Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of the O Horizon?
What is the main function of the O Horizon?
- To provide structure and support to plants
- To store leached nutrients and minerals
- To hold water and prevent erosion
- To serve as a decomposition area for organic material (correct)
Why is the A Horizon important for plant growth?
Why is the A Horizon important for plant growth?
- It is where plant roots primarily gather nutrients (correct)
- It has the largest amount of water retention
- It contains the highest concentration of minerals
- It serves as a barrier to prevent erosion
Which horizon is known for the accumulation of leached materials?
Which horizon is known for the accumulation of leached materials?
- B Horizon (correct)
- A Horizon
- O Horizon
- C Horizon
What is the difference between the C Horizon and the R Horizon?
What is the difference between the C Horizon and the R Horizon?
Which process describes material removal in the E Horizon?
Which process describes material removal in the E Horizon?
The A Horizon is known for being primarily composed of decomposed plant material and humus.
The A Horizon is known for being primarily composed of decomposed plant material and humus.
The B Horizon is typically poor in clay and minerals compared to other layers.
The B Horizon is typically poor in clay and minerals compared to other layers.
The E Horizon is characterized by the accumulation of organic matter and is generally darker in color.
The E Horizon is characterized by the accumulation of organic matter and is generally darker in color.
The C Horizon consists of completely consolidated rock with no weathering.
The C Horizon consists of completely consolidated rock with no weathering.
The R Horizon is the unweathered rock layer that lies beneath the soil profile.
The R Horizon is the unweathered rock layer that lies beneath the soil profile.
The topsoil, rich in organic material and minerals, is known as the ______ Horizon.
The topsoil, rich in organic material and minerals, is known as the ______ Horizon.
The ______ Horizon is where materials like clay, iron, or organic matter are removed.
The ______ Horizon is where materials like clay, iron, or organic matter are removed.
The subsoil, often rich in clay and minerals, is referred to as the ______ Horizon.
The subsoil, often rich in clay and minerals, is referred to as the ______ Horizon.
The parent material of the soil profile is represented by the ______ Horizon.
The parent material of the soil profile is represented by the ______ Horizon.
The ______ Horizon is the bedrock layer, consisting of unweathered rock beneath the soil.
The ______ Horizon is the bedrock layer, consisting of unweathered rock beneath the soil.
Flashcards
O Horizon
O Horizon
The top layer of soil, composed of decomposed plant material and humus. It's like a blanket of organic matter.
A Horizon
A Horizon
The topsoil layer, rich in organic matter and minerals, perfect for plant roots.
E Horizon
E Horizon
The eluviation layer where materials like clay and iron are washed out.
B Horizon
B Horizon
Signup and view all the flashcards
C Horizon
C Horizon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Soil Profile
Soil Profile
Signup and view all the flashcards
Humus
Humus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eluviation
Eluviation
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the B Horizon accumulate?
What does the B Horizon accumulate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the difference between the C and R Horizons?
What is the difference between the C and R Horizons?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the soil profile?
What is the soil profile?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens in the E Horizon?
What happens in the E Horizon?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
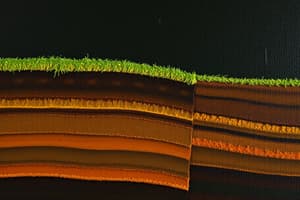
Soil Profiles and Horizons
- Soil is a vital resource supporting plant growth and providing a habitat for many organisms
- Soil is made up of layers called horizons
- These horizons vary in colour, texture, and composition
- Together, these layers form the soil profile
Soil Horizons
- O Horizon:
- Organic layer, composed of decomposed plant matter and humus
- Found on the surface
- Main function is to retain water and nutrients for plant growth
- Supports plant growth by acting as a reservoir for water and nutrients
- A Horizon:
- Topsoil
- Rich in organic material and minerals
- Site of most root activity
- Rich in organic matter and nutrients which are crucial for plant development and root growth
- Contains most of the organisms involved in the decomposition process
- E Horizon:
- Eluviation (leaching) layer
- Materials like clay, iron, or organic matter are removed
- Materials are washed downward due to water movement
- The eluviation layer is where water movement removes materials upwards
- B Horizon:
- Subsoil
- Leaching materials accumulate here
- Often rich in clay and minerals
- Accumulates materials leached from the overlying layers
- Frequently shows signs of accumulation of material lost from overlying layers
- C Horizon:
- Parent material
- Partially weathered rock or unconsolidated sediments
- R Horizon:
- Bedrock
- Unweathered rock layer beneath the soil
Visualizing the Soil Profile
- A graphic representation of soil horizons in order from top to bottom. Illustrates the layers and their main characteristics
- A diagram shows the different soil layers and their characteristics
- The sequence of layers in a soil profile is a good guide to understanding its development
- The diagram visually clarifies the transition between layers and their distinct characteristics
Review Questions
- Q1: O Horizon's main function: The organic matter layer helps retain water and nutrients for plant growth
- Q2: Why is the A Horizon important for plant growth?: Rich in organic matter and nutrients, critical for root growth and plant development. Its high biological activity supports root growth.
- Q3: Which horizon accumulates leached materials?: The B Horizon collects materials leached from the overlying layers. It accumulates these leached materials.
- Q4: Difference between C and R Horizons: The C Horizon is partially weathered parent material, whereas the R Horizon is unweathered bedrock.
- Q5: Eluviation process in the E Horizon: Materials (e.g., minerals, organics) are washed downward into lower layers due to water movement. This is a process where water percolates through layers, removing certain substances.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.