Podcast
Questions and Answers
How many tarsal bones are present in the foot?
How many tarsal bones are present in the foot?
- 14
- 12
- 5
- 7 (correct)
Which of the following bones is NOT classified as a tarsal bone?
Which of the following bones is NOT classified as a tarsal bone?
- Metacarpal (correct)
- Calcaneus
- Cuneiform
- Cuboid
What type of joint is the ankle joint classified as?
What type of joint is the ankle joint classified as?
- Fibrous joint
- Hinge joint (correct)
- Ball and socket joint
- Pivot joint
Which bones articulate at the ankle joint?
Which bones articulate at the ankle joint?
How many total phalanges are found in the foot?
How many total phalanges are found in the foot?
What type of fracture requires both internal and/or external fixation?
What type of fracture requires both internal and/or external fixation?
Which joint allows for gliding and rotation, facilitating inversion movement?
Which joint allows for gliding and rotation, facilitating inversion movement?
What describes the action of dorsiflexion at the ankle?
What describes the action of dorsiflexion at the ankle?
Which muscles are primarily responsible for the inversion of the foot?
Which muscles are primarily responsible for the inversion of the foot?
What forms the longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot?
What forms the longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot?
Which structures provide support to the arches of the foot?
Which structures provide support to the arches of the foot?
What is the primary function of the extensor retinacula?
What is the primary function of the extensor retinacula?
Which injury is commonly associated with the lateral collateral ligament of the ankle?
Which injury is commonly associated with the lateral collateral ligament of the ankle?
Which movement does eversion primarily involve?
Which movement does eversion primarily involve?
What is a significant component of the neurovascular structure in the sole of the foot?
What is a significant component of the neurovascular structure in the sole of the foot?
What are the primary functions of the arches of the foot?
What are the primary functions of the arches of the foot?
Which bones are involved in the medial part of the longitudinal arch?
Which bones are involved in the medial part of the longitudinal arch?
What structure primarily maintains the arches of the foot?
What structure primarily maintains the arches of the foot?
What is the function of the plantar aponeurosis?
What is the function of the plantar aponeurosis?
Which ligaments are associated with the medial and lateral parts of the longitudinal arch?
Which ligaments are associated with the medial and lateral parts of the longitudinal arch?
Which of the following nerves provides sensation to the sole of the foot?
Which of the following nerves provides sensation to the sole of the foot?
How many layers of muscles are organized in the sole of the foot?
How many layers of muscles are organized in the sole of the foot?
What is the role of deep fascia in the sole of the foot?
What is the role of deep fascia in the sole of the foot?
What does the Medial Plantar Nerve provide cutaneous sensation to?
What does the Medial Plantar Nerve provide cutaneous sensation to?
Which artery is larger and passes deep to muscles in the sole of the foot?
Which artery is larger and passes deep to muscles in the sole of the foot?
What structure do the medial and lateral plantar veins accompany?
What structure do the medial and lateral plantar veins accompany?
What does the Lateral Plantar Nerve primarily supply?
What does the Lateral Plantar Nerve primarily supply?
What is located midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic symphysis?
What is located midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic symphysis?
Which artery forms the deep plantar arch?
Which artery forms the deep plantar arch?
Which nerves provide motor branches to muscles in the sole of the foot?
Which nerves provide motor branches to muscles in the sole of the foot?
What joins with the Lateral Plantar Artery at the first intermetatarsal space?
What joins with the Lateral Plantar Artery at the first intermetatarsal space?
Where is the small saphenous vein positioned in relation to the lateral malleolus?
Where is the small saphenous vein positioned in relation to the lateral malleolus?
Which vein drains directly into the femoral vein?
Which vein drains directly into the femoral vein?
What happens to the popliteal vein as it passes into the adductor hiatus?
What happens to the popliteal vein as it passes into the adductor hiatus?
Which nerve is a branch of the common fibular nerve?
Which nerve is a branch of the common fibular nerve?
Which structure is found on the medial side of the dorsal venous arch?
Which structure is found on the medial side of the dorsal venous arch?
What characterizes the deep veins of the lower limb?
What characterizes the deep veins of the lower limb?
What is the fate of the femoral vein when it passes under the inguinal ligament?
What is the fate of the femoral vein when it passes under the inguinal ligament?
Which nerve is specifically responsible for sensation in the back of the thigh?
Which nerve is specifically responsible for sensation in the back of the thigh?
What role do perforating veins play in the venous system of the lower limb?
What role do perforating veins play in the venous system of the lower limb?
Where do deep veins of the leg primarily drain?
Where do deep veins of the leg primarily drain?
