Podcast
Questions and Answers
What regulates the activity of citrate synthase?
What regulates the activity of citrate synthase?
- Long-chain fatty acyl-CoA (correct)
- NADH
- ADP
- NADPH
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate?
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate?
- Pyruvate carboxylase (correct)
- Citrate synthase
- Succinate dehydrogenase
- Malate dehydrogenase
What is the fate of oxaloacetate released by citrate lyase?
What is the fate of oxaloacetate released by citrate lyase?
- It is reduced to malate. (correct)
- It directly reenters the mitochondrion.
- It is converted to citrate.
- It is phosphorylated.
Which molecule provides half of the NADPH required for fatty acid synthesis?
Which molecule provides half of the NADPH required for fatty acid synthesis?
Which vitamin coenzyme is utilized by pyruvate carboxylase?
Which vitamin coenzyme is utilized by pyruvate carboxylase?
What is the primary role of the citric acid cycle in metabolism?
What is the primary role of the citric acid cycle in metabolism?
Which substance is primarily depleted in hyperammonemia, causing impaired function of the citric acid cycle?
Which substance is primarily depleted in hyperammonemia, causing impaired function of the citric acid cycle?
Which enzyme is primarily responsible for converting pyruvate to acetyl-CoA?
Which enzyme is primarily responsible for converting pyruvate to acetyl-CoA?
What is an anaplerotic reaction in the context of the citric acid cycle?
What is an anaplerotic reaction in the context of the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following vitamins is known to function as a coenzyme in the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following vitamins is known to function as a coenzyme in the citric acid cycle?
What is the main function of the citric acid cycle besides ATP formation?
What is the main function of the citric acid cycle besides ATP formation?
Which metabolic pathway involves both anabolic and catabolic processes?
Which metabolic pathway involves both anabolic and catabolic processes?
What type of phosphorylation occurs during the reactions of the citric acid cycle?
What type of phosphorylation occurs during the reactions of the citric acid cycle?
The citric acid cycle is often described as amphibolic. What does this mean?
The citric acid cycle is often described as amphibolic. What does this mean?
What activates the dehydrogenases in the citric acid cycle?
What activates the dehydrogenases in the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following ratios reflects the energy status of the cell during the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following ratios reflects the energy status of the cell during the citric acid cycle?
How does the availability of oxidized cofactors influence the activity of the citric acid cycle?
How does the availability of oxidized cofactors influence the activity of the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following substances is a key product of the citric acid cycle that can be used for fatty acid synthesis?
Which of the following substances is a key product of the citric acid cycle that can be used for fatty acid synthesis?
Which metabolic pathways can produce intermediates for the citric acid cycle?
Which metabolic pathways can produce intermediates for the citric acid cycle?
Which vitamin coenzyme is involved in the decarboxylation processes of the citric acid cycle?
Which vitamin coenzyme is involved in the decarboxylation processes of the citric acid cycle?
What term refers to the balance of precursor and product molecules in the citric acid cycle?
What term refers to the balance of precursor and product molecules in the citric acid cycle?
Which enzyme of the citric acid cycle is most directly linked to the generation of NADH?
Which enzyme of the citric acid cycle is most directly linked to the generation of NADH?
During high energy demand in muscle contraction, what process occurs to finally produce ATP?
During high energy demand in muscle contraction, what process occurs to finally produce ATP?
What is the role of Acetyl-CoA in the citric acid cycle?
What is the role of Acetyl-CoA in the citric acid cycle?
Which process is responsible for the generation of one ATP directly in the citric acid cycle?
Which process is responsible for the generation of one ATP directly in the citric acid cycle?
What is anaplerosis in the context of the citric acid cycle?
What is anaplerosis in the context of the citric acid cycle?
Which coenzyme is involved in the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA?
Which coenzyme is involved in the conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA?
Which of the following statements best describes the amphibolic nature of the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following statements best describes the amphibolic nature of the citric acid cycle?
Which enzyme is responsible for the isomerization of citrate to isocitrate?
