Podcast
Questions and Answers
¿Cuántos huesos hay en el dedo gordo?
¿Cuántos huesos hay en el dedo gordo?
- Cinco
- Cuatro
- Dos (correct)
- Tres
¿Qué ligamentos sostienen la articulación del tobillo?
¿Qué ligamentos sostienen la articulación del tobillo?
- Los ligamentos fibular y deltoides
- Los ligamentos talofibular y calcaneofibular
- Los ligamentos anterior y posterior talofibular, el calcaneofibular y el deltoides (correct)
- Los ligamentos fibular y metatarsiano
¿Cuál es la función de los músculos del pie?
¿Cuál es la función de los músculos del pie?
- Sostener la estructura del pie
- Movilizar el tobillo
- Permitirnos standing, caminar y realizar actividades (correct)
- Controlar la temperatura del pie
¿Cuál es la articulación que se forma entre los huesos metatarsianos y los huesos proximales de cada dedo?
¿Cuál es la articulación que se forma entre los huesos metatarsianos y los huesos proximales de cada dedo?
¿Por qué es importante entender la estructura anatómica compleja del pie?
¿Por qué es importante entender la estructura anatómica compleja del pie?
¿Cuál es la función principal de los músculos plantar flexores en el pie?
¿Cuál es la función principal de los músculos plantar flexores en el pie?
¿Cuál es el nombre del hueso que se encuentra en la articulación del tobillo?
¿Cuál es el nombre del hueso que se encuentra en la articulación del tobillo?
¿Cuál es la función de los músculos evertores en el pie?
¿Cuál es la función de los músculos evertores en el pie?
¿Cuántos huesos hay en el pie?
¿Cuántos huesos hay en el pie?
¿Cuál es la función de los músculos dorsiflexores en el pie?
¿Cuál es la función de los músculos dorsiflexores en el pie?
¿Cuál es el nombre de la articulación que se encuentra en el tobillo?
¿Cuál es el nombre de la articulación que se encuentra en el tobillo?
Flashcards
Plantar Flexors
Plantar Flexors
Muscles that pull the foot downward, important for heel strike
Dorsiflexors
Dorsiflexors
Muscles that raise the front of the foot, for propulsion
Inverters
Inverters
Muscles supporting the foot's arch, for stability
Evertors
Evertors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abductors
Abductors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankle Joint
Ankle Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phalanges
Phalanges
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hallux
Hallux
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsophalangeal Joints
Metatarsophalangeal Joints
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot Bones
Foot Bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot Muscles
Foot Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Foot Anatomy: Exploring the Muscles, Ankle Structure, and Toe Anatomy
Foot Muscles
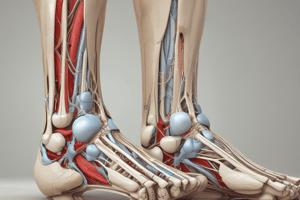
The foot is a complex anatomic structure that includes 26 bones and 29 muscles responsible for movement and stability. The primary muscles that contribute to foot function include the plantar flexors, dorsiflexors, inverters, evertors, and abductors.
-
Plantar flexors: These muscles, such as the gastrocnemius, soleus, and tibialis posterior, pull the foot downward, allowing for heel strike during walking or running.
-
Dorsiflexors: These muscles, such as the extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus, raise the front of the foot, aiding in propulsion during gait.
-
Inverters: These muscles, such as the tibialis anterior and peroneus longus, strengthen the arch of the foot, maintaining its stability during movement.
-
Evertors: These muscles, such as the peroneus brevis and fibularis longus, cause the foot to turn outward, assisting in weight distribution during gait.
-
Abductors: These muscles, such as the peroneus longus and brevis, pull the foot laterally, helping to maintain foot position during movement.
Ankle Structure
The ankle joint, also known as the tibiotalar joint, is formed by the distal tibia, distal fibula, and talus. This joint is responsible for allowing foot movement and providing stability during activities such as walking and running. The ankle joint is supported by numerous ligaments, including the anterior and posterior talofibular ligaments, the calcaneofibular ligament, and the deltoid ligament.
Toe Anatomy
The foot is also comprised of 14 phalanges, which can be further divided into the proximal, middle, and distal phalanges. The big toe, or hallux, contains only two phalanges: proximal and distal. The metatarsal-phalangeal joints are the joints between the metatarsal bones and the proximal phalanges of each toe, forming the ball of the foot.
Conclusion
Understanding the complex anatomic structure of the foot, including the muscles, ankle structure, and toe anatomy, is crucial for maintaining foot health and preventing injuries. By recognizing the importance of each component, we can better appreciate the intricate mechanisms that allow us to stand, walk, and engage in various activities.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.