Which tarsal bone articulates with the tibia and fibula at the ankle joint?
Which tarsal bone articulates with the tibia and fibula at the ankle joint?
What is the primary function of the tarsal bones?
What is the primary function of the tarsal bones?
Which of the following accurately describes the ankle joint's movement capabilities?
Which of the following accurately describes the ankle joint's movement capabilities?
Which of the following bones is NOT a part of the tarsal bones?
Which of the following bones is NOT a part of the tarsal bones?
How many phalanges are there in the foot?
How many phalanges are there in the foot?
What kind of fracture is characterized by multiple fractures of the tibia due to high axial forces?
What kind of fracture is characterized by multiple fractures of the tibia due to high axial forces?
Which tarsal joint is specifically responsible for allowing gliding and rotation involved in inversion?
Which tarsal joint is specifically responsible for allowing gliding and rotation involved in inversion?
What action is defined as moving the top of the foot towards the leg?
What action is defined as moving the top of the foot towards the leg?
Which muscles are primarily responsible for the eversion movement of the foot?
Which muscles are primarily responsible for the eversion movement of the foot?
What structure provides a pathway for tendons and nerves on the medial side of the ankle?
What structure provides a pathway for tendons and nerves on the medial side of the ankle?
Which artery contributes primarily to the vascular supply of the sole of the foot?
Which artery contributes primarily to the vascular supply of the sole of the foot?
What imaging technique is commonly used to interpret abnormalities in the foot and ankle joint?
What imaging technique is commonly used to interpret abnormalities in the foot and ankle joint?
Which veins accompany the corresponding arteries in the sole of the foot?
Which veins accompany the corresponding arteries in the sole of the foot?
Which aspect of the foot's vascularization forms the plantar arch?
Which aspect of the foot's vascularization forms the plantar arch?
Which nerves are primarily responsible for providing motor branches to the muscles in the sole of the foot?
Which nerves are primarily responsible for providing motor branches to the muscles in the sole of the foot?
What occurs during an inversion sprain of the ankle?
What occurs during an inversion sprain of the ankle?
What stabilizes the ankle joint?
What stabilizes the ankle joint?
Which ligament is injured first in an inversion ankle sprain?
Which ligament is injured first in an inversion ankle sprain?
What type of fracture is a bimalleolar ankle fracture also known as?
What type of fracture is a bimalleolar ankle fracture also known as?
Which component characterizes the lateral ligament of the ankle?
Which component characterizes the lateral ligament of the ankle?
What causes a Pott’s fracture during an everted foot movement?
What causes a Pott’s fracture during an everted foot movement?
What is the consequence of a severe inversion ankle sprain?
What is the consequence of a severe inversion ankle sprain?
Which anatomical feature of the talus contributes to joint stability when the foot is dorsiflexed?
Which anatomical feature of the talus contributes to joint stability when the foot is dorsiflexed?
What is the role of the plantar aponeurosis in the foot?
What is the role of the plantar aponeurosis in the foot?
Which ligament is described as a strong ligament that connects the sustentaculum tali to the inferior surface of the navicular?
Which ligament is described as a strong ligament that connects the sustentaculum tali to the inferior surface of the navicular?
What is included in the medial part of the longitudinal arch?
What is included in the medial part of the longitudinal arch?
Which of the following best describes the transverse arch of the foot?
Which of the following best describes the transverse arch of the foot?
Which nerves provide sensation to the plantar aspect of the foot?
Which nerves provide sensation to the plantar aspect of the foot?
What comprises the lateral part of the longitudinal arch?
What comprises the lateral part of the longitudinal arch?
Which structure functions to absorb and distribute downward forces during standing and movement?
Which structure functions to absorb and distribute downward forces during standing and movement?
What is the drainage path of the small saphenous vein?
What is the drainage path of the small saphenous vein?
What structure accompanies the deep veins in the lower limb?
What structure accompanies the deep veins in the lower limb?
Which of the following statements about the great saphenous vein is true?
Which of the following statements about the great saphenous vein is true?
Where does the popliteal vein become the femoral vein?
Where does the popliteal vein become the femoral vein?
What characterizes the common fibular nerve?
What characterizes the common fibular nerve?
Which nerve provides sensation to the lateral aspect of the calf?
Which nerve provides sensation to the lateral aspect of the calf?
Which of the following is true about the blood supply of the deep veins in the lower limb?
Which of the following is true about the blood supply of the deep veins in the lower limb?
Which neurite structure is responsible for producing sensation in the back of the thigh?
Which neurite structure is responsible for producing sensation in the back of the thigh?