Which enzyme is responsible for the isomerization of citrate to isocitrate?
The reduction of coenzymes in the respiratory chain leads to what process in the citric acid cycle?
The reduction of coenzymes in the respiratory chain leads to what process in the citric acid cycle?
Which metabolic pathway exemplifies cataplerosis from the citric acid cycle?
Which metabolic pathway exemplifies cataplerosis from the citric acid cycle?
What key feature characterizes the enzymes involved in the citric acid cycle?
What key feature characterizes the enzymes involved in the citric acid cycle?
Which vitamin coenzyme is primarily involved in the oxidative reactions of the citric acid cycle?
Which vitamin coenzyme is primarily involved in the oxidative reactions of the citric acid cycle?
What role does succinyl-CoA–acetoacetate-CoA transferase play in metabolism?
What role does succinyl-CoA–acetoacetate-CoA transferase play in metabolism?
Which vitamin is primarily linked with the coenzyme for the decarboxylation reaction in α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase?
Which vitamin is primarily linked with the coenzyme for the decarboxylation reaction in α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase?
What is a characteristic feature of the citric acid cycle regarding metabolic processes?
What is a characteristic feature of the citric acid cycle regarding metabolic processes?
What does the term 'cataplerosis' refer to in the context of metabolism?
What does the term 'cataplerosis' refer to in the context of metabolism?
In the context of the citric acid cycle, what is succinate oxidized to during its metabolism?
In the context of the citric acid cycle, what is succinate oxidized to during its metabolism?
Which of the following is involved in the synthesis of acetyl-CoA?
Which of the following is involved in the synthesis of acetyl-CoA?
What kind of reactions are primarily involved in the conversion of amino acids during the citric acid cycle?
What kind of reactions are primarily involved in the conversion of amino acids during the citric acid cycle?
Which compound serves as the substrate for the phosphorylation of ADP as per the citric acid cycle?
Which compound serves as the substrate for the phosphorylation of ADP as per the citric acid cycle?
Which key metabolic process is linked to the buildup of oxaloacetate?
Which key metabolic process is linked to the buildup of oxaloacetate?
What is the result of the dehydrogenation reaction catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase?
What is the result of the dehydrogenation reaction catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase?
What role do dehydrogenases play in the citric acid cycle?
What role do dehydrogenases play in the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following best describes anaplerosis in the context of the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following best describes anaplerosis in the context of the citric acid cycle?
Which factor influences the regulation of the citric acid cycle through energy status?
Which factor influences the regulation of the citric acid cycle through energy status?
Which statement best describes the citric acid cycle's role in metabolic pathways?
Which statement best describes the citric acid cycle's role in metabolic pathways?
What is the primary consequence of a change in calcium ion concentration during muscle contraction in relation to the citric acid cycle?
What is the primary consequence of a change in calcium ion concentration during muscle contraction in relation to the citric acid cycle?
What is the harmful effect of fluoroacetate in the metabolic pathway?
What is the harmful effect of fluoroacetate in the metabolic pathway?
Which cofactor is necessary for the decarboxylation reaction of isocitrate?
Which cofactor is necessary for the decarboxylation reaction of isocitrate?
What type of enzyme reduces ubiquinone in the electron transport chain?
What type of enzyme reduces ubiquinone in the electron transport chain?
What is a primary function of oxaloacetate in metabolic pathways?
What is a primary function of oxaloacetate in metabolic pathways?
Which reaction results from the oxidation of malate?
Which reaction results from the oxidation of malate?
What does the accumulation of isocitrate indicate in the citric acid cycle?
What does the accumulation of isocitrate indicate in the citric acid cycle?
How does the ratio of NADH to NAD+ influence the citric acid cycle?
How does the ratio of NADH to NAD+ influence the citric acid cycle?
What is an essential feature of isocitrate dehydrogenase isoenzymes found in the mitochondria?
What is an essential feature of isocitrate dehydrogenase isoenzymes found in the mitochondria?
How does hyperammonemia affect the citric acid cycle?
How does hyperammonemia affect the citric acid cycle?
