristic of imperialism tied to nationalism?
What movement is characterized by the demand for a national identity and independence from imperial control after WWII?
What movement is characterized by the demand for a national identity and independence from imperial control after WWII?
Which major world event is frequently linked to the manifestations of nationalism?
Which major world event is frequently linked to the manifestations of nationalism?
Which event marked the unification of Germany in 1870?
Which event marked the unification of Germany in 1870?
Which ideology is known for advocating freedom and individual rights while exhibiting tension with state nationalism?
Which ideology is known for advocating freedom and individual rights while exhibiting tension with state nationalism?
Which of the following nations experienced a national self-determination movement after the decline of the USSR?
Which of the following nations experienced a national self-determination movement after the decline of the USSR?
What is a characteristic of virulent nationalism as observed in history?
What is a characteristic of virulent nationalism as observed in history?
Which group is mentioned as having a nationalist reaction in opposition to imperialism?
Which group is mentioned as having a nationalist reaction in opposition to imperialism?
What was a significant factor in the emergence of smaller, more homogenous states after the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Empire?
What was a significant factor in the emergence of smaller, more homogenous states after the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Empire?
What ideology melds communism with nationalism in certain states?
What ideology melds communism with nationalism in certain states?
Which formal structure was established to recognize and legitimize nationalism and nation-states after WWII?
Which formal structure was established to recognize and legitimize nationalism and nation-states after WWII?
Which nations are known for their independence movements following the decline of the USSR?
Which nations are known for their independence movements following the decline of the USSR?
What ideological principle is primarily opposed by nationalism and fascism?
What ideological principle is primarily opposed by nationalism and fascism?
Which term is associated with a leader's strong personal influence over a totalitarian regime?
Which term is associated with a leader's strong personal influence over a totalitarian regime?
What is a primary characteristic of a neo-fascist movement?
What is a primary characteristic of a neo-fascist movement?
Which concept describes the government's control over the economy in a fascist regime?
Which concept describes the government's control over the economy in a fascist regime?
What is synonymous with the most extreme form of nationalism as described in the content?
What is synonymous with the most extreme form of nationalism as described in the content?
What common feature links totalitarian regimes as identified by Friedrich and Brzezinski?
What common feature links totalitarian regimes as identified by Friedrich and Brzezinski?
In the context of nationalism, what does the phrase 'Nothing outside the state' emphasize?
In the context of nationalism, what does the phrase 'Nothing outside the state' emphasize?
Which of the following describes a prominent aspect of the radical right's philosophy in nationalism?
Which of the following describes a prominent aspect of the radical right's philosophy in nationalism?
What aspect of governance is fundamentally challenged by the anti-democratic nature of nationalism?
What aspect of governance is fundamentally challenged by the anti-democratic nature of nationalism?
What is a strategic feature used by totalitarian governments to maintain control over citizens?
What is a strategic feature used by totalitarian governments to maintain control over citizens?
Flashcards
Central Government
Central Government
The highest level of government in a country, responsible for national policies and matters.
Regional Government
Regional Government
Government specific to a region or province within a federal system.
Local Government
Local Government
Government at the local level, responsible for services in cities, towns, or villages.
Unitary System
Unitary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Devolution
Devolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Federal System
Federal System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Continuum of Centralization
Continuum of Centralization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Confederation
Confederation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Federalism
Federalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complexities of Federalism
Complexities of Federalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Federalism in Canada
Federalism in Canada
Signup and view all the flashcards
Federal Powers: s. 91
Federal Powers: s. 91
Signup and view all the flashcards
Provincial Powers: s. 92
Provincial Powers: s. 92
Signup and view all the flashcards
Division of Powers
Division of Powers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peace, Order, and Good Government (POGG)
Peace, Order, and Good Government (POGG)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disallowance (s. 56)
Disallowance (s. 56)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reservation (s. 90)
Reservation (s. 90)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Declaratory Power (s. 92(10)(c))
Declaratory Power (s. 92(10)(c))
Signup and view all the flashcards
Residual Power
Residual Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
POGG in Action
POGG in Action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Federalism Sovereignty
Federalism Sovereignty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disallowance
Disallowance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Declaratory Power
Declaratory Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political Violence
Political Violence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regime/Government Violence
Regime/Government Violence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spontaneous Violence
Spontaneous Violence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Guerrilla Violence/Guerrilla Insurgency
Guerrilla Violence/Guerrilla Insurgency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Counter-insurgency
Counter-insurgency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Suicide Terrorism
Suicide Terrorism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lone Wolf Terrorism
Lone Wolf Terrorism
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a protest?