What happens to the femoral vein when it passes underneath the inguinal ligament?
What happens to the femoral vein when it passes underneath the inguinal ligament?
Which of the following tarsal bones is primarily responsible for articulation at the ankle joint?
Which of the following tarsal bones is primarily responsible for articulation at the ankle joint?
Which movement is primarily restricted by the anatomical structure of the ankle joint?
Which movement is primarily restricted by the anatomical structure of the ankle joint?
What is the primary artery involved in the vascular supply of the sole of the foot?
What is the primary artery involved in the vascular supply of the sole of the foot?
Which bones make up the metatarsal structure of the foot?
Which bones make up the metatarsal structure of the foot?
Which group of bones directly articulates with the talus?
Which group of bones directly articulates with the talus?
Which structure is primarily responsible for maintaining the stability of the plantar arch?
Which structure is primarily responsible for maintaining the stability of the plantar arch?
In terms of structure, how are phalanges categorized in the foot?
In terms of structure, how are phalanges categorized in the foot?
Which of the following assessments is crucial for understanding peripheral pulses in the lower limb?
Which of the following assessments is crucial for understanding peripheral pulses in the lower limb?
What is the main function of the saphenous vein in the vascular system of the lower limb?
What is the main function of the saphenous vein in the vascular system of the lower limb?
Which imaging technique is most useful for interpreting the vascular anatomy of the ankle joint?
Which imaging technique is most useful for interpreting the vascular anatomy of the ankle joint?
Which of the following structures primarily supports the arches of the foot?
Which of the following structures primarily supports the arches of the foot?
What action occurs primarily at the subtalar joint during foot inversion?
What action occurs primarily at the subtalar joint during foot inversion?
Which neurovascular structure is located in the tarsal tunnel?
Which neurovascular structure is located in the tarsal tunnel?
Which injury is specifically mentioned as occurring to the lateral collateral ligament of the ankle?
Which injury is specifically mentioned as occurring to the lateral collateral ligament of the ankle?
What is the primary function of the extensor retinacula in the lower limb?
What is the primary function of the extensor retinacula in the lower limb?
What stabilizes the ankle joint by connecting the fibula and tibia to the tarsal bones?
What stabilizes the ankle joint by connecting the fibula and tibia to the tarsal bones?
In which type of ankle sprain are the lateral ligaments most commonly affected?
In which type of ankle sprain are the lateral ligaments most commonly affected?
Which ligament is typically injured first in an ankle inversion sprain?
Which ligament is typically injured first in an ankle inversion sprain?
What is a characteristic feature of the medial (deltoid) ligament of the ankle?
What is a characteristic feature of the medial (deltoid) ligament of the ankle?
Which event typically leads to a Pott's fracture?
Which event typically leads to a Pott's fracture?
What is the result of overstretching the ligaments of the ankle?
What is the result of overstretching the ligaments of the ankle?
Which ligament is not part of the lateral ligament complex of the ankle?
Which ligament is not part of the lateral ligament complex of the ankle?
What happens during the mechanical response of the ankle during dorsiflexion?
What happens during the mechanical response of the ankle during dorsiflexion?
What is the primary role of the plantar aponeurosis?
What is the primary role of the plantar aponeurosis?
Which structure is included in the lateral part of the longitudinal arch?
Which structure is included in the lateral part of the longitudinal arch?
What component is essential for the maintenance of foot arches?
What component is essential for the maintenance of foot arches?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the sole of the foot?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the sole of the foot?
Which component primarily acts at the junction of tarsals with metatarsals?
Which component primarily acts at the junction of tarsals with metatarsals?
Which of the following plantar ligaments connects the calcaneus to the cuboid and the bases of the 2-5 metatarsal?
Which of the following plantar ligaments connects the calcaneus to the cuboid and the bases of the 2-5 metatarsal?
Which nerves provide cutaneous sensation to the lateral and medial aspects of the sole of the foot?
Which nerves provide cutaneous sensation to the lateral and medial aspects of the sole of the foot?
Which ligaments support the medial and lateral parts of the foot's longitudinal arch?
Which ligaments support the medial and lateral parts of the foot's longitudinal arch?
Which statement accurately describes the position of the small saphenous vein?
Which statement accurately describes the position of the small saphenous vein?
What is the correct pathway of the great saphenous vein?
What is the correct pathway of the great saphenous vein?
Which statement describes the relationship between deep veins and arteries in the lower limb?
Which statement describes the relationship between deep veins and arteries in the lower limb?
How does the popliteal vein change as it travels into the adductor hiatus?
How does the popliteal vein change as it travels into the adductor hiatus?