Which of the following reactions in the citric acid cycle generates reducing equivalents?
Which of the following reactions in the citric acid cycle generates reducing equivalents?
Which aspect of the citric acid cycle is primarily affected by the availability of oxidized cofactors?
Which aspect of the citric acid cycle is primarily affected by the availability of oxidized cofactors?
What is the primary consequence of impaired ATP formation from the citric acid cycle in the central nervous system?
What is the primary consequence of impaired ATP formation from the citric acid cycle in the central nervous system?
Which function in metabolism is NOT associated with the citric acid cycle?
Which function in metabolism is NOT associated with the citric acid cycle?
In what way does the citric acid cycle contribute to fatty acid synthesis?
In what way does the citric acid cycle contribute to fatty acid synthesis?
Which process is directly linked to the regeneration of citric acid cycle intermediates?
Which process is directly linked to the regeneration of citric acid cycle intermediates?
What does an increase in ATP levels signify for the activity of citrate synthase?
What does an increase in ATP levels signify for the activity of citrate synthase?
How is malate formed from oxaloacetate in the mitochondrion?
How is malate formed from oxaloacetate in the mitochondrion?
What is a key characteristic of the citric acid cycle that supports both catabolism and anabolism?
What is a key characteristic of the citric acid cycle that supports both catabolism and anabolism?
What is a consequence of hyperammonemia in metabolic processes?
What is a consequence of hyperammonemia in metabolic processes?
What role does the NADH/NAD+ ratio play in the conversion of malate to pyruvate?
What role does the NADH/NAD+ ratio play in the conversion of malate to pyruvate?
What happens to citrate when both ATP and long-chain fatty acyl-CoA levels are high?
What happens to citrate when both ATP and long-chain fatty acyl-CoA levels are high?
Which component is crucial in determining the rate of citrate formation?
Which component is crucial in determining the rate of citrate formation?
How does citrate synthase activity change with varying availability of oxaloacetate?
How does citrate synthase activity change with varying availability of oxaloacetate?
What metabolic functions does the pyruvate carboxylase enzyme perform?
What metabolic functions does the pyruvate carboxylase enzyme perform?
What is the direct entry point for propionate into gluconeogenesis?
What is the direct entry point for propionate into gluconeogenesis?
Which enzyme is inhibited by its product, thereby influencing the transport of citrate?
Which enzyme is inhibited by its product, thereby influencing the transport of citrate?
Which metabolic cycle is responsible for the production of cytosolic acetyl-CoA for fatty acid synthesis?
Which metabolic cycle is responsible for the production of cytosolic acetyl-CoA for fatty acid synthesis?
What reaction must occur for citrate to be available for transport out of the mitochondrion?
What reaction must occur for citrate to be available for transport out of the mitochondrion?
Which of the following substances is formed as a result of the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase?
Which of the following substances is formed as a result of the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase?
Which pathway uses both the products from glycolysis and citric acid cycle for energy metabolism?
Which pathway uses both the products from glycolysis and citric acid cycle for energy metabolism?
What limits the availability of citrate for exporting from the mitochondrion?
What limits the availability of citrate for exporting from the mitochondrion?
Which product of the citric acid cycle plays a role in fatty acid synthesis?
Which product of the citric acid cycle plays a role in fatty acid synthesis?
During which reaction is acetyl-CoA specifically utilized in the citric acid cycle?
During which reaction is acetyl-CoA specifically utilized in the citric acid cycle?
Which enzyme facilitates the conversion of malate to oxaloacetate in the cytosol?
Which enzyme facilitates the conversion of malate to oxaloacetate in the cytosol?