What is a protest?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is civil disobedience?
What is civil disobedience?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are insurgent groups?
What are insurgent groups?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is guerrilla warfare?
What is guerrilla warfare?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is terrorism?
What is terrorism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a revolution?
What is a revolution?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the 'alt-right' movement?
What is the 'alt-right' movement?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Antifa?
What is Antifa?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are opportunity structures in politics?
What are opportunity structures in politics?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is transnational political protest?
What is transnational political protest?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are political parties?
What are political parties?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are interest groups?
What are interest groups?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are social movements?
What are social movements?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are political party systems?
What are political party systems?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are mass parties?
What are mass parties?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are cadre parties?
What are cadre parties?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interest/Advocacy Groups
Interest/Advocacy Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Self-Interest Groups
Self-Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Public Interest Groups
Public Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Associational Interest Groups
Associational Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Institutional Interest Groups
Institutional Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Issue-Oriented/Spontaneous/Anomic Interest Groups
Issue-Oriented/Spontaneous/Anomic Interest Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Movement Party
Movement Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
One-Party System
One-Party System
Signup and view all the flashcards
One-Party Dominant System
One-Party Dominant System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Two-Party System
Two-Party System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Two-Party Plus System
Two-Party Plus System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multi-Party System
Multi-Party System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political Party
Political Party
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cadre Parties
Cadre Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pragmatic/Electoral-Professional Parties
Pragmatic/Electoral-Professional Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brokerage Parties
Brokerage Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Programmatic/Ideological/Interest Parties
Programmatic/Ideological/Interest Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interest Parties
Interest Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Personal/Personalistic Parties
Personal/Personalistic Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Programmatic/Ideological & Interest Parties
Programmatic/Ideological & Interest Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brokerage Parties (redefined)
Brokerage Parties (redefined)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Traditional Authoritarianism
Traditional Authoritarianism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transformational Authoritarianism
Transformational Authoritarianism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Statism
Statism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Guerrilla Warfare
Guerrilla Warfare
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protest
Protest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Totalitarianism
Totalitarianism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudo-democratic Rule
Pseudo-democratic Rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Control of Communications
Control of Communications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Terroristic Police Control
Terroristic Police Control
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central Control and Direction of the Economy
Central Control and Direction of the Economy
Signup and view all the flashcards
All-Powerful Leader
All-Powerful Leader
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autocracy
Autocracy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Authoritarianism
Authoritarianism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hybrid Regime
Hybrid Regime
Signup and view all the flashcards
Traditional Authoritarianism with Social Pluralism
Traditional Authoritarianism with Social Pluralism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Traditional Authoritarianism Without Transformative Ideology
Traditional Authoritarianism Without Transformative Ideology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Democratic Elections
Democratic Elections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Autocratic Elections
Autocratic Elections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plurality/Majority Electoral System
Plurality/Majority Electoral System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proportional Electoral Systems
Proportional Electoral Systems
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mixed Electoral Systems
Mixed Electoral Systems
Signup and view all the flashcards
Universal Adult Suffrage
Universal Adult Suffrage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political Freedom
Political Freedom
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accountability in Democratic Elections
Accountability in Democratic Elections
Signup and view all the flashcards
Majority-Plurality System
Majority-Plurality System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alternative/Preferential Vote System
Alternative/Preferential Vote System
Signup and view all the flashcards
First Past the Post (FPP)
First Past the Post (FPP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single-Member Plurality (SMP)
Single-Member Plurality (SMP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
More Seats, Fewer Votes
More Seats, Fewer Votes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electoral Distortion
Electoral Distortion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Majority System
Majority System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Winner-Take-All
Winner-Take-All
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regional Concentration of Votes
Regional Concentration of Votes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Underrepresentation of Minorities
Underrepresentation of Minorities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Terrorism
Terrorism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proportional Representation
Proportional Representation
Signup and view all the flashcards
List System
List System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single-Transferable Vote (STV)
Single-Transferable Vote (STV)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mixed Systems
Mixed Systems
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plurality/Majority System
Plurality/Majority System
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of democratic elections?
