Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which muscle primarily enables the thumb's opposition?
Which muscle primarily enables the thumb's opposition?
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis
- Adductor Pollicis
- Opponens Pollicis (correct)
Which of the following muscles is innervated by the ulnar nerve?
Which of the following muscles is innervated by the ulnar nerve?
- Adductor Pollicis (correct)
- Opponens Pollicis
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis
Which statement accurately describes the Abductor Digiti Minimi?
Which statement accurately describes the Abductor Digiti Minimi?
- It originates from the scaphoid.
- It allows opposition of the little finger.
- It inserts on the ulnar side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the little finger. (correct)
- It flexes the little finger.
What is the primary function of the lumbricals in the hand?
What is the primary function of the lumbricals in the hand?
Which muscle originates from the tubercle of the trapezium?
Which muscle originates from the tubercle of the trapezium?
Which categories of intrinsic muscles primarily control the thumb and little finger movements?
Which categories of intrinsic muscles primarily control the thumb and little finger movements?
Which of the following muscles does NOT belong strictly to the thenar group?
Which of the following muscles does NOT belong strictly to the thenar group?
What is the primary role of the Interossei muscles?
What is the primary role of the Interossei muscles?
Which thenar muscle inserts on the radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb?
Which thenar muscle inserts on the radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for abducting the little finger?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for abducting the little finger?
What is the primary action of the hypothenar muscles?
What is the primary action of the hypothenar muscles?
Where do the dorsal interossei muscles originate?
Where do the dorsal interossei muscles originate?
Which muscle group is primarily responsible for fine motor control through flexing the metacarpophalangeal joints?
Which muscle group is primarily responsible for fine motor control through flexing the metacarpophalangeal joints?
The origin of the flexor digiti minimi brevis is located at which anatomical structure?
The origin of the flexor digiti minimi brevis is located at which anatomical structure?
What is the main function of the thenar muscles?
What is the main function of the thenar muscles?
The palmar interossei primarily function to:
The palmar interossei primarily function to:
Which structure do the lumbricals insert onto?
Which structure do the lumbricals insert onto?
Which action is performed by the dorsal interossei?
Which action is performed by the dorsal interossei?
The insertion point of the opponens digiti minimi is located along which anatomical structure?
The insertion point of the opponens digiti minimi is located along which anatomical structure?
Which of the following is NOT an action of the thenar muscles?
Which of the following is NOT an action of the thenar muscles?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
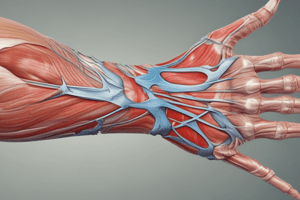
Thenar Muscles Anatomy
- Location: Base of the thumb.
- Muscles Included:
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Abducts the thumb.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Flexes the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
- Opponens Pollicis: Allows opposition of the thumb.
- Adductor Pollicis: Adducts the thumb (not strictly thenar, but functions with them).
- Innervation: Primarily by the median nerve, except for the adductor pollicis (ulnar nerve).
Hypothenar Muscles Function
- Location: Base of the little finger (pinky).
- Muscles Included:
- Abductor Digiti Minimi: Abducts the little finger.
- Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis: Flexes the proximal phalanx of the little finger.
- Opponens Digiti Minimi: Allows opposition of the little finger.
- Innervation: Ulnar nerve.
Intrinsic Muscles Overview
- Definition: Muscles originating and inserting within the hand.
- Categories:
- Thenar Muscles: Control thumb movements.
- Hypothenar Muscles: Control little finger movements.
- Lumbricals: Flex the metacarpophalangeal joints and extend the interphalangeal joints.
- Interossei: Dorsal and palmar muscles that abduct and adduct the fingers, respectively.
Muscle Origins And Insertions
- Thenar Muscles:
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Originates from the tubercle of the scaphoid; inserts on the radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Originates from the tubercle of the trapezium; inserts on the radial side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
- Opponens Pollicis: Originates from the tubercle of the trapezium; inserts along the entire length of the radial side of the 1st metacarpal.