Match the following components of the citric acid cycle with their respective functions:
Match the following components of the citric acid cycle with their respective functions:
Match the following terms related to the citric acid cycle with their definitions:
Match the following terms related to the citric acid cycle with their definitions:
Match the following enzymes with their reactions in the citric acid cycle:
Match the following enzymes with their reactions in the citric acid cycle:
Match the following metabolic processes to their descriptions:
Match the following metabolic processes to their descriptions:
Match the following coenzymes with their related functions in the citric acid cycle:
Match the following coenzymes with their related functions in the citric acid cycle:
Match the following substances with their roles in metabolism:
Match the following substances with their roles in metabolism:
Match the following enzymes with their respective reactions:
Match the following enzymes with their respective reactions:
Match the following compounds with their metabolic functions:
Match the following compounds with their metabolic functions:
Match the following ions with their roles in the citric acid cycle:
Match the following ions with their roles in the citric acid cycle:
Match the following reactions with their corresponding products:
Match the following reactions with their corresponding products:
Flashcards
Citric Acid Cycle
Citric Acid Cycle
A crucial metabolic pathway in mitochondria that oxidizes acetyl-CoA to carbon dioxide, generating energy-carrying molecules like NADH and FADH2.
Krebs Cycle
Krebs Cycle
Another name for the citric acid cycle.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
Yet another name for the citric acid cycle, highlighting the type of organic acids involved.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxidation
Oxidation
Signup and view all the flashcards
NADH and FADH2
NADH and FADH2
Signup and view all the flashcards
ATP
ATP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Citrate Synthase
Citrate Synthase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
Signup and view all the flashcards
α-ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Complex
α-ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Complex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperammonemia
Hyperammonemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anaplerotic Reactions
Anaplerotic Reactions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cataplerotic Reactions
Cataplerotic Reactions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxaloacetate
Oxaloacetate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fatty Acid Synthesis
Fatty Acid Synthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regulation
Regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electron Transport Chain
Electron Transport Chain
Signup and view all the flashcards
GTP
GTP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Coenzyme
Coenzyme
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
The Citric Acid Cycle: A Metabolic Hub
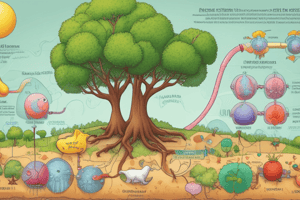
- The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle, is a vital metabolic pathway occurring within mitochondria.
- This cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins.
- The cycle oxidizes the acetyl moiety of acetyl-CoA to CO2, coupling this oxidation to the reduction of coenzymes such as NAD+ and FAD.
- These reduced coenzymes (NADH and FADH2) are then reoxidized in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, ultimately leading to the generation of ATP.
- The cycle also provides essential intermediates for various metabolic processes, including gluconeogenesis, amino acid synthesis, and fatty acid synthesis.
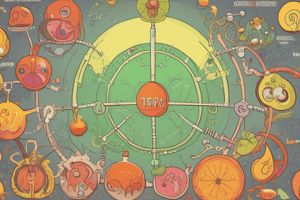
Citric Acid Cycle Reactions:
- The citric acid cycle begins with the condensation of acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate, forming citrate.
- Citrate is then isomerized to isocitrate.
- Isocitrate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to α-ketoglutarate, generating the first NADH.
- α-ketoglutarate is also oxidatively decarboxylated to succinyl-CoA, producing the second NADH.
- Succinyl-CoA is converted to succinate, generating GTP through substrate-level phosphorylation.
- Succinate is oxidized to fumarate, generating FADH2.
- Fumarate is hydrated to malate.
- Finally, malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate, producing the third NADH.
- The cycle completes a full turn with the regeneration of oxaloacetate.
The Citric Acid Cycle and Energy Production:
- Each turn of the citric acid cycle produces nine molecules of ATP via oxidative phosphorylation, and one ATP (or GTP) through substrate-level phosphorylation.
Regulation:
- The citric acid cycle is tightly regulated to ensure efficient energy production and cellular function.
- Key regulatory enzymes include citrate synthase, isocitrate dehydrogenase, and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
- ATP, NADH, and long-chain fatty acyl-CoA act as allosteric inhibitors of citrate synthase and isocitrate dehydrogenase, reflecting an energy-rich state.
- Conversely, ADP and Ca2+ act as allosteric activators, indicating an energy-demanding state.