What is the purpose of democratic elections?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the essential conditions for democratic elections?
What are the essential conditions for democratic elections?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are autocratic elections?
What are autocratic elections?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Explain the First Past the Post (FPP) electoral system.
Explain the First Past the Post (FPP) electoral system.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the goal of a proportional electoral system?
What is the goal of a proportional electoral system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are mixed electoral systems?
What are mixed electoral systems?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does universal adult suffrage mean?
What does universal adult suffrage mean?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is political freedom related to democratic elections?
How is political freedom related to democratic elections?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alternative Vote (AV) or Preferential Ballot
Alternative Vote (AV) or Preferential Ballot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proportional Representation (PR)
Proportional Representation (PR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
List System (PR)
List System (PR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mixed Member Proportional (MMP)
Mixed Member Proportional (MMP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quota/Largest Remainder (PR)
Quota/Largest Remainder (PR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Liberal/Constitutional Democracy?
What is Liberal/Constitutional Democracy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Equality of Political Rights
Equality of Political Rights
Signup and view all the flashcards
Majority Rule
Majority Rule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Political Participation
Political Participation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tyranny of the Majority
Tyranny of the Majority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conformism
Conformism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Not Rule of the Best
Not Rule of the Best
Signup and view all the flashcards
General Election for President
General Election for President
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impeachment
Impeachment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Winner-Take-All System
Winner-Take-All System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parliamentary System
Parliamentary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Presidential System
Presidential System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Selection of the Prime Minister
Selection of the Prime Minister
Signup and view all the flashcards
Selection of the President
Selection of the President
Signup and view all the flashcards
Removal of the Prime Minister
Removal of the Prime Minister
Signup and view all the flashcards
Removal of the President
Removal of the President
Signup and view all the flashcards
Powers of Government Branches
Powers of Government Branches
Signup and view all the flashcards
Constraints on Government Powers
Constraints on Government Powers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Presidential Veto
Presidential Veto
Signup and view all the flashcards
State of the Union Address
State of the Union Address
Signup and view all the flashcards
Presidential Pardon Power
Presidential Pardon Power
Signup and view all the flashcards
Confidence of the House of Commons
Confidence of the House of Commons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Institutional Checks and Balances
Institutional Checks and Balances
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism
Populism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism's Target: Elites
Populism's Target: Elites
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Leaders & Authenticity
Populist Leaders & Authenticity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Methods: Direct Democracy
Populist Methods: Direct Democracy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism in the US: Right-Wing Emphasis
Populism in the US: Right-Wing Emphasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism in Canada: Historical Context
Populism in Canada: Historical Context
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism in Europe: Immigration & Inequality
Populism in Europe: Immigration & Inequality
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism's Defining Feature: Polarization
Populism's Defining Feature: Polarization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Leaders
Populist Leaders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism in the U.S.
Populism in the U.S.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism in Canada
Populism in Canada
Signup and view all the flashcards
What Fuels Populism?
