Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which muscle is primarily responsible for the opposition of the thumb?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for the opposition of the thumb?
- Adductor Pollicis
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis
- Opponens Pollicis (correct)
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis
What is the primary action of the Abductor Pollicis Brevis?
What is the primary action of the Abductor Pollicis Brevis?
- Flexing the thumb
- Rotating the thumb
- Abducting the thumb away from the palm (correct)
- Adducting the thumb towards the palm
Which nerve provides motor innervation to all the thenar muscles?
Which nerve provides motor innervation to all the thenar muscles?
- Musculocutaneous nerve
- Radial nerve
- Ulnar nerve
- Median nerve (correct)
Which of the following is NOT a thenar muscle?
Which of the following is NOT a thenar muscle?
Which thenar muscle assists in pinching movements through flexion?
Which thenar muscle assists in pinching movements through flexion?
Where do the thenar muscles originate?
Where do the thenar muscles originate?
What unique capability is enabled by the combined actions of the thenar muscles?
What unique capability is enabled by the combined actions of the thenar muscles?
Which thumb movement is facilitated primarily by the Opponens Pollicis?
Which thumb movement is facilitated primarily by the Opponens Pollicis?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Anatomy
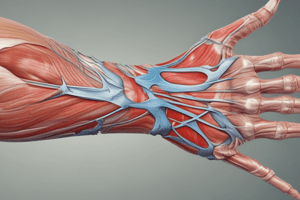
- The thenar muscles are a group of three intrinsic muscles located in the lateral aspect of the palm.
- They are responsible for the movement of the thumb.
- The three thenar muscles include:
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Located on the outer side; abducts the thumb.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Positioned next to the abductor; flexes the thumb.
- Opponens Pollicis: Deepest of the three; allows opposition of the thumb, enabling it to touch the other fingers.
- The thenar muscles originate from the tubercle of the scaphoid and trapezium bones and the flexor retinaculum.
Muscle Function
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Abducts the thumb away from the palm, crucial for grasping and holding objects.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Flexes the thumb at the carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints, aiding in pinching movements.
- Opponens Pollicis: Allows for the thumb's opposition, which is the ability to touch the tips of the other fingers, facilitating fine motor skills.
Innervation
- All thenar muscles are innervated by the median nerve.
- The exception is the adductor pollicis, which is innervated by the ulnar nerve.
- The median nerve provides motor control to the thenar muscles, enabling thumb movement and coordination.
Anatomy
- Thenar muscles comprise three intrinsic muscles located on the palm's lateral side, crucial for thumb movement.
- The three thenar muscles are:
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Abducts the thumb, positioned on the outer side.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Aids in thumb flexion, located adjacent to the abductor.
- Opponens Pollicis: The deepest muscle, responsible for opposition, enabling thumb contact with other fingers.
- Originates from the tubercle of the scaphoid and trapezium bones and the flexor retinaculum.
Muscle Function
- Abductor Pollicis Brevis: Essential for grasping and holding objects by moving the thumb away from the palm.
- Flexor Pollicis Brevis: Facilitates pinching movements by flexing the thumb at the carpometacarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints.
- Opponens Pollicis: Vital for fine motor skills, allowing the thumb to touch tips of other fingers through opposition.
Innervation
- All thenar muscles receive innervation from the median nerve, which controls thumb movement and coordination.
- The adductor pollicis is an exception, receiving innervation from the ulnar nerve.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.