Hyperammonemia and Implications:
- Hyperammonemia, an excess of ammonia in the blood, can severely impair citric acid cycle function.
- Hyperammonemia can occur due to liver disease or genetic defects in amino acid metabolism.
- High ammonia levels deplete citric acid cycle intermediates, such as α-ketoglutarate, by diverting them towards glutamate and glutamine synthesis.
- Ammonia also inhibits the oxidative decarboxylation of α-ketoglutarate.
- These effects lead to a decrease in ATP production and can cause severe neurologic deficits, including coma, convulsions, and even death.
Citric Acid Cycle
- The citric acid cycle is a key metabolic pathway located in the mitochondria
- It oxidizes the acetyl group of Acetyl-CoA to carbon dioxide
- This process is coupled to the reduction of coenzymes, which are then reoxidized in the electron transport chain
- This process is linked to the production of ATP
- The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins.
- The citric acid cycle can be regulated by the availability of certain vitamins and the energy status of a cell
- Hyperammonemia, a condition associated with advanced liver disease, can impair the citric acid cycle
- Hyperammonemia can be fatal due to impaired ATP production.
Citric Acid Cycle Reactions
- Acetyl-CoA joins with oxaloacetate to form citrate: Catalyzed by citrate synthase.
- Citrate is isomerized to isocitrate: Catalyzed by aconitase.
- Isocitrate is oxidized and decarboxylated to α-ketoglutarate: Catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase.
- α-ketoglutarate is oxidized and decarboxylated to succinyl-CoA: Catalyzed by α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
- Succinyl-CoA is converted to succinate: Catalyzed by succinyl-CoA synthetase.
- Succinate is oxidized to fumarate: Catalyzed by succinate dehydrogenase.
- Fumarate is hydrated to malate: Catalyzed by fumarase.
- Malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate: Catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase.
Citric Acid Cycle - Regulation
- Citrate synthase is inhibited by ATP and long-chain fatty acyl-CoA.
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase is activated by ADP and inhibited by ATP and NADH.
- α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex is regulated in the same way as pyruvate dehydrogenase.
- Succinate dehydrogenase is inhibited by oxaloacetate.
- The availability of oxaloacetate is controlled by malate dehydrogenase and depends on the [NADH]/[NAD+] ratio.
Citric Acid Cycle - Importance
- The citric acid cycle provides a pathway for the catabolism of amino acids.
- The citric acid cycle provides a pathway for the synthesis of certain amino acids.
- It is essential for gluconeogenesis.
- It is the major pathway for the formation of ATP.
- It is required for fatty acid synthesis.
Anaplerosis and Cataplerosis
- Anaplerosis refers to the replenishment of citric acid cycle intermediates.
- Cataplerosis refers to the removal of citric acid cycle intermediates.
- These processes are critical for maintaining the balance of the cycle.
Medical Importance
- Fluoroacetate poisoning: This poison is found in some plants and can be fatal to animals.
- Hyperammonemia: A condition associated with advanced liver disease, can impair the citric acid cycle leading to neurological damage.
- Impaired ATP Formation: Hyperammonemia leads to reduced formation of ATP, which is essential for energy production in the brain and other tissues.
Fatty Acid Synthesis
- The citric acid cycle provides citrate for the synthesis of fatty acids.
- Citrate is transported from the mitochondria to the cytosol where it is used for fatty acid synthesis.
- This pathway is essential for providing acetyl-CoA for fatty acid synthesis.
Vitamin Requirements
- Biotin: Required as a coenzyme for pyruvate carboxylase.
- Niacin: Required for NAD+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase.
- Riboflavin: Required for succinate dehydrogenase.
- Thiamine: Required for α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex.
Citric Acid Cycle Location
- Enzymes of the citric acid cycle are found in the mitochondrial matrix, either free or attached to the inner mitochondrial membrane and the crista membrane.
Citric Acid Cycle Function
- It serves as a central pathway for carbohydrate, lipid, and protein catabolism.
- The cycle must maintain a balance in the number of carbons entering and leaving.