Which nerve is responsible for sensation in the back of the thigh?
Which nerve is responsible for sensation in the back of the thigh?
What is the fate of the femoral vein after it passes underneath the inguinal ligament?
What is the fate of the femoral vein after it passes underneath the inguinal ligament?
Which structure is found between the tendons of EHL and FDL?
Which structure is found between the tendons of EHL and FDL?
Which of the following nerves arise from the common fibular nerve?
Which of the following nerves arise from the common fibular nerve?
What is the significance of perforating veins in the venous system of the lower limb?
What is the significance of perforating veins in the venous system of the lower limb?
Which statement best describes the course of the tibial nerve?
Which statement best describes the course of the tibial nerve?
Flashcards
Ankle Joint Osteology
Ankle Joint Osteology
The study of the bones that make up the ankle joint, their structure, and how they contribute to its function.
Foot Arches
Foot Arches
The curved structures in the foot that provide support and distribute weight.
Inversion/Eversion
Inversion/Eversion
Foot movements; inversion is turning the sole inward, and eversion is turning the sole outward.
Peripheral Pulses
Peripheral Pulses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tarsal Tunnel Anatomy
Tarsal Tunnel Anatomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tarsal bones
Tarsal bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal bones
Metatarsal bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phalanges
Phalanges
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankle joint
Ankle joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Talus
Talus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Talus Fracture
Talus Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pilon Fracture
Pilon Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subtalar Joint
Subtalar Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midtarsal Joint
Midtarsal Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse arch
Transverse arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Longitudinal arch
Longitudinal arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Long plantar ligament
Long plantar ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantar aponeurosis
Plantar aponeurosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial plantar nerve
Medial plantar nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral plantar nerve
Lateral plantar nerve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Plantar Arch
Deep Plantar Arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Plantar Artery
Medial Plantar Artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Plantar Artery
Lateral Plantar Artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Tibial Artery Branches
Posterior Tibial Artery Branches
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midinguinal Point
Midinguinal Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Popliteal Fossa
Popliteal Fossa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palpable pulse b/w malleoli?
Palpable pulse b/w malleoli?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Small saphenous vein path?
Small saphenous vein path?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Great saphenous vein path?
Great saphenous vein path?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep veins and arteries?
Deep veins and arteries?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep veins of the leg --> ?
Deep veins of the leg --> ?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Popliteal vein --> ?
Popliteal vein --> ?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral vein --> ?
Femoral vein --> ?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common fibular nerve origin?
Common fibular nerve origin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibial nerve origin?
Tibial nerve origin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Saphenous nerve origin?
Saphenous nerve origin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantar Arch
Plantar Arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tarsal Tunnel
Tarsal Tunnel
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dorsal Venous Arch
Dorsal Venous Arch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Saphenous Veins
Saphenous Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phalanges of the Foot
Phalanges of the Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Talus Bone
Talus Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Malleolus Fracture
Lateral Malleolus Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibula - What's its function?
Fibula - What's its function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Ligament - What does it do?
Lateral Ligament - What does it do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Ligament - How does it work?
Medial Ligament - How does it work?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inversion Sprain - What's the injury type?
Inversion Sprain - What's the injury type?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eversion Sprain - What's the difference?
Eversion Sprain - What's the difference?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pott’s Fracture - What is it?
Pott’s Fracture - What is it?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture - How is it related to ligaments?
Avulsion Fracture - How is it related to ligaments?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankle Sprains - What's important to remember?
Ankle Sprains - What's important to remember?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot Arches: How many?
Foot Arches: How many?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Longitudinal Arch: Two Parts?
Longitudinal Arch: Two Parts?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantar Aponeurosis: Function?
Plantar Aponeurosis: Function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantar Ligaments: Which one is the 'spring'?
Plantar Ligaments: Which one is the 'spring'?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Long Plantar Ligament: Where is it?
Long Plantar Ligament: Where is it?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sole of the Foot: Innervation?
Sole of the Foot: Innervation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot Muscles: How many layers?
Foot Muscles: How many layers?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse Arch: Where do we find it?
Transverse Arch: Where do we find it?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palpable Pulse Location
Palpable Pulse Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Veins of the Leg Drain Into?
Deep Veins of the Leg Drain Into?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Popliteal Vein Becomes?
Popliteal Vein Becomes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Vein Becomes?
Femoral Vein Becomes?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankle Joint: What bones are involved?
Ankle Joint: What bones are involved?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot Arches: What are their functions?
Foot Arches: What are their functions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inversion/Eversion: What makes these movements?
Inversion/Eversion: What makes these movements?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral Pulses: Where are they located?