What Fuels Populism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Rhetoric
Populist Rhetoric
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populism's Potential
Populism's Potential
Signup and view all the flashcards
Populist Movements: Genuine vs. Exploitative
Populist Movements: Genuine vs. Exploitative
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tradeable Pollution Quotas/Emissions Trading (Cap & Trade)
Tradeable Pollution Quotas/Emissions Trading (Cap & Trade)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Ecology
Deep Ecology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Green Parties
Green Parties
Signup and view all the flashcards
Environmental Interest/Advocacy Groups
Environmental Interest/Advocacy Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ecological Sabotage ('Ecotage')
Ecological Sabotage ('Ecotage')
Signup and view all the flashcards
Environmentalism
Environmentalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anthropocentrism
Anthropocentrism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biocentrism
Biocentrism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conservationism
Conservationism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shallow Ecology
Shallow Ecology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Environmentalism as Political Expression
Environmentalism as Political Expression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human Welfare Ecology
Human Welfare Ecology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Air Pollution and Global Health
Air Pollution and Global Health
Signup and view all the flashcards
Climate Change and its Evidence
Climate Change and its Evidence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biodiversity and the IUCN Red List
Biodiversity and the IUCN Red List
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tragedy of the Commons
Tragedy of the Commons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sustainable Development Principles
Sustainable Development Principles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Free Market Environmentalism
Free Market Environmentalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Incentivizing Environmental Responsibility
Incentivizing Environmental Responsibility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Environmental Challenges and Solutions
Environmental Challenges and Solutions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Women's Suffrage
Women's Suffrage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temperance Movement
Temperance Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
The Persons Case
The Persons Case
Signup and view all the flashcards
Agnes Macphail
Agnes Macphail
Signup and view all the flashcards
Second Wave Feminism
Second Wave Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Micropolitics of Gender Equality
Micropolitics of Gender Equality
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intersectionality
Intersectionality
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gender and Sexual Minorities (GSMs)
Gender and Sexual Minorities (GSMs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feminism
Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gender Gap
Gender Gap
Signup and view all the flashcards
Women in STEM
Women in STEM
Signup and view all the flashcards
Time's Up
Time's Up
Signup and view all the flashcards
2SLGBTQQIA
2SLGBTQQIA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wage Gap
Wage Gap
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gendered Leadership Gap
Gendered Leadership Gap
Signup and view all the flashcards
Social Media Activism
Social Media Activism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feminist Ideological Spectrum
Feminist Ideological Spectrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
First Wave Feminism
First Wave Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Third Wave Feminism
Third Wave Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fourth Wave Feminism
Fourth Wave Feminism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patriarchy
Patriarchy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feminism Beyond the Traditional Ideological Spectrum
Feminism Beyond the Traditional Ideological Spectrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Feminism?
What is Feminism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nationalism
Nationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
National Self-Determination
National Self-Determination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nation-State Formation
Nation-State Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Communism/Socialism
Communism/Socialism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Imperialism
Imperialism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decolonization
Decolonization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tension between Nationalism and Liberalism
Tension between Nationalism and Liberalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Virulent Nationalism
Virulent Nationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ethnic Nationalism
Ethnic Nationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Civic Nationalism
Civic Nationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protectionism
Protectionism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Irredentism
Irredentism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Minority Oppression
Minority Oppression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Censorship
Censorship
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aggressive Nationalism
Aggressive Nationalism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fascism
Fascism
Signup and view all the flashcards
National Socialism
National Socialism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insurgency
Insurgency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
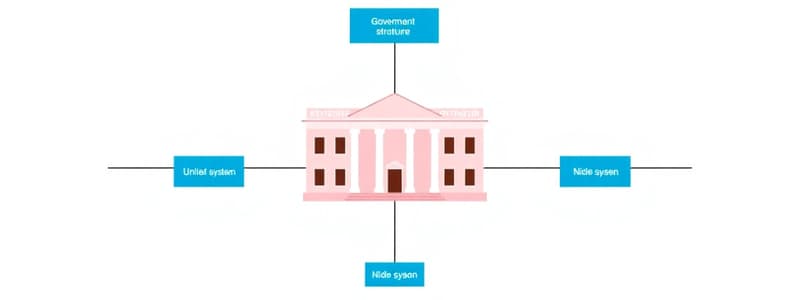
Multiple Governments: Unitary and Federal Systems
- Unitary systems have a single, sovereign government controlling all aspects of the country.