- Acetyl-CoA (two carbon molecule) combines with oxaloacetate (four carbon molecule) to form citrate (six carbon molecule).
- During each turn of the cycle, citrate is converted back to oxaloacetate, and two carbons are released as CO2.
- Anaplerosis refers to the addition of carbon to the cycle, like pyruvate to oxaloacetate for gluconeogenesis.
- Cataplerosis is the removal of carbon from the cycle, such as oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate.
- Anaplerosis must equal cataplerosis to sustain the citric acid cycle.
Citric Acid Cycle Reactions
- Citrate Synthesis: Acetyl-CoA reacts with oxaloacetate catalyzed by citrate synthase to form citryl-CoA, which is hydrolyzed, releasing citrate and CoASH.
- Isomerization: Citrate is isomerized to isocitrate by aconitase through dehydration to cis-aconitate and rehydration to isocitrate.
- Oxidative Decarboxylation of Isocitrate: Isocitrate is dehydrogenated to oxalosuccinate, which is enzyme-bound and undergoes decarboxylation to α-ketoglutarate, catalyzed by isocitrate dehydrogenase.
- Oxidative Decarboxylation of α-ketoglutarate: α-ketoglutarate is converted to succinyl-CoA in a reaction catalyzed by α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, which requires cofactors like thiamin diphosphate, lipoate, NAD+, FAD, and CoA.
- Succinyl-CoA to Succinate: Succinyl-CoA is converted to succinate by succinate thiokinase, generating ATP or GTP through substrate-level phosphorylation.
- Succinate to Fumarate: Succinate is oxidized to fumarate by succinate dehydrogenase, reducing FAD to FADH2.
- Fumarate to Malate: Fumarate is hydrated to malate by fumarase.
- Malate to Oxaloacetate: Malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate by malate dehydrogenase, reducing NAD+ to NADH.
ATP Production
- One turn of the citric acid cycle generates a total of 10 ATPs.
- The cycle produces three NADH and one FADH2 molecules per acetyl-CoA oxidized.
- During oxidative phosphorylation, reoxidation of NADH yields ~2.5 ATP, and reoxidation of FADH2 yields ~1.5 ATPs.
- Substrate-level phosphorylation in the conversion of succinyl-CoA to succinate generates 1 ATP.
Regulation of the Citric Acid Cycle
- The citric acid cycle is primarily regulated by the availability of oxidized cofactors (NAD+).
- Regulation of individual enzymes:
- Citrate synthase is allosterically inhibited by ATP and long-chain fatty acyl-CoA.
- Isocitrate dehydrogenase is allosterically activated by ADP, counteracted by ATP and NADH.
- α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase is regulated similarly to pyruvate dehydrogenase.
- Succinate dehydrogenase is inhibited by oxaloacetate.
Vitamins and the Citric Acid Cycle
- Four B vitamins are essential for the citric acid cycle:
- Riboflavin (as FAD) is a cofactor for succinate dehydrogenase.
- Niacin (as NAD+) is an electron acceptor for isocitrate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and malate dehydrogenase.
- Thiamin (as thiamin diphosphate) is a cofactor for α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
- Biotin is a coenzyme for pyruvate carboxylase, which carboxylates pyruvate to oxaloacetate.
Citric Acid Cycle and Fatty Acid Synthesis
- Citrate, as a source of acetyl-CoA, can be transported to the cytosol for fatty acid synthesis.
- The accumulation of isocitrate inhibits aconitase, making citrate "free" to be transported to the cytosol.
- Malic enzyme, which converts malate to pyruvate, utilizes NADPH, a co-substrate in fatty acid synthesis.
Hyperammonemia
- Hyperammonemia, elevated ammonia levels in the blood, can occur in liver disease or genetic diseases of amino acid metabolism.
- Hyperammonemia depletes citric acid cycle intermediates by removing α-ketoglutarate for the synthesis of glutamate and glutamine.
- This depletion further decreases citric acid cycle flux and ATP generation.
- Ammonia inhibits the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, further reducing the citric acid cycle flux.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.