Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the average number of times a normal adult swallows per day?
What is the average number of times a normal adult swallows per day?
- 600 (correct)
- 1,000
- 100
- 300
What is the approximate time it takes for a bolus to pass from the oral cavity to the esophagus during normal deglutition?
What is the approximate time it takes for a bolus to pass from the oral cavity to the esophagus during normal deglutition?
- Less than 2 seconds (correct)
- Less than 1 second
- More than 5 seconds
- About 3 seconds
Which of the following is NOT involved in the swallowing mechanism?
Which of the following is NOT involved in the swallowing mechanism?
- Peripheral nervous system (correct)
- Cranial nerves
- Cervical nerve segments
- Medulla oblongata
What is the primary function of the swallowing center in the medulla oblongata?
What is the primary function of the swallowing center in the medulla oblongata?
What does research suggest about aspiration?
What does research suggest about aspiration?
Where is the base of the tongue located?
Where is the base of the tongue located?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the larynx?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of the larynx?
What is the function of the cricopharyngeal muscle?
What is the function of the cricopharyngeal muscle?
Which of these muscles helps to constrict the oropharynx?
Which of these muscles helps to constrict the oropharynx?
Which part of the pharynx is closest to the esophagus?
Which part of the pharynx is closest to the esophagus?
Which of these structures is NOT a part of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES)?
Which of these structures is NOT a part of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES)?
Which of the following is considered a function of the epiglottis?
Which of the following is considered a function of the epiglottis?
What is the location of the valleculae?
What is the location of the valleculae?
Which cranial nerves are involved in neural control related to swallowing?
Which cranial nerves are involved in neural control related to swallowing?
Which muscles are innervated by the C1-C3 nerves?
Which muscles are innervated by the C1-C3 nerves?
What role does the medulla oblongata play in swallowing?
What role does the medulla oblongata play in swallowing?
Which of the following statements about geniohyoid and thyrohyoid is correct?
Which of the following statements about geniohyoid and thyrohyoid is correct?
Which cranial nerve controls the movement of the majority of the tongue muscles involved in swallowing?
Which cranial nerve controls the movement of the majority of the tongue muscles involved in swallowing?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for the movement of the lips?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for the movement of the lips?
Which of the following muscles plays a significant role in mastication?
Which of the following muscles plays a significant role in mastication?
What structure is formed by the combination of the hard palate and the soft palate?
What structure is formed by the combination of the hard palate and the soft palate?
Which intrinsic muscle of the tongue alters its shape for speech and swallowing?
Which intrinsic muscle of the tongue alters its shape for speech and swallowing?
Which of the following muscles is part of the lateral group of mastication muscles?
Which of the following muscles is part of the lateral group of mastication muscles?
Which muscle assists in the movement of the base of the tongue?
Which muscle assists in the movement of the base of the tongue?
What is the primary function of the palatopharyngeus muscle?
What is the primary function of the palatopharyngeus muscle?
Which of the following refers to the arch located at the back of the mouth?
Which of the following refers to the arch located at the back of the mouth?
Flashcards
Deglutition
Deglutition
The process of swallowing, moving food from the mouth to the stomach.
Oral Phase of Swallowing
Oral Phase of Swallowing
A voluntary action that begins the swallowing process by moving the bolus (food) to the back of the mouth.
Pharyngeal Phase of Swallowing
Pharyngeal Phase of Swallowing
A reflex action controlled by the brain, transporting the bolus from the pharynx to the esophagus.
Esophageal Phase of Swallowing
Esophageal Phase of Swallowing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aspiration
Aspiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial Nerves for Swallowing
Cranial Nerves for Swallowing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orbicularis Oris
Orbicularis Oris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mandible
Mandible
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maxilla
Maxilla
Signup and view all the flashcards
Buccinator
Buccinator
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mastication Muscles
Mastication Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oral Tongue
Oral Tongue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intrinsic Muscles of the Tongue
Intrinsic Muscles of the Tongue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extrinsic Muscles of the Tongue
Extrinsic Muscles of the Tongue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nasopharynx
Nasopharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oropharynx
Oropharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypopharynx
Hypopharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Valleculae
Valleculae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laryngeal vestibule
Laryngeal vestibule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyriform sinus
Pyriform sinus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Upper esophageal sphincter (UES)
Upper esophageal sphincter (UES)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lower esophageal sphincter (LES)
Lower esophageal sphincter (LES)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
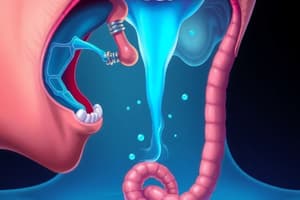
Anatomy of Swallowing Mechanism
- Normal swallowing involves both voluntary and reflexive components, occurring roughly 600 times per day in adults.
- Normal swallowing takes less than 2 seconds to move bolus from oral cavity to esophagus.
- This process requires at least six cranial nerves (V, VII, IX, X, XI, XII), the first three cervical nerves, and the swallowing center in the medulla oblongata.
- Aspiration, the entry of food into the lungs, can sometimes occur without significant negative effects. Current research suggests it can be part of normal physiology. This material is usually cleared by normal airway defenses.
Oral Cavity
- Lips, including the orbicularis oris muscle
- Mandible (lower jaw)
- Maxilla (upper jaw)
- Buccinator (facial) muscles
- Mastication muscles (temporalis, masseter, medial pterygoid, and lateral pterygoid)
- Teeth
- Floor of the mouth (mylohyoid, geniohyoid, anterior belly of digastric muscle)
Nasopharynx
- Pharyngeal segment from base of skull to soft palate
- Superior pharyngeal constrictor
Oropharynx
- Pharyngeal segment from soft palate to valleculae
- Hyoid bone
- Base of tongue
- Epiglottis
- Valleculae
- Middle pharyngeal constrictors
- Lateral and posterior pharyngeal walls
Hypopharynx
- Pharyngeal segment from hyoid bone to cricoid cartilage
- This section includes the larynx and esophagus
Larynx
- Aryepiglottic folds
- Laryngeal vestibule
- False vocal folds
- True vocal folds
- Arytenoids
- Pyriform/Puriform sinus
- Inferior pharyngeal constrictors
- Cricopharyngeal muscle (C6 level)
- Cricoid cartilage (important structure in the larynx)
Esophagus
- Upper esophageal sphincter (UES)
- Inferior pharyngeal constrictor, cricopharyngeus, and proximal esophageal muscles
- Esophagus
- Lower esophageal sphincter (LES)
Neural Control
- Cranial nerves (CNs V, VII, IX, X, XI, XII) involved in swallowing process
- Cervical nerves (C1-C3) as well, controlling related muscles
- Swallowing center in the medulla oblongata (brainstem)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.