Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the tendons and ligaments during standing and walking in relation to the arches of the foot?
What is the primary function of the tendons and ligaments during standing and walking in relation to the arches of the foot?
- To stabilize the arches and maintain their shape (correct)
- To rotate the foot during movement
- To absorb shock and distribute pressure
- To facilitate pronation and supination
Which of the following joints is not involved in the movement of the foot?
Which of the following joints is not involved in the movement of the foot?
- Tibiofemoral joint (correct)
- Metatarsophalangeal joint
- Subtalar joint
- Midtarsal joint
What is the term for the movement of the foot in which the sole of the foot faces inward?
What is the term for the movement of the foot in which the sole of the foot faces inward?
- Dorsiflexion
- Supination (correct)
- Pronation
- Eversion
Which arch of the foot is formed by the calcaneus, cuboid, cuneiform bones, and the bases of the first three metatarsal bones?
Which arch of the foot is formed by the calcaneus, cuboid, cuneiform bones, and the bases of the first three metatarsal bones?
What is the term for the muscles of the foot that are located within the foot itself?
What is the term for the muscles of the foot that are located within the foot itself?
Which nerve is responsible for the cutaneous distribution to the lateral aspect of the foot?
Which nerve is responsible for the cutaneous distribution to the lateral aspect of the foot?
What type of joint is the talonavicular joint?
What type of joint is the talonavicular joint?
Which ligament strengthens the floor of the talocalcaneonavicular joint?
Which ligament strengthens the floor of the talocalcaneonavicular joint?
What is the direction of the axis around which inversion and eversion take place?
What is the direction of the axis around which inversion and eversion take place?
What is the movement of the foot accompanied by plantar-flexion and adduction of the forefoot?
What is the movement of the foot accompanied by plantar-flexion and adduction of the forefoot?
What happens to the medial arch of the foot when it is in supination?
What happens to the medial arch of the foot when it is in supination?
What happens to the weight distribution of the body when the foot is in supination?
What happens to the weight distribution of the body when the foot is in supination?
What is the effect of supination on the hindfoot?
What is the effect of supination on the hindfoot?
What happens to the calcaneus when the foot is in supination?
What happens to the calcaneus when the foot is in supination?
Which muscle adjusts the line of pull of the long flexors to flex the toes along their long axis?
Which muscle adjusts the line of pull of the long flexors to flex the toes along their long axis?
What is the function of the lumbricals?
What is the function of the lumbricals?
Which muscle has a bifurcate tendon that inserts either side of the proximal phalanx of the hallux?
Which muscle has a bifurcate tendon that inserts either side of the proximal phalanx of the hallux?
What is the origin of the transverse head of the adductor hallucis?
What is the origin of the transverse head of the adductor hallucis?
Which muscle arises from the base of the 5th metatarsal bone?
Which muscle arises from the base of the 5th metatarsal bone?
What is the function of the plantar interossei muscles?
What is the function of the plantar interossei muscles?
Which layer of muscles contains the flexor hallucis brevis?
Which layer of muscles contains the flexor hallucis brevis?
What is the difference between the plantar and dorsal interossei muscles?
What is the difference between the plantar and dorsal interossei muscles?
What is the primary function of the long tendons from the leg in arch support?
What is the primary function of the long tendons from the leg in arch support?
Which of the following ligaments arises from the calcaneus and runs on the sole of the foot to the navicular bone?
Which of the following ligaments arises from the calcaneus and runs on the sole of the foot to the navicular bone?
Which muscle provides some strength and support to the transverse arch?
Which muscle provides some strength and support to the transverse arch?
What is the attachment point of the tibialis posterior tendon?
What is the attachment point of the tibialis posterior tendon?
What is the function of the tibialis posterior tendon in arch support?
What is the function of the tibialis posterior tendon in arch support?
Which ligaments hold up the lateral longitudinal set of bones?
Which ligaments hold up the lateral longitudinal set of bones?
Which of the following tendons provides support to the medial longitudinal arch?