- Hypothenar Muscles:
- Abductor Digiti Minimi: Originates from the pisiform; inserts on the ulnar side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the little finger.
- Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis: Originates from the hook of the hamate; inserts on the ulnar side of the base of the proximal phalanx of the little finger.
- Opponens Digiti Minimi: Originates from the hook of the hamate; inserts along the ulnar border of the 5th metacarpal.
- Lumbricals: Originate from the flexor digitorum profundus tendons; insert on the extensor expansion of the fingers.
- Interossei:
- Dorsal Interossei: Originate from adjacent sides of metacarpals; insert on the extensor expansion of the corresponding digit.
- Palmar Interossei: Originate from specific metacarpals; insert on the extensor expansion of the corresponding digit.
Muscle Actions And Movements
- Thenar Muscles:
- Allow complex thumb movements: opposition, abduction, flexion, and adduction.
- Hypothenar Muscles:
- Enable movements of the little finger: abduction, flexion, and opposition.
- Lumbricals:
- Flex the metacarpophalangeal joints and extend the interphalangeal joints, enabling fine motor control.
- Interossei:
- Dorsal interossei: Abduction of fingers (spreading apart).
- Palmar interossei: Adduction of fingers (bringing together).
Thenar Muscles Anatomy
- Located at the base of the thumb.
- Comprises four key muscles:
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Responsible for thumb abduction.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Flexes the proximal phalanx of the thumb.
- Opponens Pollicis: Facilitates thumb opposition, crucial for grasping.
- Adductor Pollicis: Adducts the thumb; functions alongside thenar muscles but primarily innervated by the ulnar nerve.
- Innervation: Mostly by the median nerve, except for the adductor pollicis.
Hypothenar Muscles Function
- Found at the base of the little finger.
- Includes three major muscles:
- Abductor Digiti Minimi: Abducts the little finger.
- Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis: Flexes the proximal phalanx of the little finger.
- Opponens Digiti Minimi: Permits opposition of the little finger.
- Innervation: All are innervated by the ulnar nerve.
Intrinsic Muscles Overview
- Defined as muscles that originate and insert within the hand.
- Two main categories are:
- Thenar Muscles: Control and coordinate thumb movements.
- Hypothenar Muscles: Manage movements of the little finger.
- Additional muscles include:
- Lumbricals: Flex the metacarpophalangeal joints while extending the interphalangeal joints.
- Interossei:
- Dorsal Interossei: Abduct fingers.
- Palmar Interossei: Adduct fingers.
Muscle Origins And Insertions
- Thenar Muscles:
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Originates from the tubercle of the scaphoid; inserts onto the radial side of the thumb's proximal phalanx.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Originates from the tubercle of the trapezium; inserts similarly to abductor pollicis brevis.
- Opponens Pollicis: Originates from the tubercle of the trapezium; inserts along the radial side of the 1st metacarpal.
- Hypothenar Muscles:
- Abductor Digiti Minimi: Originates from the pisiform; inserts on the ulnar side of the little finger's proximal phalanx.
- Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis: Originates from the hook of the hamate; inserts on the similar ulnar region of the little finger's proximal phalanx.
- Opponens Digiti Minimi: Originates from the hook of the hamate; inserts along the ulnar border of the 5th metacarpal.
- Lumbricals: Originate from the flexor digitorum profundus tendons; insert into the extensor expansion of the fingers.
- Interossei:
- Dorsal Interossei: Originate from adjacent sides of metacarpals; insert on the extensor expansion of the corresponding digit.
- Palmar Interossei: Originate from specific metacarpals; insert on the extensor expansion of the corresponding digit.
Muscle Actions And Movements
- Thenar Muscles: Enable complex thumb movements including opposition, abduction, flexion, and adduction.
- Hypothenar Muscles: Facilitate movements of the little finger such as abduction, flexion, and opposition.
- Lumbricals: Act to flex the metacarpophalangeal joints while extending the interphalangeal joints, enhancing fine motor control.
- Interossei:
- Dorsal interossei allow abduction of fingers (spreading apart).
- Palmar interossei provide adduction of fingers (bringing together).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.