Peripheral Pulses: Where are they located?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tarsal Tunnel: What's inside?
Tarsal Tunnel: What's inside?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tarsal Bones: How many?
Tarsal Bones: How many?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metatarsal Bones: Their role?
Metatarsal Bones: Their role?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phalanges: What are they?
Phalanges: What are they?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Talus Bone: Function?
Talus Bone: Function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibula Articulation
Fibula Articulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankle Joint Stability
Ankle Joint Stability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankle Ligaments: Lateral
Ankle Ligaments: Lateral
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ankle Ligaments: Medial
Ankle Ligaments: Medial
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inversion Sprain
Inversion Sprain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eversion Sprain
Eversion Sprain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pott's Fracture
Pott's Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avulsion Fracture
Avulsion Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foot Arches: Function?
Foot Arches: Function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plantar Calcaneonavicular Ligament: What is it called?
Plantar Calcaneonavicular Ligament: What is it called?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transverse Arch: Where is it?
Transverse Arch: Where is it?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Ankle, Foot, Peripheral Pulses and Venous Drainage of the Lower Limb
- The foot is composed of 7 tarsal bones, 5 metatarsal bones, and 14 phalanges.
- The ankle joint is a synovial joint involving the talus of the foot and the distal ends of the tibia and fibula.
- The ankle joint allows hinge-like dorsi- and plantarflexion.
- The articular surface is covered by hyaline cartilage. The talus is wider anteriorly than posteriorly, which makes the joint more stable when dorsiflexed.
- The ankle is stabilised by medial and lateral ligaments.
- The lateral ligament is composed of three separate ligaments: anterior talofibular, calcaneofibular, and posterior talofibular ligaments.
- The medial (deltoid) ligament of the ankle is large, strong, and triangular-shaped, composed of four separate ligaments.
- Ankle sprains occur when ligaments are overstretched but not completely ruptured.
- Inversion (inward) sprains primarily stretch the lateral ligaments. Eversion sprains (outward), less common, stretch the medial ligaments.
- Pott's fracture-bimalleolar ankle fractures involve the foot forcefully everting, medial ligament pulling on the medial malleolus, and talus moving laterally, causing lateral malleolus fracture.
- A pilon fracture is a multiple fracture of the tibia, often caused by high axial forces, potentially involving the talus or fibula, and requiring fixation.
- Tarsal joints include the subtalar, talocalcaneonavicular, calcaneocuboid joints, and midtarsal/inter/transverse tarsal joints. Movements include inversion and eversion.
- The tarsal tunnel is on the medial side of the ankle, between the tarsal bones and the flexor retinaculum.
- Movements at the ankle include dorsiflexion (moving the top of the foot towards the leg), plantarflexion (moving the plantar surface of the foot away from the leg), inversion (directing the sole of the foot medially), and eversion (directing the sole of the foot laterally).
- The arches of the foot (longitudinal and transverse) absorb and distribute downward forces during standing and movement. The medial part of the longitudinal arch involves the calcaneus, talus, navicular, cuneiforms, and first three metatarsals.
- The lateral part of the longitudinal arch involves the calcaneus, cuboid, and lateral two metatarsals. The transverse arch is formed by the junction of the tarsals with the metatarsals, including the cuboid and cuneiforms.
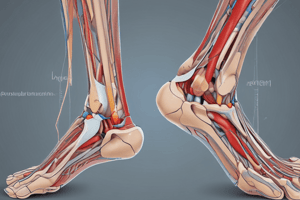
- The sole of the foot has thick skin, firmly attached to fascia, containing plantar nerves, and sweat glands. The plantar aponeurosis protects the neurovascular bundle and helps maintain arches. Planter ligaments include strong ligaments originating between the calcaneus, cuboid, and metatarsal bases, and connecting the calcaneus and navicular.
- The sole of the foot is organized into four layers of muscles. The tibial nerve branches into medial and lateral plantar nerves, supplying motor and sensory functions to the muscles in the sole.
- Peripheral pulses can be palpated in various locations in the lower limb, including the femoral, popliteal, posterior tibial, and dorsalis pedis pulses.
- Superficial veins of the lower limb include the small saphenous vein (lateral side) and great saphenous vein (medial side). These veins drain into the popliteal and femoral veins, respectively.
- Deep veins accompany arteries, connecting superficial and deep veins through perforating veins and draining into the popliteal vein, which becomes the femoral vein. The femoral vein becomes the external iliac vein when passing under the inguinal ligament.
- The nerves related to the lower limb discussed include superficial and deep fibular, tibial nerves, saphenous nerve, and multiple branches and variations.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.