Which of the following tendons provides support to the medial longitudinal arch?
What is the role of the peroneus longus tendon in arch support?
What is the role of the peroneus longus tendon in arch support?
What type of movement is possible at the metatarsophalangeal joint?
What type of movement is possible at the metatarsophalangeal joint?
What is the name of the joint that permits pronation and supination of the foot?
What is the name of the joint that permits pronation and supination of the foot?
What is the name of the joint referred to as the Lisfranc joint?
What is the name of the joint referred to as the Lisfranc joint?
What is the type of movement possible at the interphalangeal joints?
What is the type of movement possible at the interphalangeal joints?
What is the benefit of supination of the foot?
What is the benefit of supination of the foot?
What is the name of the surgeon who described the amputation procedure across the Lisfranc joint?
What is the name of the surgeon who described the amputation procedure across the Lisfranc joint?
What is the benefit of the movement at the metatarsophalangeal joint?
What is the benefit of the movement at the metatarsophalangeal joint?
What is the abbreviation used to refer to the interphalangeal joints?
What is the abbreviation used to refer to the interphalangeal joints?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
The Joints of the Foot
- The foot has several joints, including the subtalar joint, midtarsal joint, and joints of the forefoot.
- The subtalar joint is a complex joint that allows for inversion and eversion movements.
- The axis of the subtalar joint runs upwards and medially, and inversion is a clockwise rotation around this axis.
Supination of the Foot
- Supination is a movement that involves plantar flexion and adduction of the forefoot.
- When the foot is in supination, the intrinsic ligaments within the foot tighten, and the foot becomes a rigid lever.
- Supination is ideal for lifting the body off the ground during walking or running.
The Arches of the Foot
- The foot has three arches: medial longitudinal, lateral longitudinal, and transverse.
- The medial longitudinal arch is supported by the tibialis posterior and flexor hallucis longus tendons.
- The long tendons from the leg provide lift and support to the arches from above.
Joints of the Midfoot and Forefoot
- The talonavicular joint is a ball and socket joint.
- The calcaneocuboid joint allows for gliding movements.
- The tarsometatarsal joints are together referred to as the Lisfranc joint.
- The metatarsophalangeal joints are condyloid joints that allow for bi-axial movements.
- The interphalangeal joints are pure hinges.
Arch Support: Ligaments and Tendons
- The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament, or spring ligament, supports the medial longitudinal arch.
- The long and short plantar ligaments support the lateral longitudinal arch.
- The long tendons from the leg provide lift and support to the arches from above.
- The peroneal tendons support the lateral longitudinal arch.
- The deep flexor tendons support the medial longitudinal arch.
Muscles of the Sole of the Foot
- The second layer of muscles contains the lumbricals and flexor digitorum accessorius.
- The lumbricals flex the MTP joints and extend the interphalangeal joints.
- The third layer of muscles contains the flexor hallucis brevis, adductor hallucis, and flexor digiti minimi brevis.
- The fourth layer of muscles contains the plantar and dorsal interossei muscles.
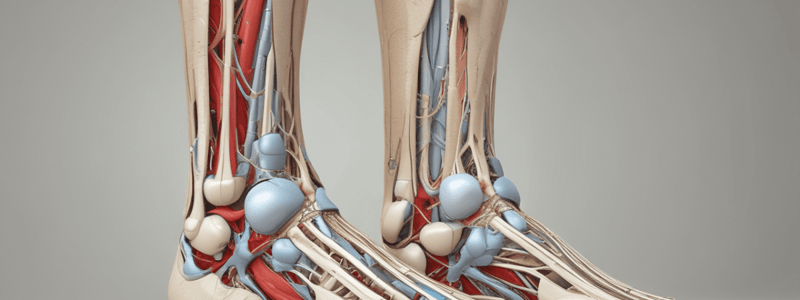
Neurovascular Structures
- The neurovascular structures in the foot include the nerves and blood vessels that supply the foot.
- The cutaneous distribution of the nerves is important to understand.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.