Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which muscle is responsible for abducting the thumb?
Which muscle is responsible for abducting the thumb?
- Adductor Pollicis
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis
- Opponens Pollicis
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis (correct)
What is the primary function of the Opponens Pollicis muscle?
What is the primary function of the Opponens Pollicis muscle?
- Extending the thumb
- Adducting the thumb
- Opposition of the thumb (correct)
- Flexing the thumb
Which nerve innervates all of the thenar muscles?
Which nerve innervates all of the thenar muscles?
- Ulnar nerve
- Median nerve (correct)
- Radial nerve
- Musculocutaneous nerve
Which muscle assists in flexing the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint?
Which muscle assists in flexing the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint?
Which of the following is not a thenar muscle?
Which of the following is not a thenar muscle?
How do the thenar muscles contribute to hand dexterity?
How do the thenar muscles contribute to hand dexterity?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the flexor pollicis brevis, deep head?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the flexor pollicis brevis, deep head?
What is the primary action performed by the opponens pollicis?
What is the primary action performed by the opponens pollicis?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for the abduction of the thumb?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for the abduction of the thumb?
Which function is associated with the capability of the thumb to move across the palm?
Which function is associated with the capability of the thumb to move across the palm?
The primary muscle responsible for adducting the thumb is?
The primary muscle responsible for adducting the thumb is?
Which function does NOT pertain to the thenar muscles?
Which function does NOT pertain to the thenar muscles?
Which intrinsic muscle of the hand is NOT typically classified with the thenar muscles?
Which intrinsic muscle of the hand is NOT typically classified with the thenar muscles?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Muscle Anatomy
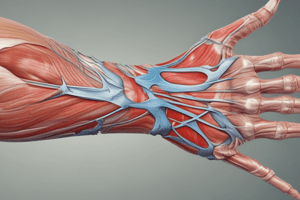
- The thenar muscles are a group of three intrinsic muscles located at the base of the thumb.
- These muscles include:
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Positioned on the radial side; responsible for abduction of the thumb.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Located below the abductor; assists in flexing the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint.
- Opponens Pollicis: Found deep to the other two; facilitates opposition of the thumb, allowing it to touch the other fingers.
Innervation
- All thenar muscles are innervated by the median nerve.
- The exception is the Adductor Pollicis, which, while not a thenar muscle, is relevant and innervated by the ulnar nerve.
Functions of Thenar Muscles
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Abducts the thumb, assisting in grasping and pinching.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Flexes the thumb, contributing to a strong grip.
- Opponens Pollicis: Enables opposition, which is critical for the thumb's unique range of motion and functionality in gripping objects.
- Overall, these muscles play a key role in thumb movements necessary for fine motor skills and hand dexterity.
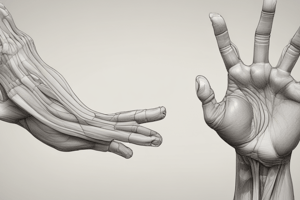
Muscle Anatomy
- Thenar muscles consist of three intrinsic muscles at the base of the thumb, critical for thumb movement.
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Located on the radial side, this muscle abducts the thumb, allowing it to move away from the hand.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Situated below the abductor, this muscle flexes the thumb at the metacarpophalangeal joint, essential for gripping.
- Opponens Pollicis: Positioned deep to the other two muscles, it enables the thumb's opposition, allowing it to touch other fingers, enhancing grasp capability.
Innervation
- All thenar muscles receive innervation primarily from the median nerve, which coordinates their movements.
- The Adductor Pollicis, while not classified as a thenar muscle, is innervated by the ulnar nerve, showcasing a distinct innervation pattern in the hand.
Functions of Thenar Muscles
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Essential for grasping and pinching; plays a crucial role in hand dexterity.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Vital for flexing the thumb, contributing significantly to a strong and effective grip.
- Opponens Pollicis: Facilitates opposition and enhances the thumb's unique motion range, critical for manipulating and gripping objects.
- Collectively, thenar muscles contribute to fine motor skills, underpinning many hand functions required in daily activities.
Muscle Anatomy
- Thenar muscles are situated at the base of the thumb in the palm, facilitating thumb movements.
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Responsible for abducting the thumb, moving it away from the hand.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Functions to flex the thumb, bringing it closer to the palm.
- Opponens Pollicis: Enables opposition, allowing the thumb to touch the other fingers, essential for grasping.
- Adductor Pollicis: Primarily adducts the thumb, bringing it towards the index finger, enhancing grip (not always classified within thenar muscles).
Innervation
- Median Nerve: Innervates crucial muscles including abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis (superficial head), and opponens pollicis, allowing thumb movement control.
- Ulnar Nerve: Innervates the deep head of flexor pollicis brevis and adductor pollicis, contributing to thumb adduction and flexion.
Functions Of Thenar Muscles
- Opposition: Essential for grasping and pinching, allowing thumb mobility across the palm.
- Abduction: Critical for moving the thumb away from the palm, vital for hand positioning.
- Flexion: Enables bending of the thumb toward the palm, enhancing grip strength.
- Adduction: Facilitates movement of the thumb towards the index finger for precision in tasks.
- Fine Motor Skills: Collectively, these muscles support intricate hand movements necessary for activities like writing and typing.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.