- Federal systems divide sovereignty between central and regional (provincial/state) governments.
Definitions
- Unitary System: A single sovereign government controls all aspects of the country; the central government is sovereign. Administrative changes involve a transfer of power from the central government.
- Techniques include devolution (transfer of power) and statutes.
- Federal System: Sovereignty is divided between central and state/provincial governments. It's a union of partially self-governing regions under a central government. The sovereignty of regional governments is stated in the constitution.
Levels of Government:
- Central Government (National): The highest level of government, like the Government of Canada.
- Regional Government (Provincial/State): Present in federal systems; example, Government of Alberta.
- Local Government (Municipal): The lowest level, like the city of Calgary.
Continuum of Centralization
- Separation (Decentralized): Sovereign states, no central government. Sovereignty is retained through constituent governments. (e.g., no specific examples are given)
- Confederation: Central government, with sovereignty retained by constituent governments. (e.g., no specific examples are given)
- Federalism: Sovereignty is shared between central and constituent governments. (e.g., no specific examples are given)
- Devolution: Constituent governments exist, but sovereignty is monopolized by central government. (e.g., no specific examples are given)
- Integration (Centralized): Unitary state: no constituent governments. (e.g., no specific examples are given)
Unitary vs. Federal Countries
- A world map illustrating the distribution of Federal and Unitary states. [No additional detail currently available].
Why Federalism?
- Geography: Geographical factors influencing decisions.
- Sharing Government Responsibilities: Dividing responsibilities across levels of government.
- Cultural/Linguistic/Religious Divisions: Acknowledging diverse groups.
- Checks on Government Power: Creating checks and balances.
- Legal and Practical: Considerations regarding both legal and practical aspects, upwards and downwards federal government checks.
- Local Representation: Ensuring local voices are heard. Federalist 10: James Madison.
Explicit Powers (Canada)
- Section 91 (Federal Powers): Trade & Commerce, Taxation, Militia, Currency, Public Debt, Postal service, Navigation, Banking, Indians and their lands, Marriage, Criminal law, Peace, Order, and Good Government (POGG).
- Section 92 (Provincial Powers): General local matters, Direct taxation, Licenses, Property, Administration of justice, Prisons, Health, Welfare, Hospitals, Provincial control Municipal institutions, Education, and Natural resources.
Complexities of Federalism
- Constitutional Provisions vs. Political Practice: Canada's design to concentrate power in the federal government.
- Constitutional Mechanisms of Federal Interference with Provincial Powers: Historical constitutional mechanisms of federal interference. Examples:
- Section 56 disallowance (last used 1943)
- Section 90 reservation (last used 1961)
- Section 92 (10)(c) declaratory power (up to 1961)
- Residual Power: Powers not specifically listed.
- Peace, Order, and Good Government (POGG): Grants federal government flexibility. This doctrine grants the federal government wide-ranging powers.
- National Concern Doctrine: Relevant to federal involvement with areas like carbon tax. This doctrine justifies federal intervention in areas of national concern, such as the carbon tax.
- Bicameral Legislatures: Two houses in the legislature (checks on majority rule). Examples include Canadian Senate & US Senate.
- Executive Federalism: Central government leveraging regional government collective power via First Ministers' Conferences.
- Asymmetrical Federalism: Regional differences in sovereignty. [No further details are given].
Challenges to Federalism in Canada
- Meech Lake Accord (1987)
- Charlottetown Accord (1992)
- Quebec Referendum (1995)
- Alberta Fair Deal Panel
- Alberta Sovereignty Act
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.