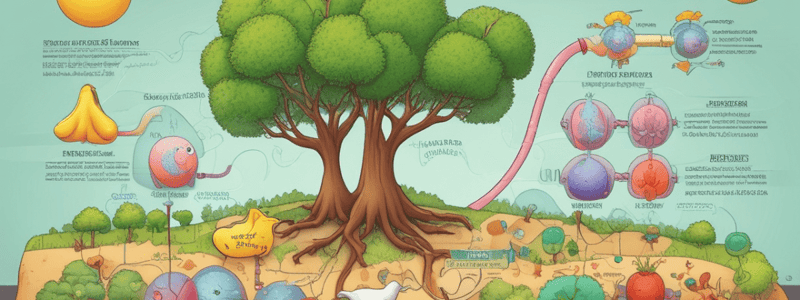
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the role of PFK1 in glycolysis?
What is the role of PFK1 in glycolysis?
- Controlling the irreversible step of glycolysis (correct)
- Acting as a promoter for glycolysis
- Inhibiting glucose entry into glycolysis
- Producing citrate in the citric acid cycle
Which molecules inhibit PFK1 in glycolysis?
Which molecules inhibit PFK1 in glycolysis?
- ATP and AMP
- AMP and citrate
- Insulin and glucagon
- Citrate and ATP (correct)
How does AMP affect PFK1 activity in glycolysis?
How does AMP affect PFK1 activity in glycolysis?
- Activates PFK1 (correct)
- Inhibits PFK1
- Converts PFK1 to ATP
- Enhances citrate production
What is the function of insulin in blood sugar regulation?
What is the function of insulin in blood sugar regulation?
How do hexokinase enzymes contribute to glycolysis?
How do hexokinase enzymes contribute to glycolysis?
Which molecules signal PFK1 to slow down glycolysis when cellular energy is abundant?
Which molecules signal PFK1 to slow down glycolysis when cellular energy is abundant?
What is the primary function of the citric acid cycle?
What is the primary function of the citric acid cycle?
What molecules carry high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain during cellular respiration?
What molecules carry high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain during cellular respiration?
Which scientist is honored by the alternative name 'Krebs cycle' for the citric acid cycle?
Which scientist is honored by the alternative name 'Krebs cycle' for the citric acid cycle?
What is the main role of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
What is the main role of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
How is acetyl CoA formed during cellular respiration?
How is acetyl CoA formed during cellular respiration?
Which process in cellular respiration results in the production of NADH?
Which process in cellular respiration results in the production of NADH?
What is the role of insulin in the body?
What is the role of insulin in the body?
Which hormone is responsible for converting stored glycogen back into glucose?
Which hormone is responsible for converting stored glycogen back into glucose?
In Diabetes Mellitus, what happens when insulin isn't functioning properly?
In Diabetes Mellitus, what happens when insulin isn't functioning properly?
What type of diabetes involves the body's immune system attacking insulin-producing cells?
What type of diabetes involves the body's immune system attacking insulin-producing cells?
How does glucagon help ensure a steady supply of energy to other cells in the body?
How does glucagon help ensure a steady supply of energy to other cells in the body?
What is the primary consequence of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in Diabetes Mellitus?
What is the primary consequence of abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in Diabetes Mellitus?
What is a common symptom of type 2 diabetes according to the text?
What is a common symptom of type 2 diabetes according to the text?
Why might unintended weight loss occur in individuals with diabetes?
Why might unintended weight loss occur in individuals with diabetes?
How do high blood sugar levels affect blood vessels and organs?
How do high blood sugar levels affect blood vessels and organs?
What is a key management strategy for diabetes according to the text?
What is a key management strategy for diabetes according to the text?
What are the long-term consequences of chronic high blood sugar levels?
What are the long-term consequences of chronic high blood sugar levels?
Why does elevated blood sugar levels in diabetes lead to cellular hunger?
Why does elevated blood sugar levels in diabetes lead to cellular hunger?
What is the main reason for the development of Type 1 diabetes?
What is the main reason for the development of Type 1 diabetes?
Which age group is Type 1 diabetes most likely to affect?
Which age group is Type 1 diabetes most likely to affect?
What distinguishes Type 1 diabetes from Type 2 diabetes in terms of insulin production?
What distinguishes Type 1 diabetes from Type 2 diabetes in terms of insulin production?
What is the primary cause of Type 2 diabetes?
What is the primary cause of Type 2 diabetes?
What do later stages of Type 2 diabetes involve regarding insulin production?
What do later stages of Type 2 diabetes involve regarding insulin production?
How does Type 2 diabetes differ from Type 1 diabetes in terms of prevalence?
How does Type 2 diabetes differ from Type 1 diabetes in terms of prevalence?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying